Functional Group Priorities For Naming Organic Compounds With Multiple Functional Functional
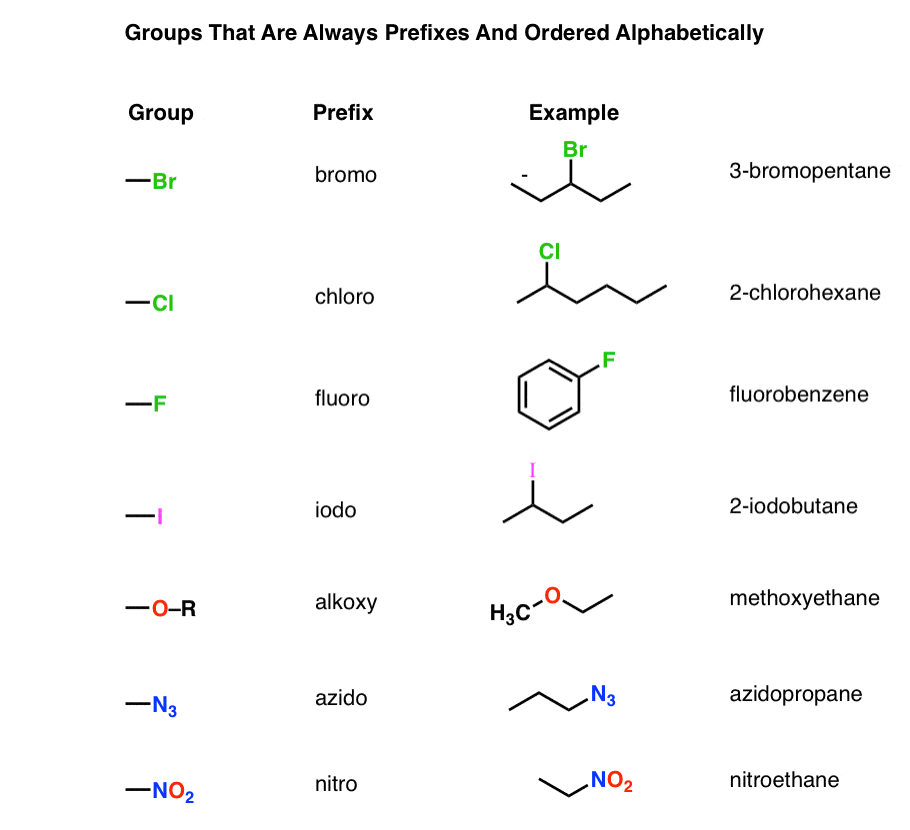
Table Of Functional Group Priorities For Nomenclature вђ Master Organic He functional group with the highest priority will be the one which gives its suffix to the name of the molecule. so in example #1 above, the suffix of the molecule will be “ oic acid” , not “ one”, because carboxylic acids are given higher priority. however, if a ketone is present with an alcohol (example 3) then we will use the suffix. For naming purposes, the functional groups are assigned with priorities (table 2.3). if the compound includes more than one functional groups, the one with the highest priority is the “parent structure” and determines the “parent name”; the other groups will be regarded as “substituents”. “suffix” is used to indicate the name of.
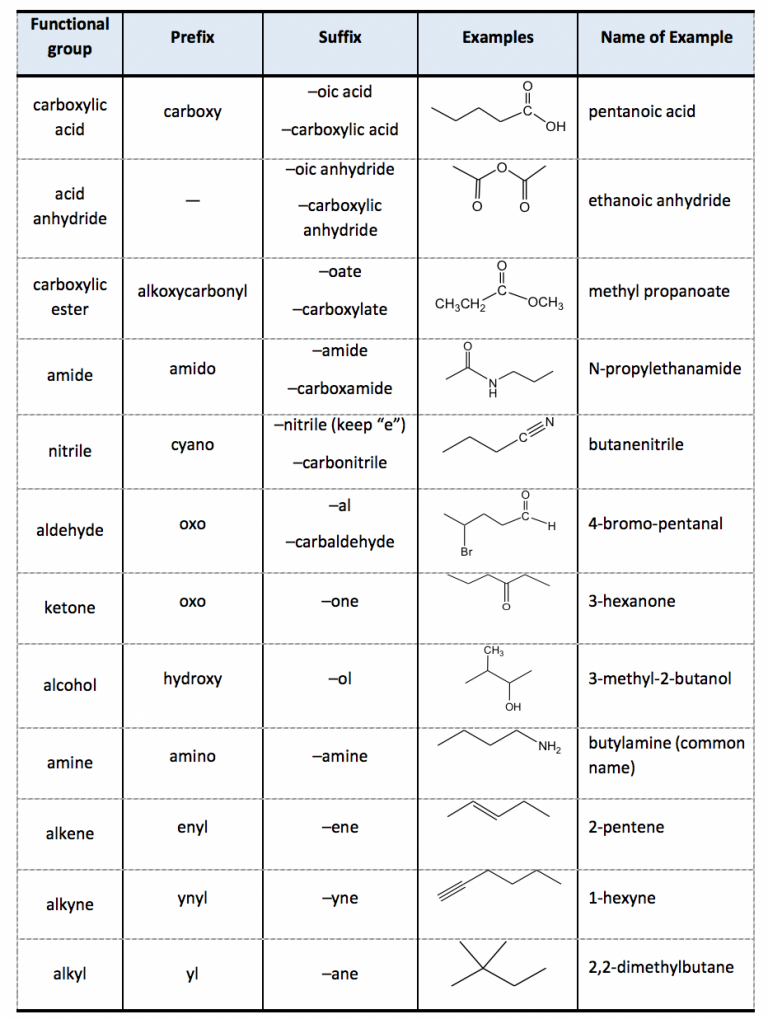
2 4 Iupac Naming Of Organic Compounds With Functional Groups вђ Org Step 3. number the parent chain starting from the highest priority group and add the substituent (s) alphabetically: it is also noteworthy that if there is a functional group suffix and a substituent, the functional group suffix gets the lowest possible number. for example, alcohols have higher priority than amines and therefore, when naming a. In the iupac nomenclature system, organic molecules are grouped into specific classes of compounds determined by the main functional group present in the structure. a system of priorities is used to determine the main functional group, which determines the identity of the compound. all other functional groups are treated as substituents. Identify the functional groups (other than alkanes) in the following organic compounds. state whether alcohols and amines are primary, secondary, or tertiary. solutions to exercises. a) carboxylate, sulfide, aromatic, two amide groups (one of which is cyclic) b) tertiary alcohol, thioester. c) carboxylate, ketone. Organic chemistry functional groups: a complete guide to recognizing, drawing, and naming ( priority cheat sheet at bottom) a functional group is a specific group of atoms that helps determine the chemistry and reactivity of the overall molecule. when classifying functional groups, we look at both the specific atoms present, as well as the.

Comments are closed.