Gram Positive And Negative Cell Wall Gram Staining Gram

Cell Wall Gram Positive Vs Gram Negative Nibhtrapid Gram staining is a differential staining technique that differentiates between gram negative and gram positive groups by colouring these cells purple or pink. as a result of the presence of a thick layer of peptidoglycan in its cell walls, gram positive bacteria stain purple, by retaining the crystal violet that these cells get stained with. Gram positive bacteria have thick cell wall peptidoglycan in their cell wall which will make it to retain the complex of crystal violet and iodine when decolorized by acid which will make it to appear as blue or purple. while gram negative bacteria have thin cell wall peptidoglycan when decolorized by an acid, the complex removed due to it’s cell wall and it takes the color of safranin.
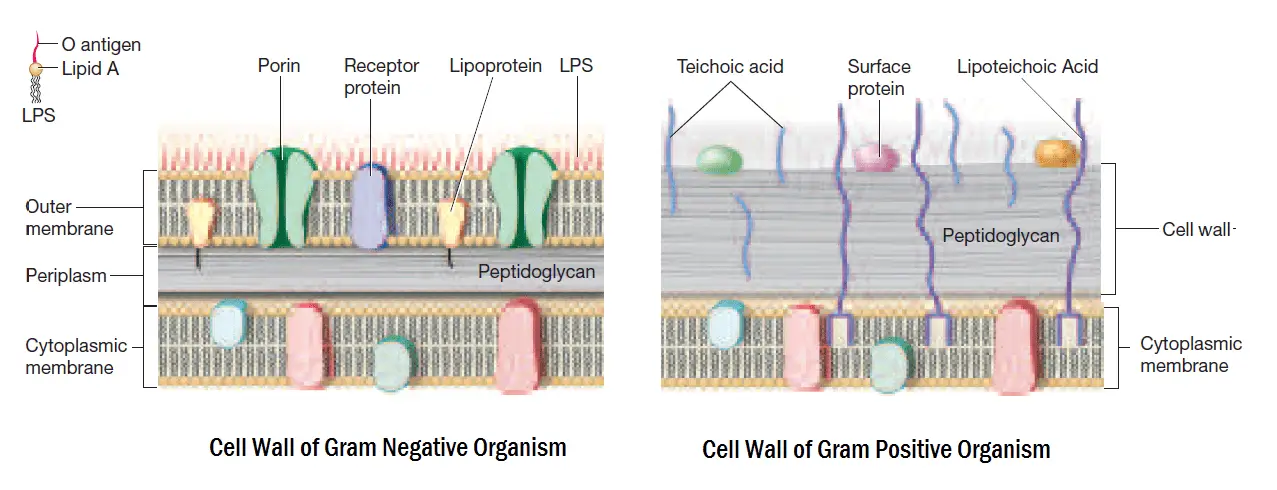
Gram Staining Principle Procedure Interpretation And Animation Gram positive bacteria show blue or purple after gram staining in a laboratory test. they have thick cell walls. gram negative bacteria show pink or red on staining and have thin walls. The cell walls of gram negative bacteria contain only a thin layer of peptidoglycan, but they also have an outer membrane that is absent in gram positive bacteria. gram staining is a technique that uses violet dye to distinguish between gram positive and gram negative bacteria. The gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. it gets its name from the danish bacteriologist hans christian gram, who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.[1] often, the first test performed, gram staining, involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color.[2] the term for organisms that retain. Principle of gram stain image 2: cell wall of gram positive and gram negative bacteria. the differences in gram positive and gram negative bacteria cell wall composition account for the gram staining differences. gram positive cell wall contains a thick layer of peptidoglycan with numerous teichoic acid cross linking, which resists decolorization.
