Forearm Fractures Wrist Fractures Clinical Anatomy Kenhub
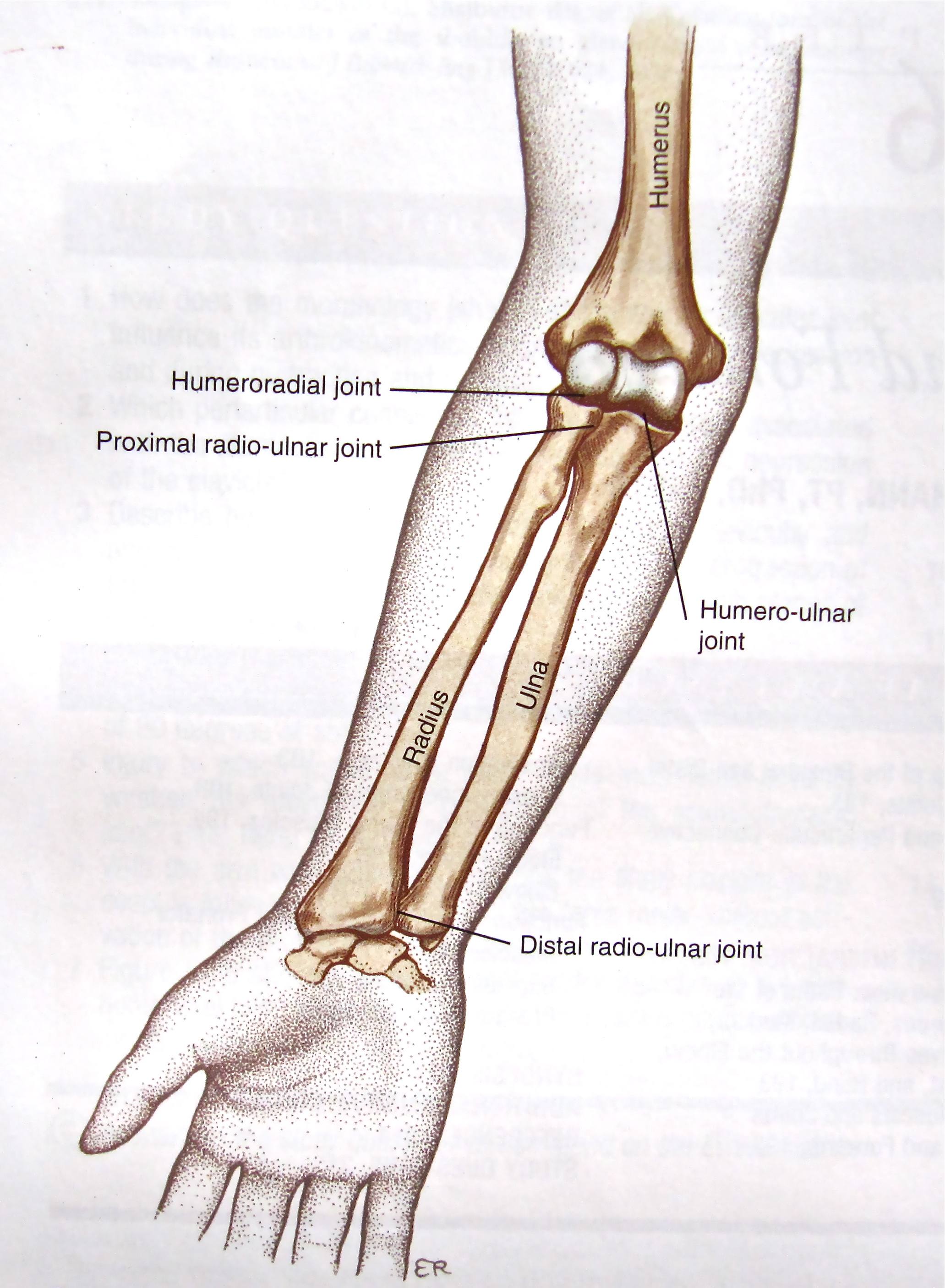
Forearm Fractures вђ Core Em In this video, we cover colles' fractures, smith fractures, barton's fractures and chauffeur fractures. to learn more about the anatomy of the radius and uln. The forearm consists of two relatively parallel bones that connect two joints: elbow and wrist. besides, the two bones themselves form joints that help in supination and pronation; therefore, forearm fractures are considered intra articular fractures. proper management of such fractures is necessary to restore forearm functions, including supination and pronation, elbow and wrist movements.

Forearm Fractures Radiology Key Clinical presentation and assessment. the clinical presentation of colles fracture is frequently described as a dinner fork deformity distal fracture of the radius causes posterior displacement of the distal fragment, causing the forearm to be angled posteriorly just proximal to the wrist. with the hand displaying its normal forward arch, the. The radiocarpal joint is an articulation between the distal portion of the radius and three of the four proximal carpal bones; the scaphoid, lunate and triquetrum. the articular surface of the distal radius is roughly triangular and concave in appearance, presenting two articular facets separated by a slight anteroposterior ridge. these are the. In most cases of adult forearm fractures, both bones are broken. fractures of the forearm can occur near the wrist at the farthest (distal) end of the bone, in the middle of the forearm, or near the elbow at the top (proximal) end of the bone. this article focuses on fractures that occur in the middle segments of the radius and ulna. The clinical presentation of fractures of the distal radius is similar to several other fractures of the wrist: 5. scaphoid fracture: commonly caused by a foosh as well. however, the main complaint is typically localised pain and tenderness over the anatomical snuffbox (triangular depression over lateral, dorsal hand).

Comments are closed.