Figure 1 From Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy For L5 S1
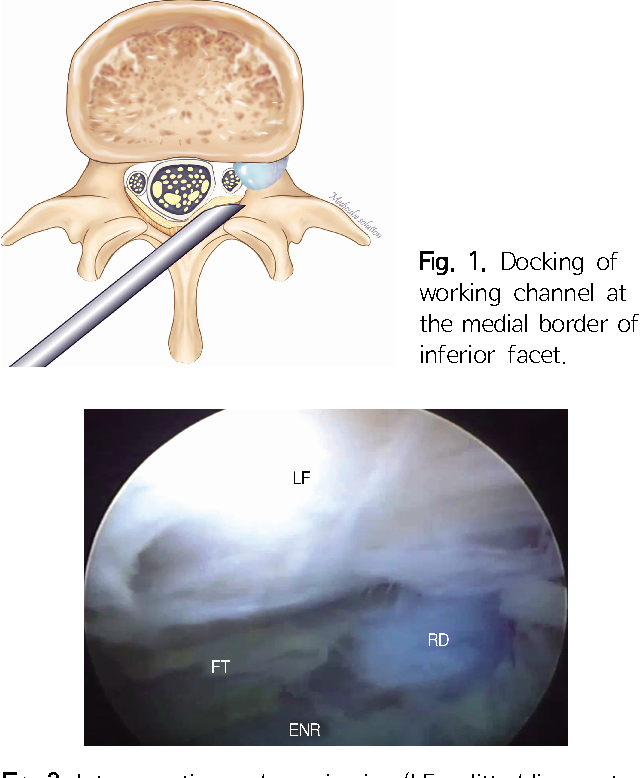
Figure 1 From Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy For L5 о 1. introduction. percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (peld) is a minimally invasive treatment for lumbar disc herniation (ldh). the benefits of peld over open lumbar discectomy include less intraoperative blood loss, better paravertebral muscle preservation, and shorter hospital stays. Citation: cheng y, zhang q, li y, chen x and wu h (2022) percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for l5 s1 calcified lumbar disc herniation: a retrospective study. front. surg. 9:998231. doi: 10.3389 fsurg.2022.998231. received: 19 july 2022; accepted: 6 september 2022; published: 23 september 2022.

Figure 1 From Percutaneous Endoscopic Interlaminar Discectomy Wi Fig. 1. the iliac height was defined as the vertical distance (arrow) from the s1 plate to the highest iliac bone in the lateral radiography (a). the iliolumbar angle was defined as the angle between a line from the superior and medial point of the s1 pedicle to the highest iliac point and a horizontal line in ap radiography (b). "percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy for l5 s1 disc. First, ield is a complementary surgical technique to teld. the use of teld alone in situations such as highly migrated disc herniation or large disc herniation may put patients at risk of neural injury or incomplete surgery, 9,10 but these challenges can be addressed using ield. 5,11–13 second, advanced techniques, such as endoscopic. Minimally invasive techniques accurately targeting pathological tissue are being developed for spine surgery. percutaneous endoscopic laminar discectomy (peld) is a typical representative minimally invasive discectomy surgery that can be classified into percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd) and percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (peid), according to the approach. Background: percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (peld) is a minimally invasive spinal technique. the unique anatomic features of the l5–s1 space include a large facet joint, narrow foramen, small disc space, and a wide interlaminar space. peld can be performed via 2 routes, transforaminal (tf peld) or interlaminar (il peld).

Figure 1 From The Effective Of Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Minimally invasive techniques accurately targeting pathological tissue are being developed for spine surgery. percutaneous endoscopic laminar discectomy (peld) is a typical representative minimally invasive discectomy surgery that can be classified into percutaneous endoscopic transforaminal discectomy (petd) and percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy (peid), according to the approach. Background: percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy (peld) is a minimally invasive spinal technique. the unique anatomic features of the l5–s1 space include a large facet joint, narrow foramen, small disc space, and a wide interlaminar space. peld can be performed via 2 routes, transforaminal (tf peld) or interlaminar (il peld). The s1 root exits at the l5–s1 disc space with an average 22° (range, 18°–26°) of take off angle, and it is possible to access the herniation in the axilla of the s1 root within this angle.[5,11] in cases of a posterolateral herniated l5–s1 disc, the nerve root is displaced and this creates more space for entry because of the mass. Objective: to compare the results of percutaneous endoscopic lumbar discectomy in l5 s1 disc herniation through an interlaminar or transforaminal approach. summary of background data: the transforaminal and interlaminar techniques are both acceptable approaches for l5 s1 disc herniation. this is the first study to compare these two approaches.

Comments are closed.