Functional Tics вђ Functional Neurological Disorder Fnd

Thread By Jonstoneneuro On Thread Reader App Thread Reader App Tics are a type of repetitive movement or sound that can be seen in a variety of conditions, including tourette syndrome . tics can also occur as part of a functional neurological disorder, or fnd, when they are called ‘functional tics’. people with tourette syndrome may also develop functional tics. tics are defined as sudden, rapid. Functional neurologic disorder (fnd) refers to a neurological condition caused by changes in how brain networks work, rather than changes in the structure of the brain itself, as seen in many other neurological disorders. physical symptoms of fnd are genuine but cannot be explained by changes in the brain structure.

Functional Tics The Pandemic And Social Media Acnr Functional neurological disorder (fnd), previously regarded as a diagnosis of exclusion, is now a rule in diagnosis with available treatments. this represents a major step toward destigmatizing the disorder, which was often doubted and deemed untreatable. fnd is prevalent, generally affecting young and middle aged adults, and can cause severe disability in some individuals. an early diagnosis. Functional neurological disorder (fnd) describes a problem with how the brain receives and sends information to the rest of the body. it’s often helpful to think of your brain as a computer. in someone who has fnd, there’s no damage to the hardware, or structure, of the brain. it’s the software, or program running on the computer, that. Functional movement disorder (fmd), encompassing abnormal movements and weakness, is a common subtype of functional neurologic symptom disorder (fnd), with a motor dominant presentation seen in 61% of a cohort of people with fnd. fmd accounts for 2% to 20% of referrals to movement disorder clinics. 1,2 women are more frequently affected than. Management of functional neurological disorder. functional neurological disorder (fnd) is a common cause of persistent and disabling neurological symptoms. these symptoms are varied and include abnormal control of movement, episodes of altered awareness resembling epileptic seizures and abnormal sensation and are often comorbid with chronic.
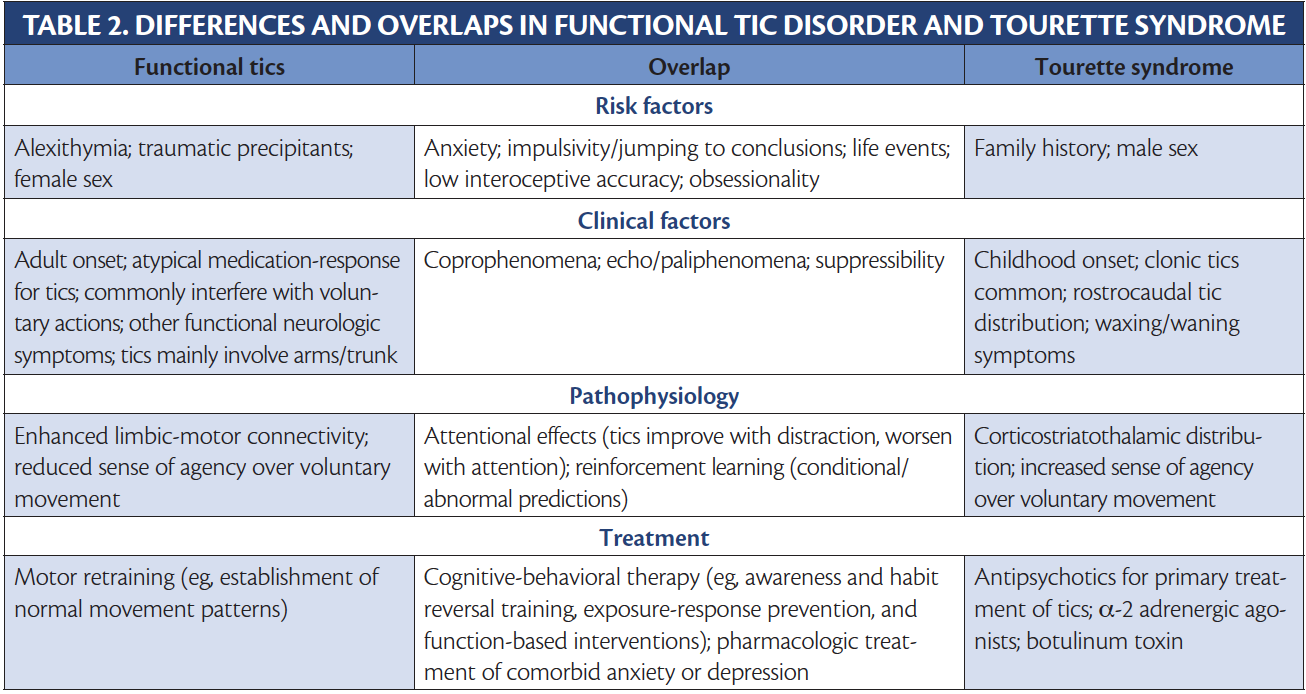
Functional Tic Disorder A Pandemic In A Pandemic Practical Neurology Functional movement disorder (fmd), encompassing abnormal movements and weakness, is a common subtype of functional neurologic symptom disorder (fnd), with a motor dominant presentation seen in 61% of a cohort of people with fnd. fmd accounts for 2% to 20% of referrals to movement disorder clinics. 1,2 women are more frequently affected than. Management of functional neurological disorder. functional neurological disorder (fnd) is a common cause of persistent and disabling neurological symptoms. these symptoms are varied and include abnormal control of movement, episodes of altered awareness resembling epileptic seizures and abnormal sensation and are often comorbid with chronic. Go to: fnd is a common cause of disability and distress, especially in neurological practice. functional disorders represent the second commonest reason to see a neurologist after headache. 1 more tightly defined fnd still accounts for at least 5%–10% of new neurological consultations. estimates of incidence are conservatively 12 per 100,000. Functional neurologic disorder (fnd) is a “rule in” diagnosis, characterized by positive examination signs or semiological features. similar to other clinical diagnoses, providers should ideally see robustly present features, including if possible the identification of multiple features consistent with fnd for the diagnosis to be made with a high degree of certainty. diagnostic pitfalls.

Comments are closed.