Guide To Detecting Ovulation With Cervical Mucus
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/1960279-checking-cervical-mucus-to-get-pregnant-faster-01-5ae09ac2c06471003916b7cb.png)
How To Check Cervical Mucus Discharge To Detect Ovulation Look for egg white discharge – this cervical mucus is clear and stretchy like raw egg whites. (egg white discharge means it's your most fertile time to try for a baby!) to see the various cervical mucus stages, check out the photos below. wipe your vagina with clean white toilet paper before you pee, and notice any discharge. Contact us. for clinicians. manage subscriptiontry flo today. product. product. product. tracking cycle. getting pregnant. what is cervical mucus, and how do you check it? with the help of a doctor, we break down what to know about your ovulation discharge.

Guide To Detecting Ovulation With Cervical Mucus Cervical mucus is a fluid produced by and released from the cervix (the opening to the uterus). hormones cause your cervical mucus to change in texture, volume and color throughout your menstrual cycle. it can be used to identify when you’re most fertile. your mucus is thick, white and dry before ovulation (when your ovary releases an egg). The role of cervical mucus. cervical mucus, also known as cervical fluid, is produced by glands in the cervix – the narrow passage between the uterus and vagina. the quality and quantity of this fluid ebbs and flows according to the hormonal changes across the menstrual cycle. during the fertile window when a woman is ovulating and most. Cervical mucus is a hydrogel secreted by your cervical crypts. your cervix is the entrance to your uterus, and it responds to throughout your cycle (specifically estrogen and progesterone). prior to ovulation, an egg is being recruited to mature while estrogen slowly builds, triggering the creation of estrogenic cervical mucus. Your menstrual cycle: your cervical mucus can change during each stage of your cycle. immediately before and during ovulation, the mucus is typically clear, stretchy, and slippery. after ovulation.
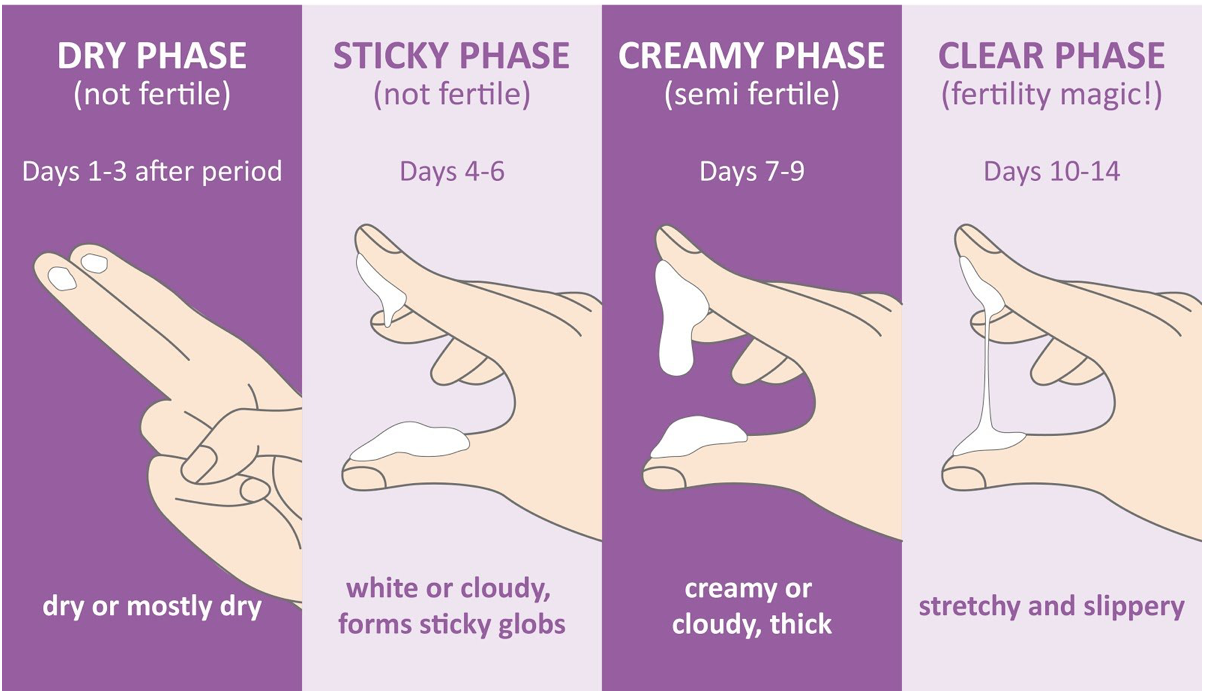
Fertile Cervical Mucus вђ Dr Kendra Zamick Nd Cervical mucus is a hydrogel secreted by your cervical crypts. your cervix is the entrance to your uterus, and it responds to throughout your cycle (specifically estrogen and progesterone). prior to ovulation, an egg is being recruited to mature while estrogen slowly builds, triggering the creation of estrogenic cervical mucus. Your menstrual cycle: your cervical mucus can change during each stage of your cycle. immediately before and during ovulation, the mucus is typically clear, stretchy, and slippery. after ovulation. Cervical mucus (cm) otherwise known as vaginal discharge, is secreted by glands found in and around the cervix. hormonal changes throughout a person's reproductive and ovulation cycle change the. About one day before ovulation, bbt typically dips about 0.5 degrees to its lowest point (on average, 97 to 97.5 degrees f). ovulation. once you ovulate – around day 14 of your menstrual cycle – progesterone production causes a rise above your baseline bbt of 0.5 to 1.0 degrees f. luteal phase. bbt stays high throughout much of this phase.
