Fascial Space Infections
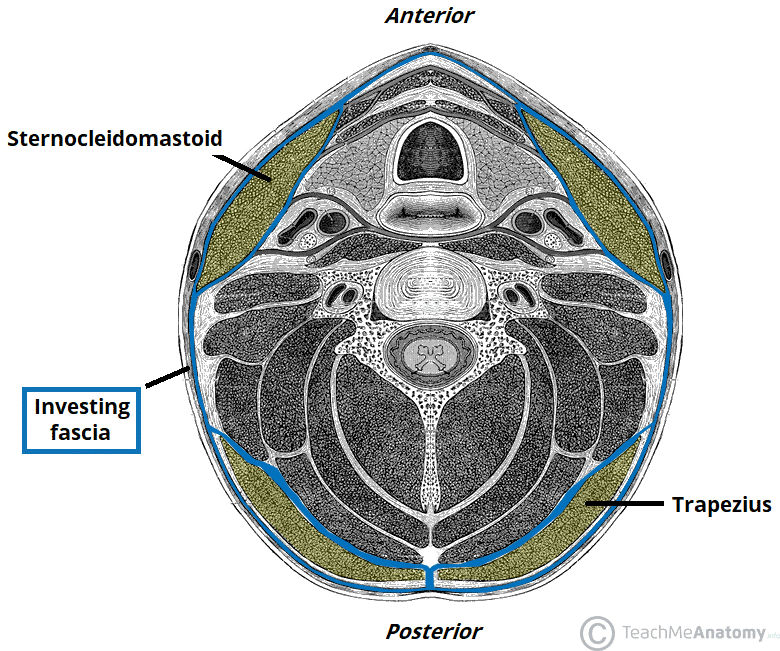
Deep Neck Space Infections Teachmesurgery Objectives: identify the common pathogens and pathogenesis of odontogenic and orofacial infections. review the anatomy and fascial spaces for the spread of infection into the maxilla and neck from dental abscesses. identify the signs and symptoms of an airway emergency secondary to an odontogenic infection and its treatment. The fascial spaces in the head and neck are the potential spaces between the various fascia normally filled with loose connective tissue and bounded by the anatomical barriers usually of bone, muscle, or fascial layers [2]. facial planes offer anatomic highways for infection to spread superficially to deep planes.
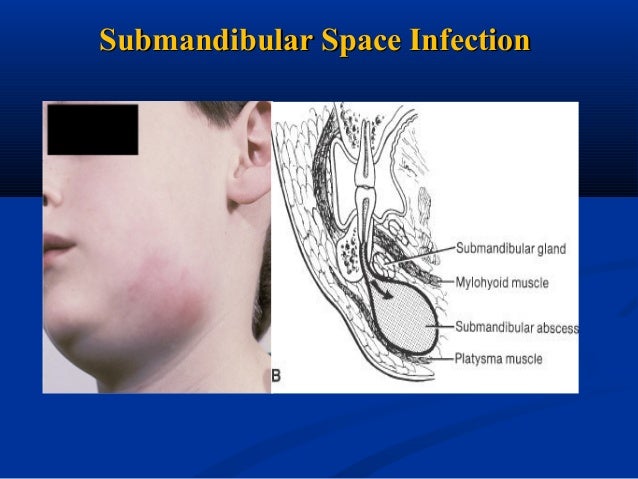
Fascial Space Infections In severe cases, the infection can spread into the surrounding tissues, causing serious health problems such as space infection [4, 8]. space infection occurs when an infection spreads to the deep. Introduction. deep neck space infections most commonly arise from a septic focus of the mandibular teeth, tonsils, parotid gland, deep cervical lymph nodes, middle ear, or sinuses. these deep cervical space infections have become relatively uncommon in the post antibiotic era. consequently, many clinicians are unfamiliar with these conditions. Mri is superior to usg in identifying deep fascial space infections. nevertheless, usg is a readily available, noninvasive, low cost diagnostic tool that has a clear role in predicting the phase of infection and precise anatomic area in superficial space infections. In addition to producing pain and discomfort, odontogenic infections can extend beyond natural barriers and result in potentially life threatening complications, such as infections of the deep fascial spaces of the head and neck. (see "deep neck space infections in adults".).

Odontogenic Space Infection Part 1 Fascial Spaces Of Head And Neck Mri is superior to usg in identifying deep fascial space infections. nevertheless, usg is a readily available, noninvasive, low cost diagnostic tool that has a clear role in predicting the phase of infection and precise anatomic area in superficial space infections. In addition to producing pain and discomfort, odontogenic infections can extend beyond natural barriers and result in potentially life threatening complications, such as infections of the deep fascial spaces of the head and neck. (see "deep neck space infections in adults".). Ultrasonography (usg) is an effective imaging modality in evaluating the anatomic location of fascial space infections and highly predictable in determining the stage of infection. usg is quick, non invasive, sensitive, widely available, affordable, pain less and is relatively a new diagnostic aid in dentistry. Mri was superior in recognizing deep fascial space infections compared to usg. however, usg is a significant addition and has a definite role in prognosticating the stage of infection and exact anatomic location in superficial space infections.

Comments are closed.