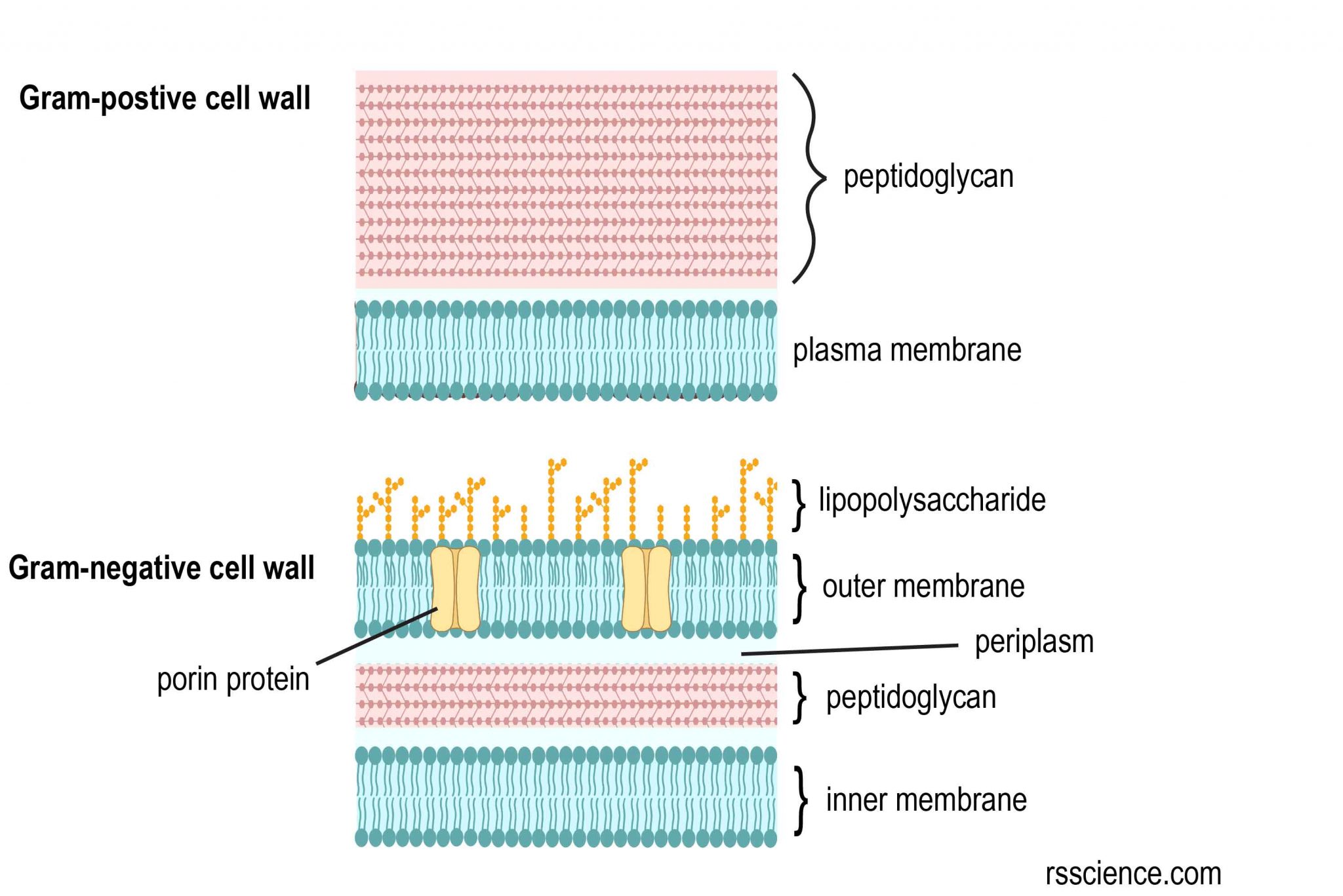
Observing Bacteria Under The Microscope Gram Stain Steps Rs Science The gram staining is one of the most crucial staining techniques in microbiology. it gets its name from the danish bacteriologist hans christian gram, who first introduced it in 1882, mainly to identify organisms causing pneumonia.[1] often, the first test performed, gram staining, involves the use of crystal violet or methylene blue as the primary color.[2] the term for organisms that retain. Principle of gram stain image 2: cell wall of gram positive and gram negative bacteria. the differences in gram positive and gram negative bacteria cell wall composition account for the gram staining differences. gram positive cell wall contains a thick layer of peptidoglycan with numerous teichoic acid cross linking, which resists decolorization. Gram negative bacteria: thickness of cell wall: thicker than gram negative bacteria, around 20 to 25 nm: the cell wall of gram negative bacteria is generally thinner, 11 to 15 nm in diameter: gram reaction: gram positive bacteria stain a deep blue color (violet purple) in the gram staining technique. gram negative bacteria stain pink to red. Summary of differences between gram positive and gram negative bacteria. the gram stain differentiates bacteria based on the nature of their cell wall. in gram positive bacteria, crystal violet forms a complex with iodine in the thick outer peptidoglycan layer. alcohol dehydrates the layer and shrinks it.

Comments are closed.