Hard Disk Drive 3 Read Write Operation Of Hard Drive How Hard

Hard Disk Drive 3 Read Write Operation Of Hard Drive How Hard Copyright: deb shekhar laha#operatingsystem #harddrive #gate examination #hdd #harddiskdrive#readoperation #writeoperation #harddiskdriveexplainedprevious. The read write (r w) head moves over the rotating hard disk. it is this read write head that performs all the read and write operations on the disk and hence, the position of the r w head is a major concern. to perform a read or write operation on a memory location, we need to place the r w head over that position.

Hard Disk Read Write Operations 3 Hd Youtube Read write heads are responsible for reading and writing data to the platters inside the hard disk drive. as described by disk structure, read write heads are mechanical arms that move across the surface of the platters to read or write data. the heads float very close above the platter surface, with clearance typically less than the width of a. There are two read write heads for each platter, one to read the top surface and one to read the bottom, so a hard drive that has five platters (say) would need ten separate read write heads. the read write heads are mounted on an electrically controlled arm that moves from the center of the drive to the outer edge and back again. Once positioned, the hard drive’s write operation begins. the read write heads induce changes in the magnetic coating of the platters, aligning the magnetic particles in a way that represents the binary data. these changes are permanent and will remain on the platters until modified or overwritten in the future. 37.3 a simple disk drive. let’s understand how disks work by building up a model one track at a time. assume we have a simple disk with a single track (figure 37.1). this track has just 12 sectors, each of which is 512 bytes in size (our typical sector size, recall) and addressed therefore by the numbers 0 through 11.

Working Of Hard Disk With Diagram Once positioned, the hard drive’s write operation begins. the read write heads induce changes in the magnetic coating of the platters, aligning the magnetic particles in a way that represents the binary data. these changes are permanent and will remain on the platters until modified or overwritten in the future. 37.3 a simple disk drive. let’s understand how disks work by building up a model one track at a time. assume we have a simple disk with a single track (figure 37.1). this track has just 12 sectors, each of which is 512 bytes in size (our typical sector size, recall) and addressed therefore by the numbers 0 through 11. A hard disk drive (hdd for short) is a type of storage commonly used as the primary storage system both laptop and desktop computers. it functions like any other type of digital storage device by writing bits of data and then recalling them later. it stands to mention that an hdd is what’s referred to as “non volatile”, which simply means. The hard drive contains a spinning platter with a thin magnetic coating. a "head" moves over the platter, writing 0's and 1's as tiny areas of magnetic north or south on the platter. to read the data back, the head goes to the same spot, notices the north and south spots flying by, and so deduces the stored 0's and 1's.
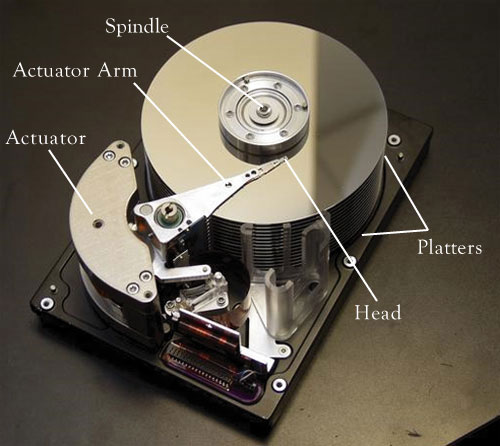
How A Hard Drive Works Online Computer Tips A hard disk drive (hdd for short) is a type of storage commonly used as the primary storage system both laptop and desktop computers. it functions like any other type of digital storage device by writing bits of data and then recalling them later. it stands to mention that an hdd is what’s referred to as “non volatile”, which simply means. The hard drive contains a spinning platter with a thin magnetic coating. a "head" moves over the platter, writing 0's and 1's as tiny areas of magnetic north or south on the platter. to read the data back, the head goes to the same spot, notices the north and south spots flying by, and so deduces the stored 0's and 1's.

Storage 101 Understanding The Hard Disk Drive Simple Talk

Comments are closed.