High Serum Albumin And Diabetes Diabetestalknet
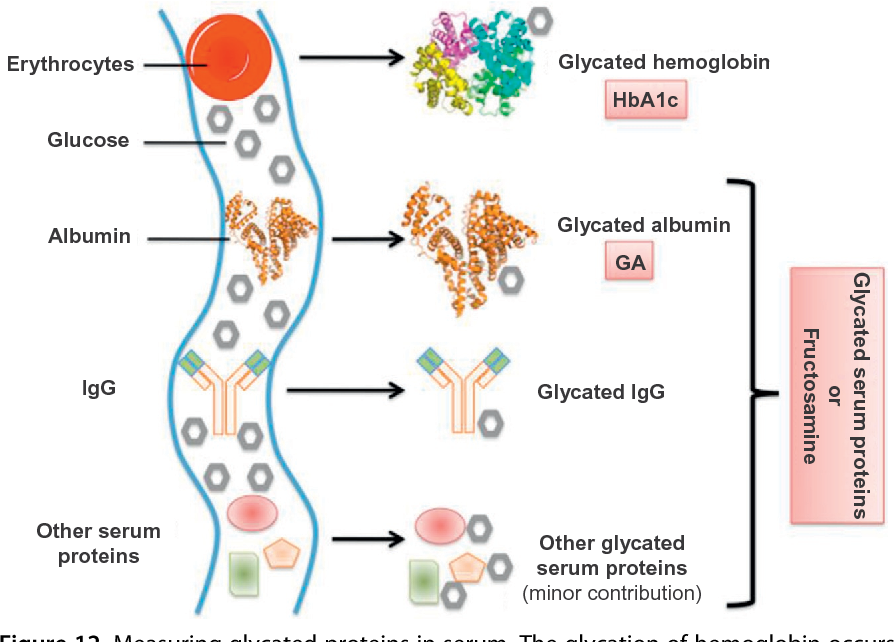
High Serum Albumin And Diabetes Diabetestalknet These results suggest that serum albumin is associated with insulin resistance. insulin resistance is a principal cause of type 2 diabetes and serum albumin has been associated with insulin resistance [6, 17 19]. however, in our study, serum albumin did not have independent effect on the development of diabetes. Human serum albumin (hsa) is the most abundant protein in human plasma, which undergoes severe non enzymatic glycation with glucose in patients with diabetes; this modifies the structure and function of hsa. furthermore, the advanced glycation end products produced by glycated hsa can cause pathological damage to the human body through various.

High Serum Albumin And Diabetes Diabetestalknet Glycated albumin values of 16.5% and 17.8% are “equivalent” (i.e., the same percentile) as a fpg of 126 mg dl (6.99 mmol l) and hb a 1c of 6.5% in us adult without diagnosed diabetes. glycated albumin values were truncated at the 1st percentile in (a) and (b) for clarity. all figures are presented on the log scale. In this issue, bae et al. reported that a high serum albumin level is associated with insulin resistance, but they failed to show a significant correlation between serum albumin level and the development of diabetes in a longitudinal follow up. the authors analyzed data for a large cohort from a health promotion center located in an urban area. Two major protein components, hemoglobin and serum albumin, serve as important markers of the extent of glycemic control in patients. while hba1c (glycated hemoglobin) is the most widely used glycemic indicator, serum albumin has been advanced as a potentially viable biomarker for short term monitoring [57], [58], [59]. the emergence of tri. Long term hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes leads to human serum albumin (hsa) glycation, which may impair hsa function as a transport protein and affect the therapeutic efficacy of anticoagulants in patients with diabetes.

High Serum Albumin And Diabetes Diabetestalknet Two major protein components, hemoglobin and serum albumin, serve as important markers of the extent of glycemic control in patients. while hba1c (glycated hemoglobin) is the most widely used glycemic indicator, serum albumin has been advanced as a potentially viable biomarker for short term monitoring [57], [58], [59]. the emergence of tri. Long term hyperglycemia in patients with diabetes leads to human serum albumin (hsa) glycation, which may impair hsa function as a transport protein and affect the therapeutic efficacy of anticoagulants in patients with diabetes. Human serum albumin (hsa) is the most abundant protein in human plasma, which undergoes severe non enzymatic glycation with glucose in patients with diabetes; this modifies the structure and function of hsa. furthermore, the advanced glycation end products produced by glycated hsa can cause pathological damage to the human body through various. Human serum albumin (hsa) is a multifaceted protein with vital physiological functions. it is the most abundant plasma protein with inherent capability to bind to diverse ligands, and thus susceptible to various post translational modifications (ptms) which alter its structure and functions. one such ptm is glycation, a non enzymatic reaction.

High Serum Albumin And Diabetes Diabetestalknet Human serum albumin (hsa) is the most abundant protein in human plasma, which undergoes severe non enzymatic glycation with glucose in patients with diabetes; this modifies the structure and function of hsa. furthermore, the advanced glycation end products produced by glycated hsa can cause pathological damage to the human body through various. Human serum albumin (hsa) is a multifaceted protein with vital physiological functions. it is the most abundant plasma protein with inherent capability to bind to diverse ligands, and thus susceptible to various post translational modifications (ptms) which alter its structure and functions. one such ptm is glycation, a non enzymatic reaction.

Comments are closed.