Figure 10 3 The Structure Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Vrogue Co
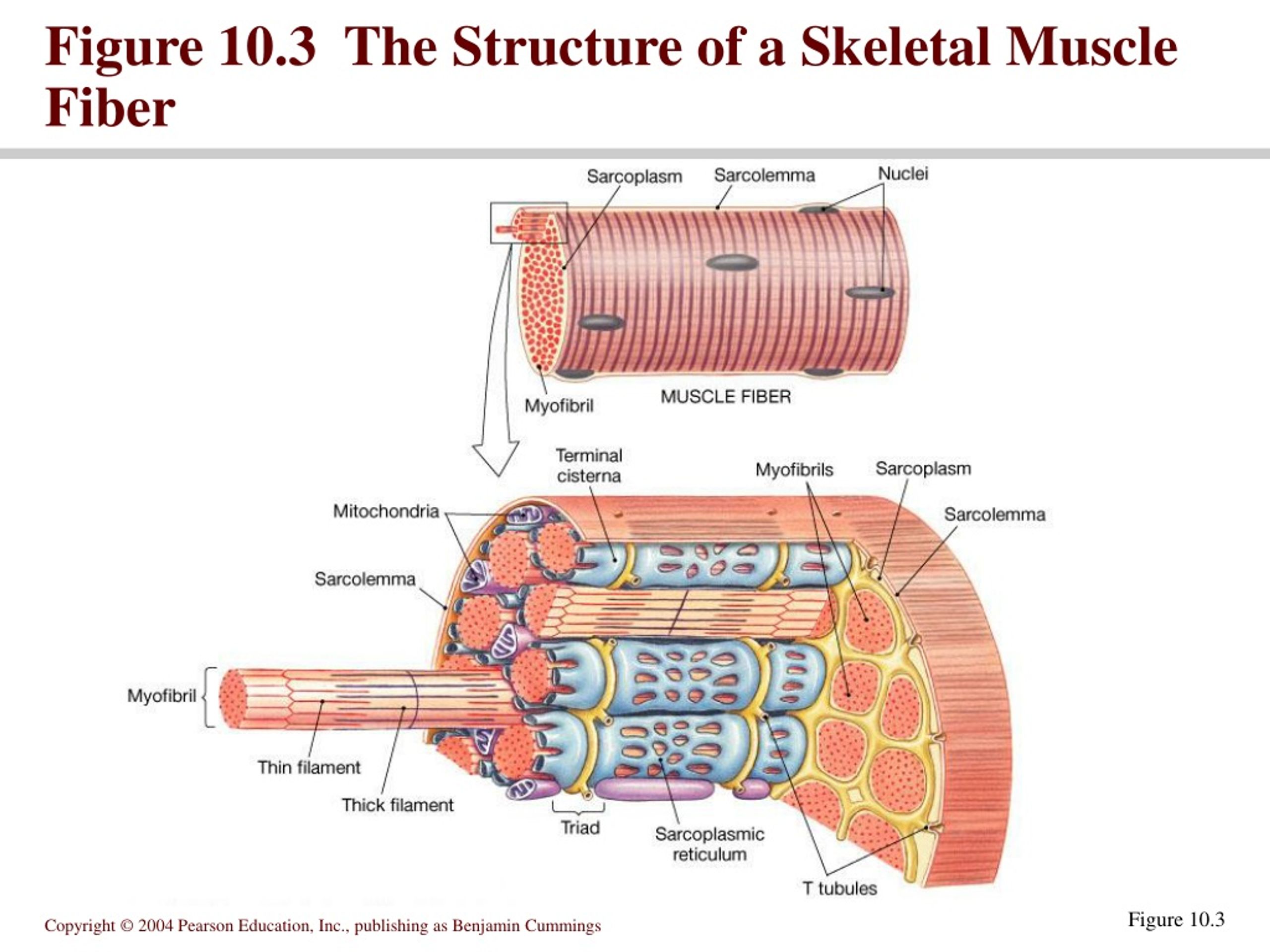
Figure 10 3 The Structure Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Vrogue Co Each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called mysia) that enclose it, provide structure to the muscle, and compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (figure 10.2.1). each muscle is wrapped in a sheath of dense, irregular connective tissue called the epimysium , which allows a muscle to contract and move powerfully while maintaining its structural integrity. Excitation signalling of action potentials from the motor neuron are coupled with calcium release. thus, the excitation contraction coupling process begins with signaling from the nervous system at the neuromuscular junction ( figure 10.3.1) and ends with calcium release for muscle contraction. figure 10.3.1 – motor end plate and innervation.
