Gas Welding Principle Working Equipment Application Advantages And

Gas Welding Principle Working Equipment Application Advantage Today we will learn about gas welding and its principle, working, equipment’s, types, application, advantages and disadvantages. gas welding is a type of liquid state welding process in which fuel gases burns to generate heat. this heat is further used to melt interface surfaces of welding plates which are held together to form a joint. Cheap equipment costs: the initial required capital for gas welding is very low when compared to other forms of welding. for some applications, this is very beneficial. doesn’t require.
Gas Welding Principle Working Equipment Application Advantages And In the last session, we had discussed electric arc welding process along with arc recovery time and arc characteristics whereas, in today's session, we can discuss gas welding process with its definition, equipment, working principle, types of flames, advantages, disadvantages & applications in a detailed way. One of the primary uses of gas welding services is repair work. this technique is better than most at bridging gaps between parts. other applications of gas welding include: fabrication of sheet metal. joining of aircraft parts. automotive chassis and frame fabrication. joining of high carbon steel. The following are the applications of gas welding: to join most ferrous and non ferrous metals, carbon steels, alloy steels, cast iron, aluminum and its alloys, nickel, magnesium, copper and its alloys, etc. to join thin metals. for joining metals in the aircraft industries and automotive. Principle gas welding is the most vital kind of welding process. it is finished by consumption of fuel gases with the assistance of oxygen which frames a concentrated fire of high temperature. this fire straightforwardly strikes the weld zone and melts the weld surface and filler material. the dissolved piece of welding plates diffused in.

