Figure 7 From Relevant Surgical Anatomy Of The Chest Wall Semantic

Figure 7 From Relevant Surgical Anatomy Of The Chest Wall Semantic Fig. 3. anterior chest wall showing the sternum. note where the costal cartilages articulate with the sternum. in the intercostal space lie different structures: several kinds of intercostal muscles, intercostal arteries and associated veins, lymphatics, and nerves. (from rendina ea, ciccone am. the intercostal space. thorac surg clin 2007;17(4):491e501; with permission.) "relevant surgical. The chest wall, like other regional anatomy, is a remarkable fusion of form and function. principal functions are the protection of internal viscera and an expandable cylinder facilitating variable gas flow into the lungs. knowledge of the anatomy of the whole cylinder (ribs, sternum, vertebra, diaphragm, intercostal spaces, and extrathoracic.

Pdf Relevant Surgical Anatomy Of The Chest Wall Semantic Schola Relevant surgical anatomy of the chest wall pala b. rajesh a and babu v. naidu a,b a heart of england nhs foundation trust bordesley green east birmingham b9 5ss tel: 44 (0) 121 424 2000 b the university of warwick coventry cv4 7al t: 44 (0)24 7657 4880 corresponding author: [email protected]. Relevant surgical anatomy of the chest wall babu v. naidu, mbbs (mmed sci trauma), md, frcs (cth)a,b,*, pala b. rajesh, mbbs, frcs (cth)a skeletal structures ribs the ribs and costal cartilages form the lateral aspects of the thoracic cylinder.1 ribs have a head, a neck, a tubercle, an articular facet, and a shaft (fig. 1). Owing to equal or less layer of muscles [3] [4] [5] having serratus anterior muscle in front of the rib cage in antero lateral approach, and either oblique external or parts of anterior serratus. In this chapter, the typical presentation of the thorax is covered along with commonly seen variants. the normal musculoskeletal structure of the upper body functions primarily in respiration but also protects the vital organs of the thoracic cavity and supports movement of the upper extremities. the thorax is comprised of the sternum, ribs, clavicles, scapula, vertebra, various muscles, and.

Anatomy Of Chest Surgical Anatomy Of The Chest Wall S Vrogue Co Owing to equal or less layer of muscles [3] [4] [5] having serratus anterior muscle in front of the rib cage in antero lateral approach, and either oblique external or parts of anterior serratus. In this chapter, the typical presentation of the thorax is covered along with commonly seen variants. the normal musculoskeletal structure of the upper body functions primarily in respiration but also protects the vital organs of the thoracic cavity and supports movement of the upper extremities. the thorax is comprised of the sternum, ribs, clavicles, scapula, vertebra, various muscles, and. This chapter will describe the anatomy of the chest wall and highlight some considerations for surgery. the thoracic wall consists of the osseo cartilaginous throacic cage, the interconnecting muscles, the muscles on top, the fascia, the nerves and vasculature, the sub cutaneous tissue, the skin, and the mammary glands that lie within the. Abstract. the normal musculoskeletal structure of the upper body functions primarily in respiration but also protects the vital organs of the thoracic cavity and supports movement of the upper extremities. the thorax is comprised of the sternum, ribs, clavicles, scapula, vertebra, various muscles, and neurovascular structures.
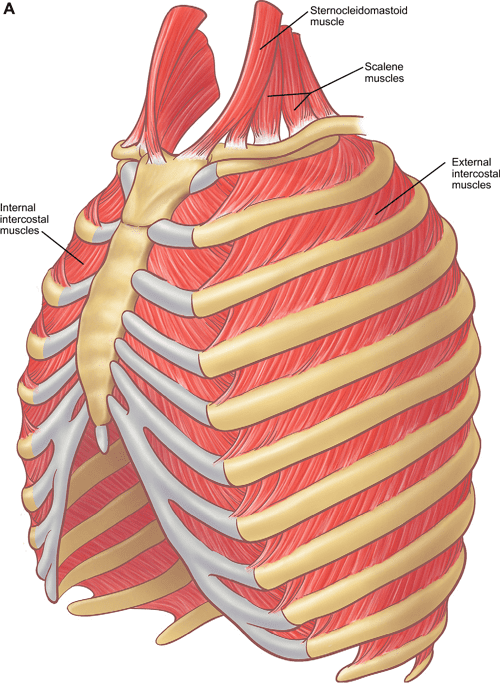
Figure 7 From The Anatomy Of The Ribs And The Sternum And Their This chapter will describe the anatomy of the chest wall and highlight some considerations for surgery. the thoracic wall consists of the osseo cartilaginous throacic cage, the interconnecting muscles, the muscles on top, the fascia, the nerves and vasculature, the sub cutaneous tissue, the skin, and the mammary glands that lie within the. Abstract. the normal musculoskeletal structure of the upper body functions primarily in respiration but also protects the vital organs of the thoracic cavity and supports movement of the upper extremities. the thorax is comprised of the sternum, ribs, clavicles, scapula, vertebra, various muscles, and neurovascular structures.

Comments are closed.