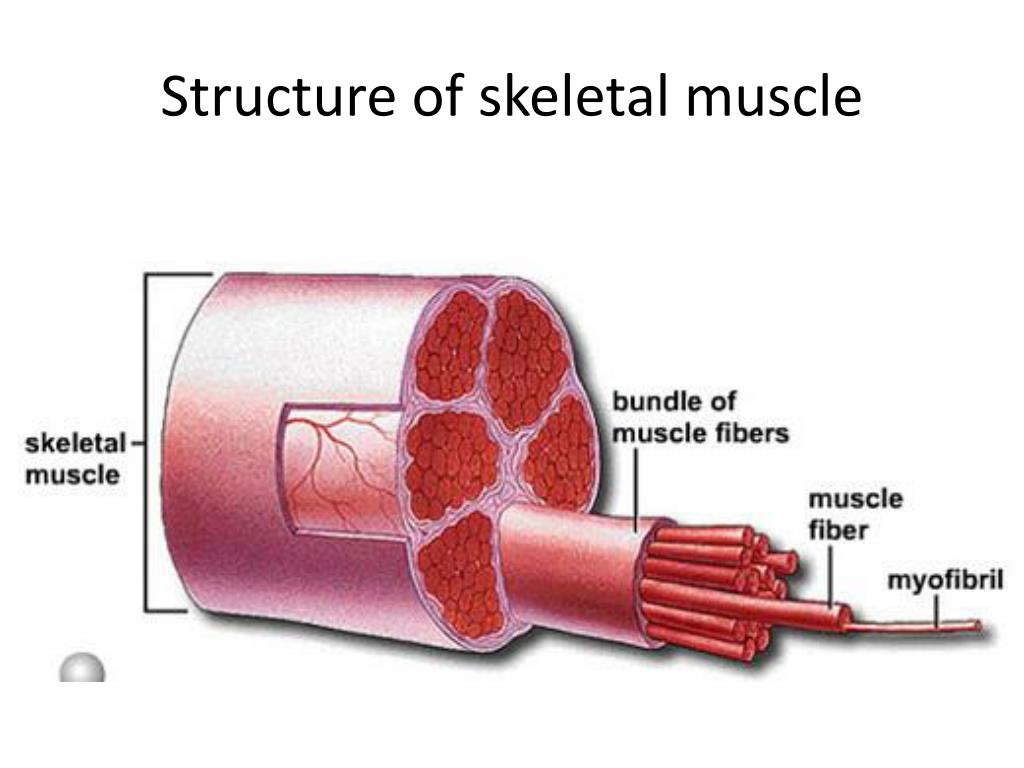
Figure 10 3 The Structure Of A Skeletal Muscle Fiber Vrogue Co Skeletal muscle fibers. because skeletal muscle cells are long and cylindrical, they are commonly referred to as muscle fibers. skeletal muscle fibers can be quite large for human cells, with diameters up to 100 μm and lengths up to 30 cm (11.8 in) in the sartorius of the upper leg. during early development, embryonic myoblasts, each with its. Figure 10 1 skeletal muscle fiber. use figure 10 1 to answer the following question: identify the structure labeled "1." mitochondria. a fascicle is a. group of muscle fibers that are encased in the perimysium. a muscle producing almost peak tension during rapid cycles of contraction and relaxation is said to be in. Skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. the sarcoplasmic reticulum (sr) is a form of endoplasmic reticulum. Figure 10.3.1 10.3. 1: the three connective tissue layers bundles of muscle fibers, called fascicles, are covered by the perimysium. muscle fibers are covered by the endomysium. inside each skeletal muscle, muscle fibers are organized into individual bundles, each called a fascicle, by a middle layer of connective tissue called the perimysium.

Comments are closed.