Framing Bias Explaination Cognitive Biases
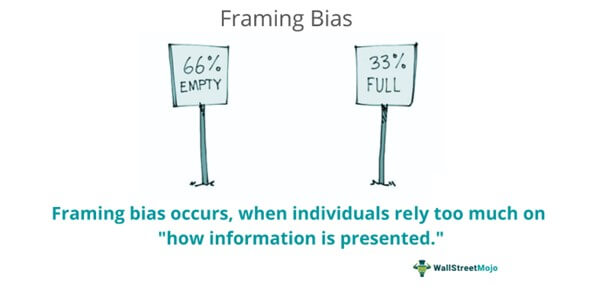
Cognitive Heuristics Biases Hema Nookala The framing effect is the cognitive bias wherein an individual’s choice from a set of options is influenced more by how the information is worded than by the information itself. the framing of an issue, whether presented in a positive (gain oriented) or negative (loss oriented) light, significantly impacts how people make decisions. The framing effect is a result of different mental processes that take place when we are faced with a decision. here are a few of the mechanisms that can help explain why the framing effect occurs: loss aversion: people value a certain gain more than a probable gain, even if the probable gain has a greater expected value.
What Is Cognitive Bias Types Examples Framing effect (psychology) the framing effect is a cognitive bias in which people decide between options based on whether the options are presented with positive or negative connotations. [ 1] individuals have a tendency to make risk avoidant choices when options are positively framed, while selecting more loss avoidant options when presented. Framing effects have been shown to influence legal proceedings. a paper written in 2004 by stephanos bibas, a u.s. law professor and judge, looked into how various cognitive biases influence plea bargains in legal trials. he concluded that “framing plays a powerful role in plea bargaining.”. Confirmation bias, hindsight bias, mere exposure effect, self serving bias, base rate fallacy, anchoring bias, availability bias, the framing effect , inattentional blindness, and the ecological fallacy are some of the most common examples of cognitive bias. another example is the false consensus effect. cognitive biases directly affect our. Among the myriad cognitive biases that influence our judgment, framing bias stands out as a subtle yet powerful force. this cognitive quirk influences the way information is presented, leading.

Cognitive Biases In Medicine вђў Framing Effect вђў Grepmed Confirmation bias, hindsight bias, mere exposure effect, self serving bias, base rate fallacy, anchoring bias, availability bias, the framing effect , inattentional blindness, and the ecological fallacy are some of the most common examples of cognitive bias. another example is the false consensus effect. cognitive biases directly affect our. Among the myriad cognitive biases that influence our judgment, framing bias stands out as a subtle yet powerful force. this cognitive quirk influences the way information is presented, leading. The framing effect is a key concept in behavioral economics and psychology, demonstrating that human decision making is not always logical or consistent. influence of cognitive biases : this effect is part of a broader set of cognitive biases that affect how people perceive and react to information. The framing effect is a cognitive bias that distorts our decisions and judgments based on how information is presented or ‘framed.’. this effect isn’t about lying or twisting the truth. it’s about the same cold, hard facts making us think and act differently just by changing their packaging. things look nicer inside these frames!.

Framing Bias Explained Cognitive Biases Cognitive Bias Cognit The framing effect is a key concept in behavioral economics and psychology, demonstrating that human decision making is not always logical or consistent. influence of cognitive biases : this effect is part of a broader set of cognitive biases that affect how people perceive and react to information. The framing effect is a cognitive bias that distorts our decisions and judgments based on how information is presented or ‘framed.’. this effect isn’t about lying or twisting the truth. it’s about the same cold, hard facts making us think and act differently just by changing their packaging. things look nicer inside these frames!.

Comments are closed.