Gross Anatomy Bone Remodeling Ditki Medical Biological Scienc
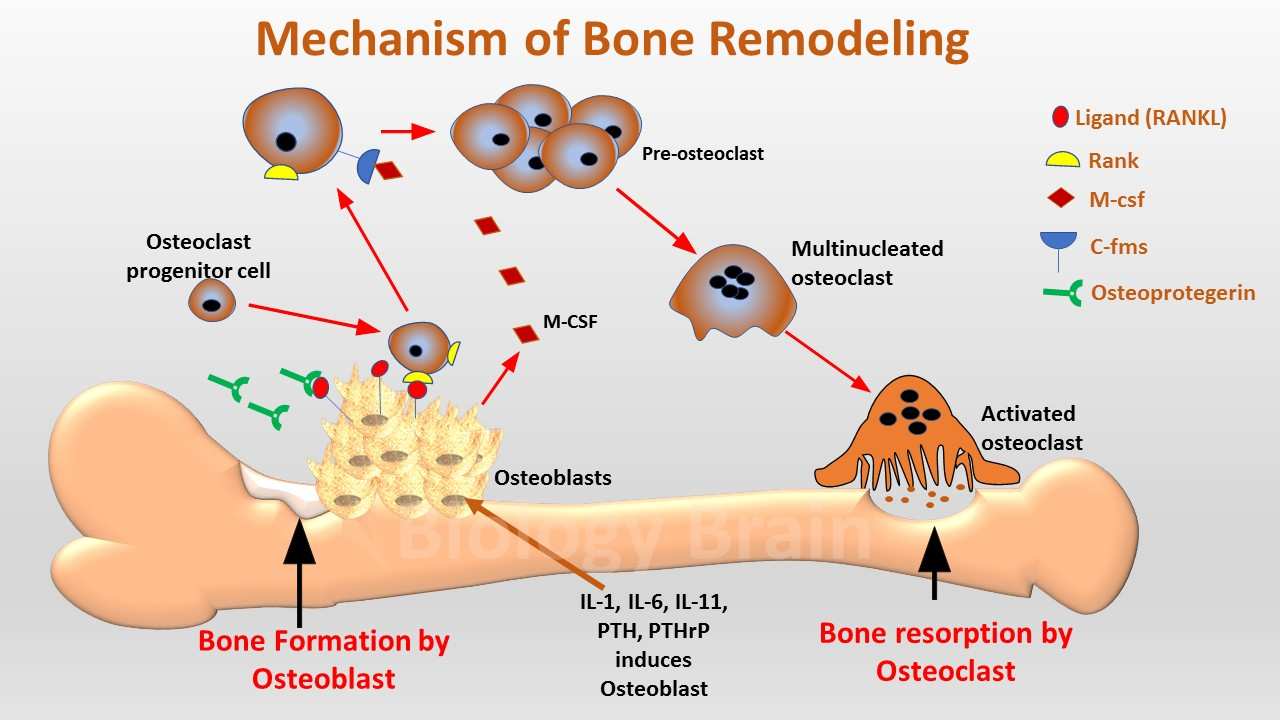
Bone Remodeling Process Steps And Main Factors Biology Brain Lie along bone matrix. bone matrix comprises an inorganic component: hydroxyapatite and an organic component: osteoid. osteoblasts are critical to bone formation, they: secrete osteoid (the organic (unmineralized) portion of bone – ie, the type 1 collagen fibers and ground substance). To begin, let's address the homeostatic process of bone remodeling, which regulates calcium blood levels, repairs worn out bone, and responds to bone stress. draw a bone and a blood vessel. show that osteoblasts form bone from calcium in blood. then, indicate that osteoclasts break down bone and push calcium into blood. now, start a small table.

Bone Remodeling Cycle Bone Remodeling Occurs In Four Phases 1 General anatomy of bonegross structure bone tissuesbone tissues divide into two forms: compact bone see compact bone (aka cortical bone) the outer dense bony layer.spongy bone see spongy bone also known as trabecular, cancellous, or medullary bone. it is the inner bony meshwork. bone regionsdiaphysis the shaft. notably comprises the marrow cavity.metaphysis comprises spongy bone. epiphysis the. Bones are not inert structures within the human body; they continue to change over the course of a lifespan. this process of skeletal change is known as bone remodeling, which both protects the structural integrity of the skeletal system and metabolically contributes to the body's balance of calcium and phosphorus. remodeling entails the resorption of old or damaged bone, followed by the. Modelling. modelling is a dynamic and constructive process which adjusts the size, shape and strength of bone in order to achieve its structural potential during ontogeny, specifically in response to physiological and mechanical influences through out physical maturation [ 22, 79, 111, 122, 257 259 ]. Bone remodeling occurs through a five step process, starting with the initiating event, followed by bone resorption, reversal, formation, and then finally ending with quiescence (fig. 17.2) [11, 23, 24]. two key concepts of remodeling are that (1) it is spatially coordinated, where the region targeted and removed by osteoclasts is then re formed by osteoblasts and (2) it is temporally.
