Hemiplegic Gait Youtube
Applied Sciences Free Full Text The Relationship Between Gait Video includes both a lateral view and an anterior posterior view.case studies are strictly for educational purposes. for more information about mission gait. More medical videos on : medicofiles hemiplegic gait demonstrationthe patient has unilateral weakness and spasticity with the upper extremity held.

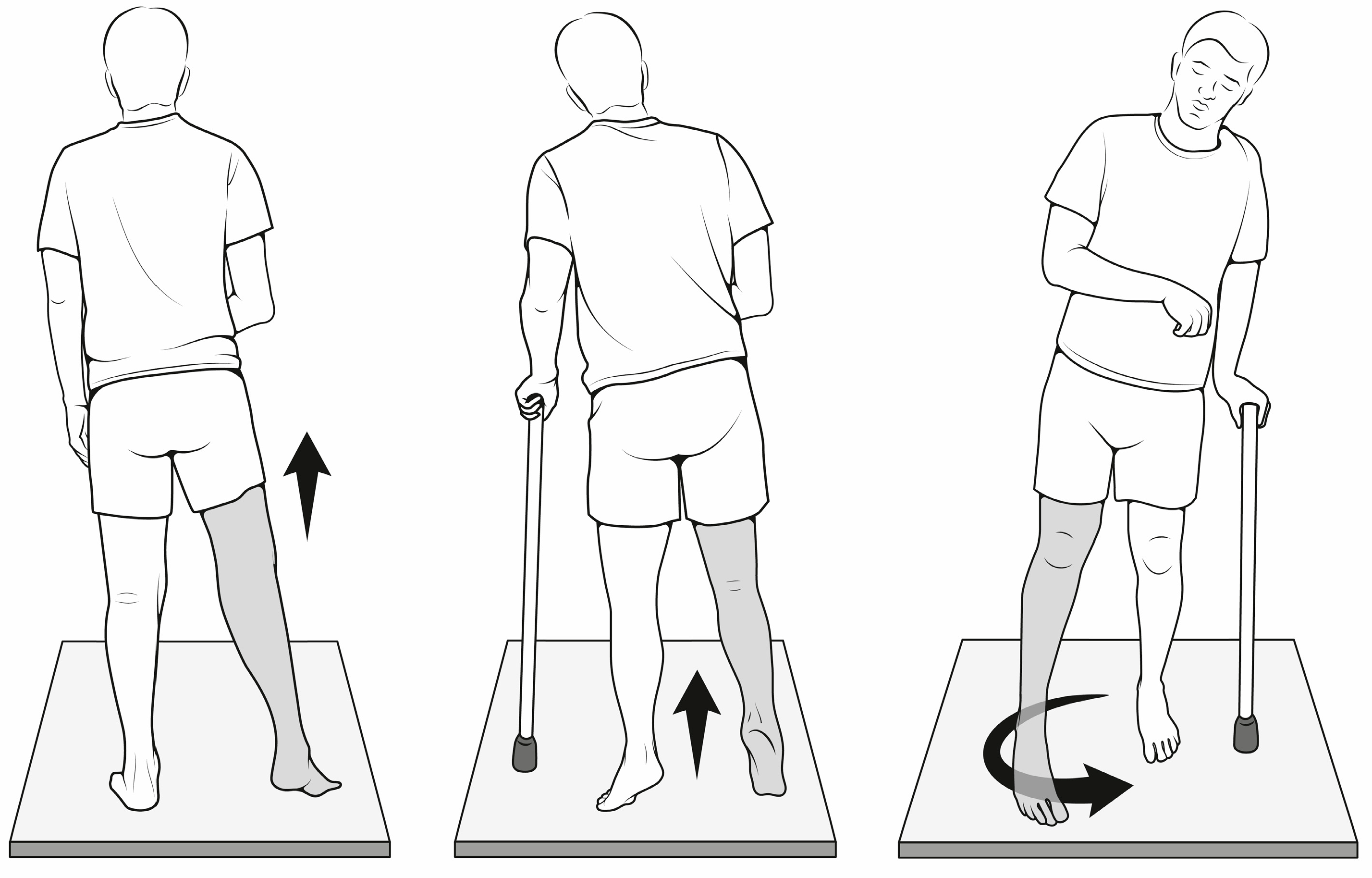
Hemiplegic Gait Clinical Medicine Youtube Dr. tom novacheck, gillette children's, describes the characteristics of the 4 types of unilateral, otherwise known as hemiplegic gait, and how the use of cl. Current findings of post stroke hemiplegic gait as a result of altered neural control are then summarized. based on recent advances on pathophysiology of muscle weakness and spasticity after stroke, a new perspective of understanding post stroke hemiplegic gait is proposed. its clinical implications for management of hemiplegic gait are discussed. Diplegic gait demonstration. the patient has spasticity in the lower extremities greater than the upper extremities. the hips and knees are flexed and adducted with the ankles extended and internally rotated. when the patient walks both lower extremities are circumducted and the upper extremities are held in a mid or low guard position. Compensatory gait patterns are developed to walk with the paralysis, weakness and spasticity caused by a hemiplegic stroke. the loss or decreased ability to flex the knee and hip and dorsiflex the ankle lead to issues with foot clearance on the affected side. a common compensatory pattern to gain foot clearance is circumduction.
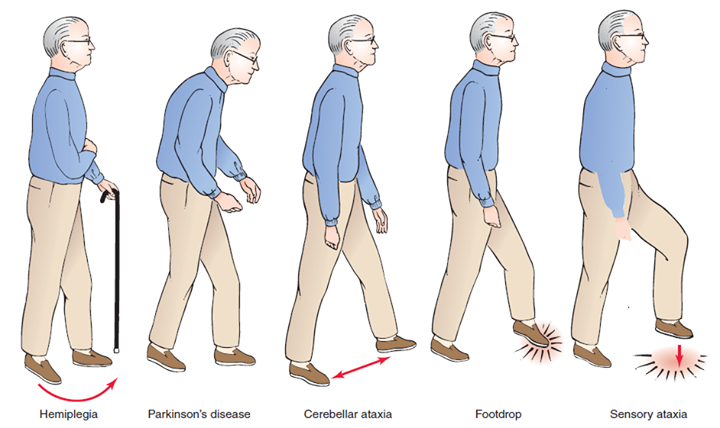
Neuro Exam Post Stroke Hemiplegic Gait вђ Strokesciences Diplegic gait demonstration. the patient has spasticity in the lower extremities greater than the upper extremities. the hips and knees are flexed and adducted with the ankles extended and internally rotated. when the patient walks both lower extremities are circumducted and the upper extremities are held in a mid or low guard position. Compensatory gait patterns are developed to walk with the paralysis, weakness and spasticity caused by a hemiplegic stroke. the loss or decreased ability to flex the knee and hip and dorsiflex the ankle lead to issues with foot clearance on the affected side. a common compensatory pattern to gain foot clearance is circumduction. Gait abnormalities. there are eight basic pathological gaits that can be attributed to neurological conditions: hemiplegic, spastic diplegic, neuropathic, myopathic, parkinsonian, choreiform, ataxic (cerebellar) and sensory. observation of these gait are an important aspect of diagnosis that may provide information about several musculoskeletal. Neuropathic gait (a.k.a. high steppage gait) is caused by weakness of the muscles in the distal limb (typically the dorsiflexors of the foot) as a result of damage to the peripheral nerves providing motor innervation. weakness of the dorsiflexors of the foot results in foot drop and dragging of the toes during the swing phase of the gait cycle.

Comments are closed.