Gas Welding Principle Working Equipment Application Advantage The following are the applications of gas welding: to join most ferrous and non ferrous metals, carbon steels, alloy steels, cast iron, aluminum and its alloys, nickel, magnesium, copper and its alloys, etc. to join thin metals. for joining metals in the aircraft industries and automotive. Principle gas welding is the most vital kind of welding process. it is finished by consumption of fuel gases with the assistance of oxygen which frames a concentrated fire of high temperature. this fire straightforwardly strikes the weld zone and melts the weld surface and filler material. the dissolved piece of welding plates diffused in. Gas welding also allows for greater control over heat input, resulting in less distortion and warping. the flame produced by gas welding is highly concentrated, enabling precise and intricate welds. another advantage of gas welding is its ability to work in various positions, including vertical and overhead. Gas welding. gas welding is accomplished by melting the edges or surfaces and mixing with a gas flame and allowing the molten metal to flow together, thus forming a solid continuous joint when cooled. this process is particularly suitable for joining metal sheets and plates with thicknesses of 20 to 50 mm. the filler material of more than 15 mm.
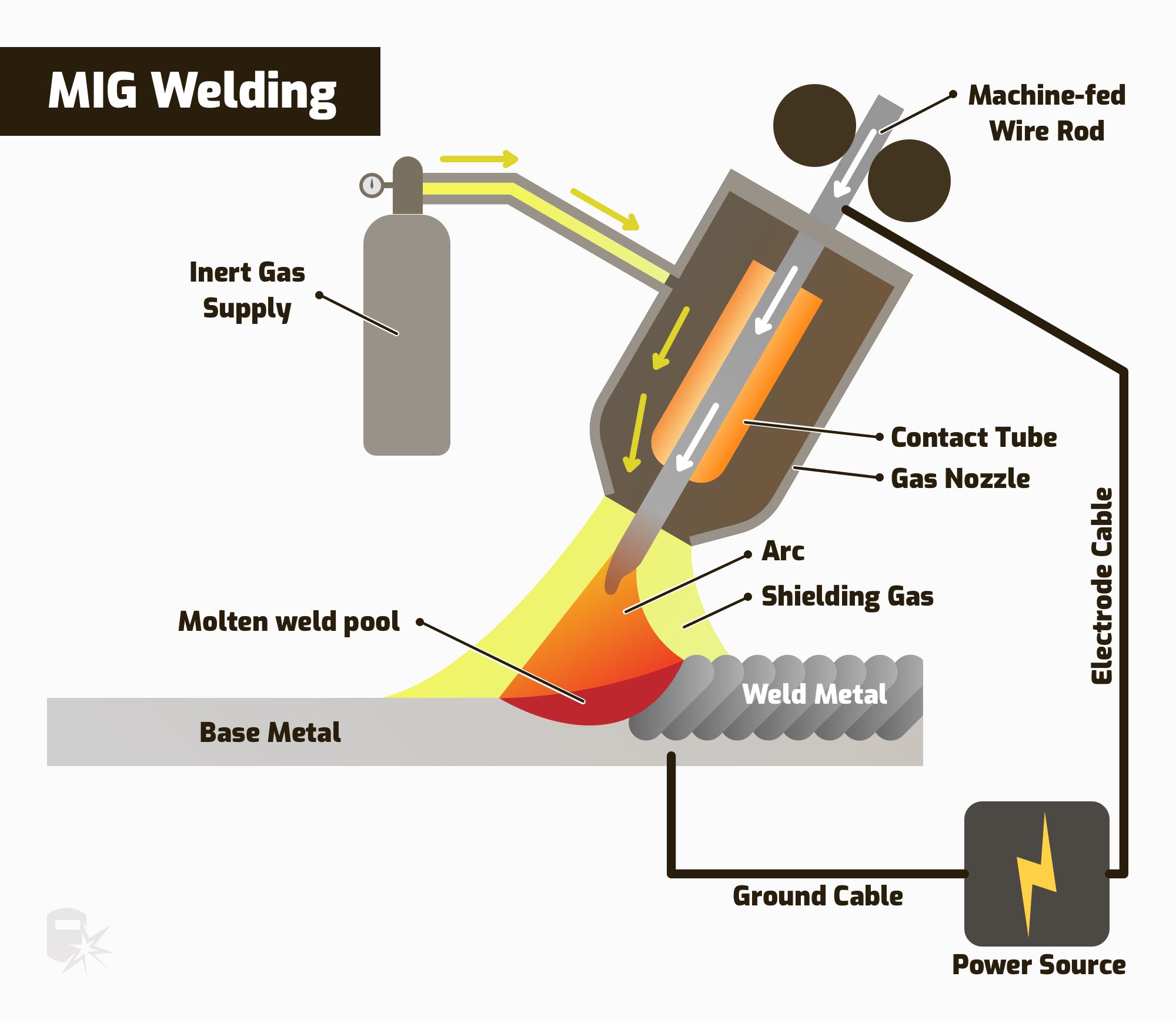
Gas Welding Circuit Diagram Gas welding also allows for greater control over heat input, resulting in less distortion and warping. the flame produced by gas welding is highly concentrated, enabling precise and intricate welds. another advantage of gas welding is its ability to work in various positions, including vertical and overhead. Gas welding. gas welding is accomplished by melting the edges or surfaces and mixing with a gas flame and allowing the molten metal to flow together, thus forming a solid continuous joint when cooled. this process is particularly suitable for joining metal sheets and plates with thicknesses of 20 to 50 mm. the filler material of more than 15 mm.
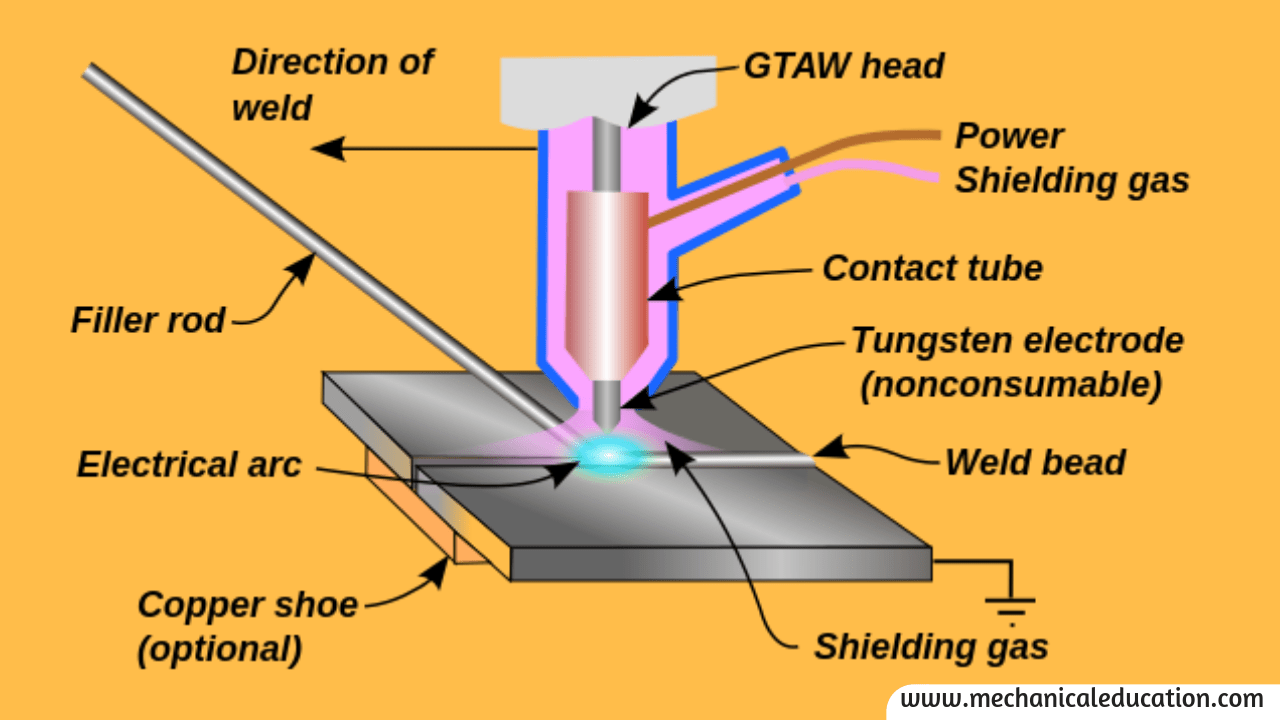
Tungsten Inert Gas Welding Process Advantages Disadvantages And

Comments are closed.