Heinrich S Accident Triangle Theory Unsafe Condition Unsafe Act
Heinrich S Accident Triangle We Ask And You Answer The Best Answer The accident triangle, also known as heinrich's triangle or bird's triangle, is a theory of industrial accident prevention. it shows a relationship between serious accidents, minor accidents and near misses. this idea proposes that if the number of minor accidents is reduced then there will be a corresponding fall in the number of serious. According to heinrich, 88 percent of accidents are caused by unsafe acts of persons and 10 percent by unsafe machines (with 2 percent being unavoidable). decades later, heinrich’s theories – including the domino theory and accident triangle – continue to draw followers and critics. in his 2002 book, “heinrich revisited: truisms or myths.

Using The Accident Triangle To Grow Your Safety Culture Excellerate Heinrich is most famous for originating the concept of the “ safety pyramid ”. he also developed the “five domino model” of accident causation, a sequential accident model which has been influential in the development of occupational safety thinking. his “domino theory” represents an accident sequence as a causal chain of events. The most famous result is the incident accident pyramid, also known as the “safety pyramid”, the “accident triangle” and “heinrich’s law”. the pyramid, as illustrated by heinrich in the 1941 edition of his book, is shown below. the “accident pyramid”, as depicted by h. heinrich in the second edition of his book industrial. The safety triangle, also known as heinrich’s triangle, bird’s triangle, accident triangle, or safety pyramid, and often confused as incident pyramid, is a theory of industrial accident prevention. the heinrich triangle seeks to develop links between fatal accidents, minor accidents, and near misses. it suggests that reducing the number of. The unsafe acts of people, 10% were caused by unsafe conditions and 2% were not preventable. unfortunately, heinrich’s original work and data are not available and no one has been able to verify or cat egorically refute his findings. his defini tions of serious or minor injuries are also unclear. today, many believe that hein.

Los Alamos And Santa Fe Bikes Unsafe Behavior Crash Precursor On The safety triangle, also known as heinrich’s triangle, bird’s triangle, accident triangle, or safety pyramid, and often confused as incident pyramid, is a theory of industrial accident prevention. the heinrich triangle seeks to develop links between fatal accidents, minor accidents, and near misses. it suggests that reducing the number of. The unsafe acts of people, 10% were caused by unsafe conditions and 2% were not preventable. unfortunately, heinrich’s original work and data are not available and no one has been able to verify or cat egorically refute his findings. his defini tions of serious or minor injuries are also unclear. today, many believe that hein. Heinrich’s causation theory: the 88 10 2 ratio. heinrich professes that among the direct and proximate causes of industrial accidents: 88% are unsafe acts of persons; nical or physical condi tio. ;2% are unpreventable (h 5).according to heinrich, man failure is the problem and psychology is an imp. 4. heinrich's 88 10 2 ratios indicate that among the direct and proximate causes, 88 percent are unsafe acts, 10 percent are unsafe mechanical or physical conditions and 2 percent are unpreventable the methodology used in arriving at those ratios cannot be supported. current causation knowledge indicates the premise to be invalid.
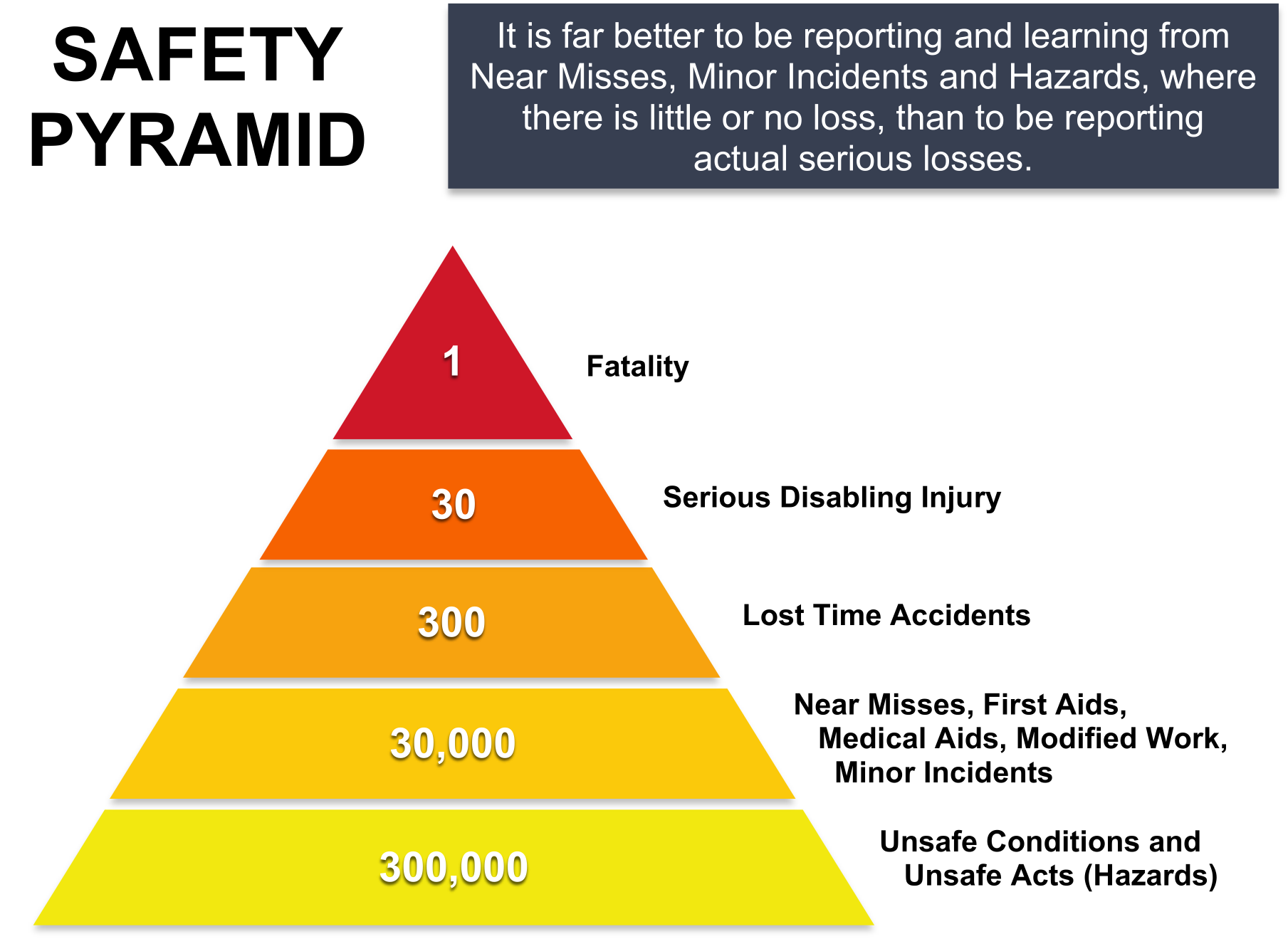
Safety Pyramid Explained Heinrich’s causation theory: the 88 10 2 ratio. heinrich professes that among the direct and proximate causes of industrial accidents: 88% are unsafe acts of persons; nical or physical condi tio. ;2% are unpreventable (h 5).according to heinrich, man failure is the problem and psychology is an imp. 4. heinrich's 88 10 2 ratios indicate that among the direct and proximate causes, 88 percent are unsafe acts, 10 percent are unsafe mechanical or physical conditions and 2 percent are unpreventable the methodology used in arriving at those ratios cannot be supported. current causation knowledge indicates the premise to be invalid.
The вђњsafety Triangle вђќ A Useful Yet Complicated 40 Off

Comments are closed.