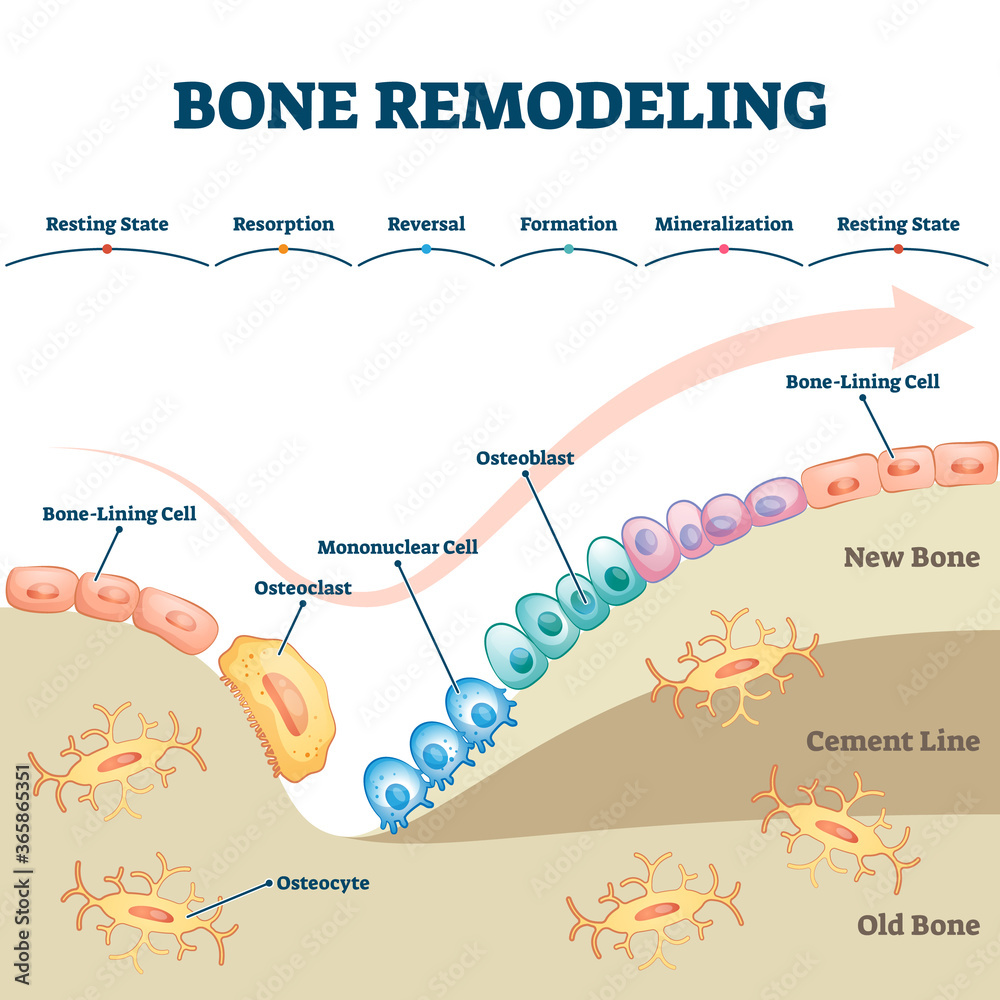
Bone Remodeling Process Educational Explanation With Labeled Structure Modelling. modelling is a dynamic and constructive process which adjusts the size, shape and strength of bone in order to achieve its structural potential during ontogeny, specifically in response to physiological and mechanical influences through out physical maturation [ 22, 79, 111, 122, 257 259 ]. Bone remodeling occurs through a five step process, starting with the initiating event, followed by bone resorption, reversal, formation, and then finally ending with quiescence (fig. 17.2) [11, 23, 24]. two key concepts of remodeling are that (1) it is spatially coordinated, where the region targeted and removed by osteoclasts is then re formed by osteoblasts and (2) it is temporally. Gross anatomy of bones. a long bone has two main regions: the diaphysis and the epiphysis ( figure 6.3.1). the diaphysis is the hollow, tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of the bone. inside the diaphysis is the medullary cavity, which is filled with yellow bone marrow in an adult. Sign up at ditki for a free trial and save 20% with code: 20we use a simple, stepwise approach to learning the basic and medical sciences that pro.

Comments are closed.