Facial Bones
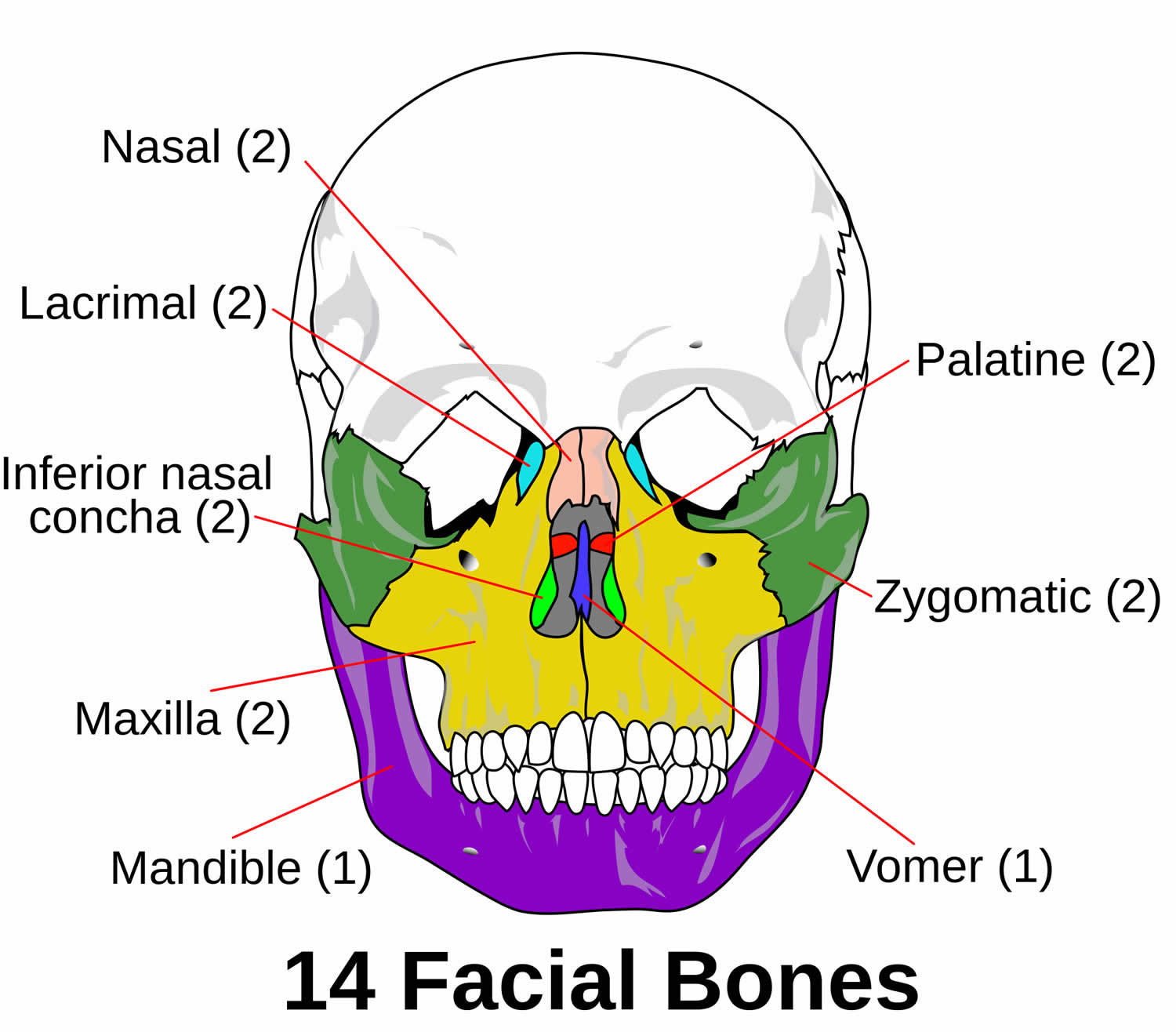
Facial Fractures Causes Types Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Recovery Learn about the 14 facial bones that form the front part of the skull, their locations, articulations, and roles. see a labeled diagram and a mnemonic device to remember their names. Learn about the fourteen bones that form the human facial skeleton, their structure, variations and development. see images and 3d model of the facial skeleton and its relation to the neurocranium.