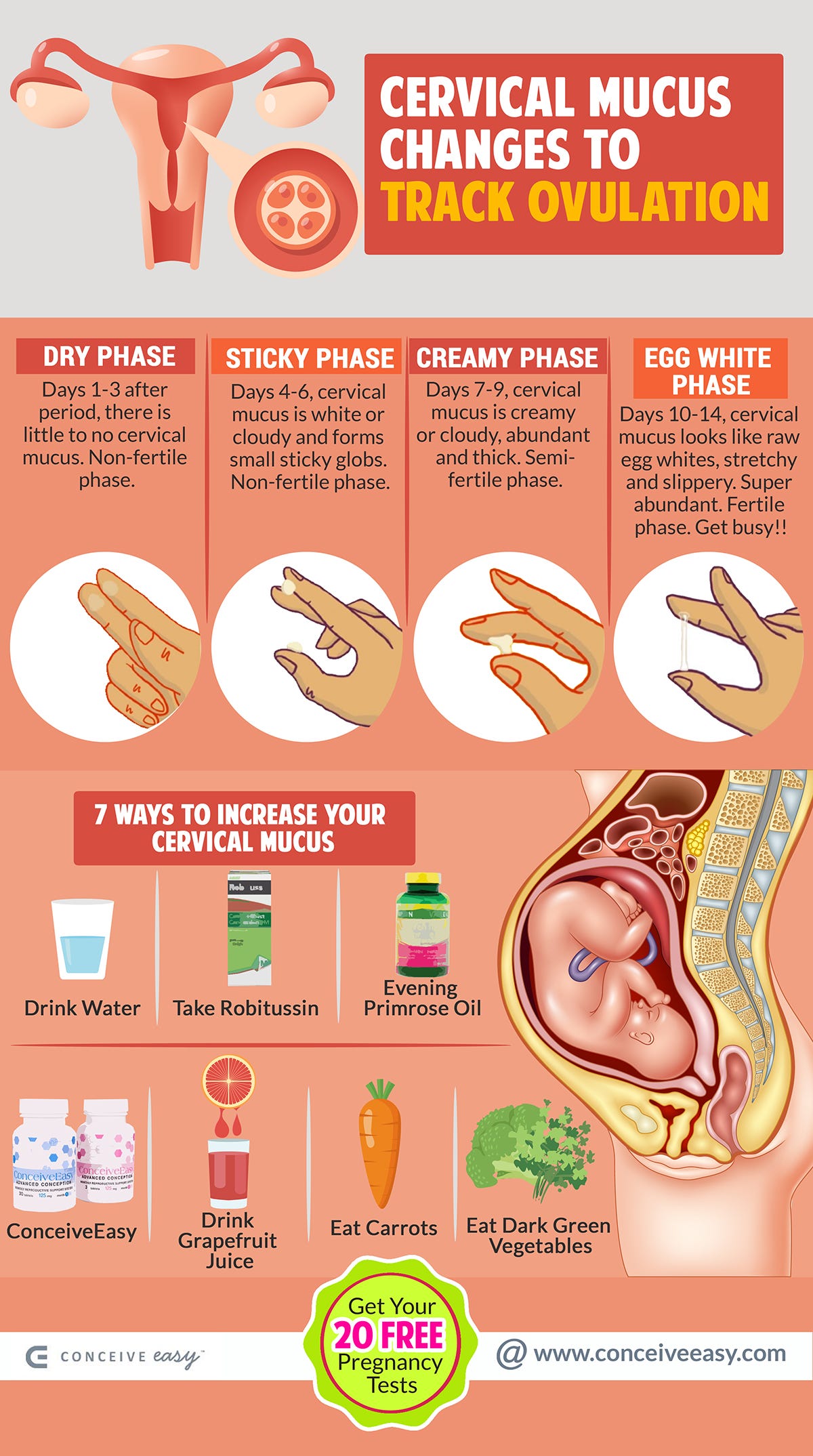
How To Track Ovulation With Cervical Mucus Changes Infographic By Cervical mucus (cm) otherwise known as vaginal discharge, is secreted by glands found in and around the cervix. hormonal changes throughout a person's reproductive and ovulation cycle change the. About one day before ovulation, bbt typically dips about 0.5 degrees to its lowest point (on average, 97 to 97.5 degrees f). ovulation. once you ovulate – around day 14 of your menstrual cycle – progesterone production causes a rise above your baseline bbt of 0.5 to 1.0 degrees f. luteal phase. bbt stays high throughout much of this phase.

Comments are closed.