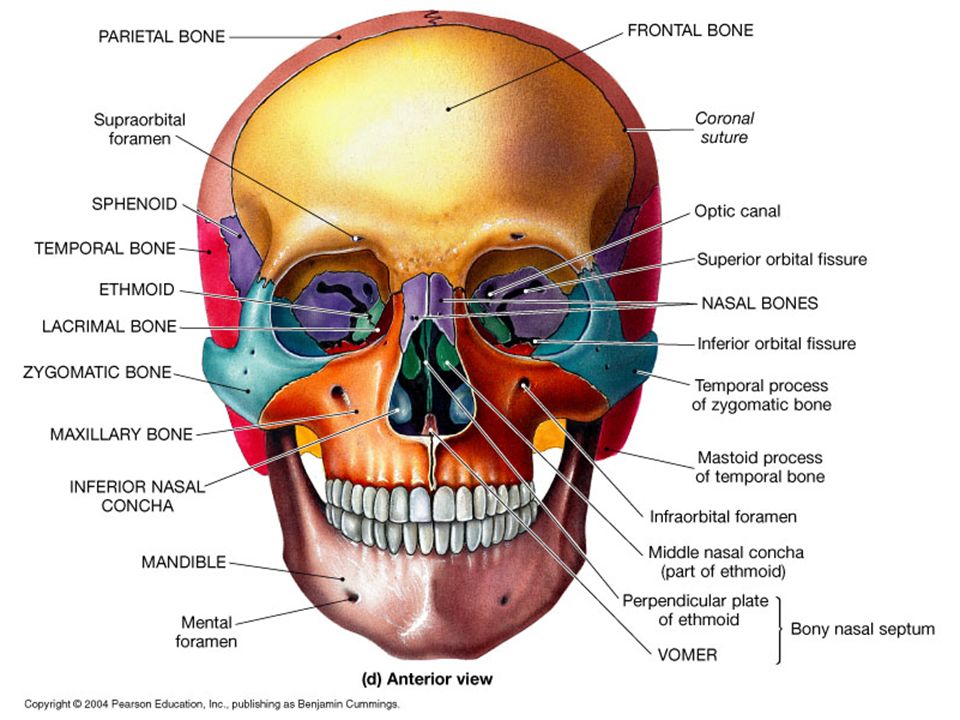
Facial Bone вђ Liberal Dictionary Learn about the 14 facial bones that make up the face skeleton, their anatomical features, functions and embryological development. the viscerocranium includes paired and unpaired bones that form the shape, protection and attachment of the face. Learn about the facial bones that make up most of the front of the skull and support the face, head, and neck. find out how many facial bones there are, what they do, and how they are imaged medically. The human face is the most anterior portion of the human head. it refers to the area that extends from the superior margin of the forehead to the chin, and from one ear to another. the basic shape of the human face is determined by the underlying facial skeleton (i.e. viscerocranium), the facial muscles and the amount of subcutaneous tissue. Learn about the 14 facial bones that form the viscerocranium, the anterior and lower part of the skull. see their names, functions, and articulations with other bones.
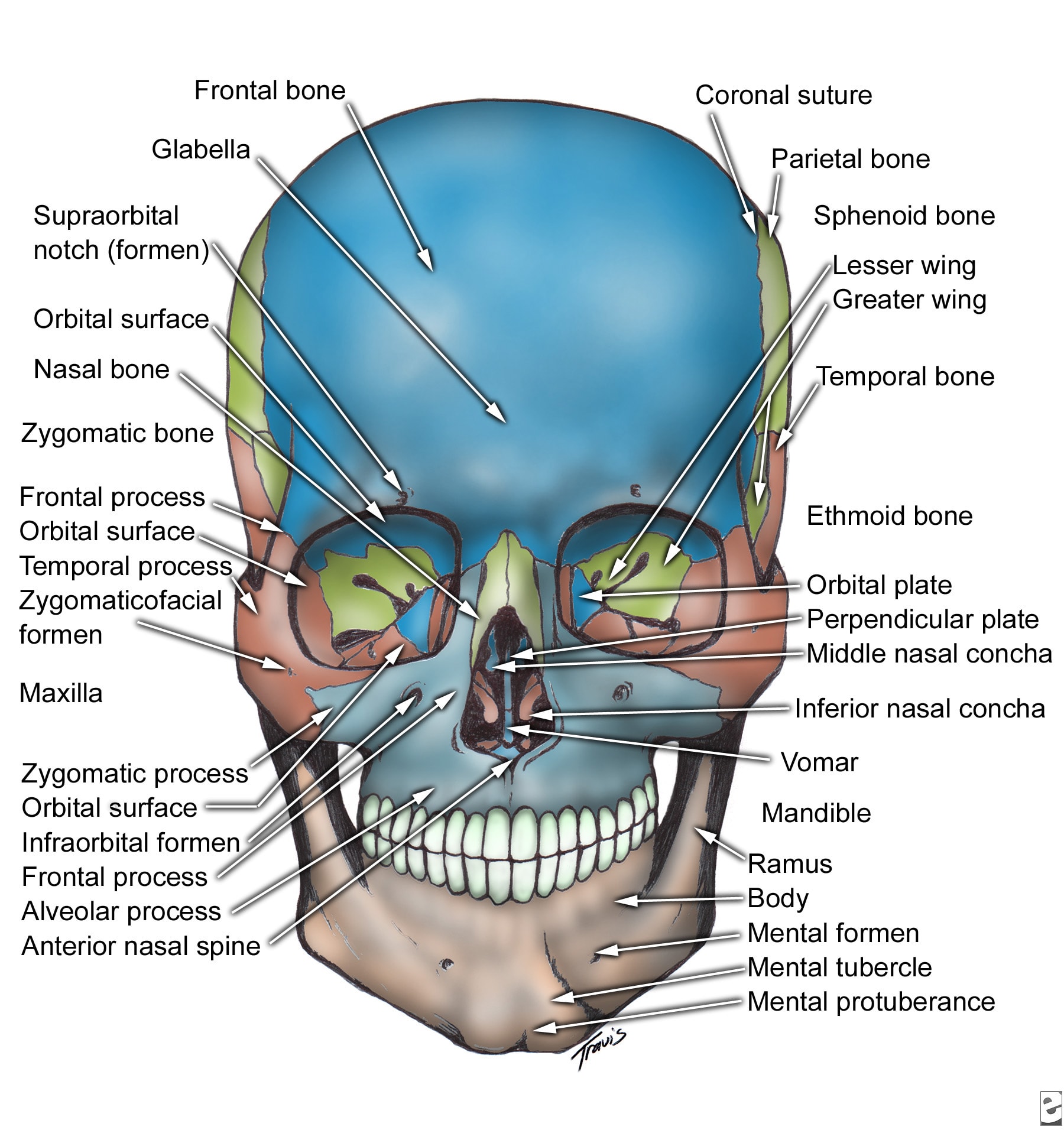
Oral Maxillo Facial Surgery Facial Bone Anatomy The human face is the most anterior portion of the human head. it refers to the area that extends from the superior margin of the forehead to the chin, and from one ear to another. the basic shape of the human face is determined by the underlying facial skeleton (i.e. viscerocranium), the facial muscles and the amount of subcutaneous tissue. Learn about the 14 facial bones that form the viscerocranium, the anterior and lower part of the skull. see their names, functions, and articulations with other bones. Overview. the facial skeleton serves to protect the brain; house and protect the sense organs of smell, sight, and taste; and provide a frame on which the soft tissues of the face can act to facilitate eating, facial expression, breathing, and speech. the primary bones of the face are the mandible, maxilla, frontal bone, nasal bones, and zygoma. Learn about the 14 bones that make up the facial skeleton, their characteristics, parts and ossification. the facial skeleton supports the facial muscles, houses the eyes, nose, mouth and sinuses, and forms the jaw and cheekbones.

Comments are closed.