Hip Dysplasia Adolescent Description
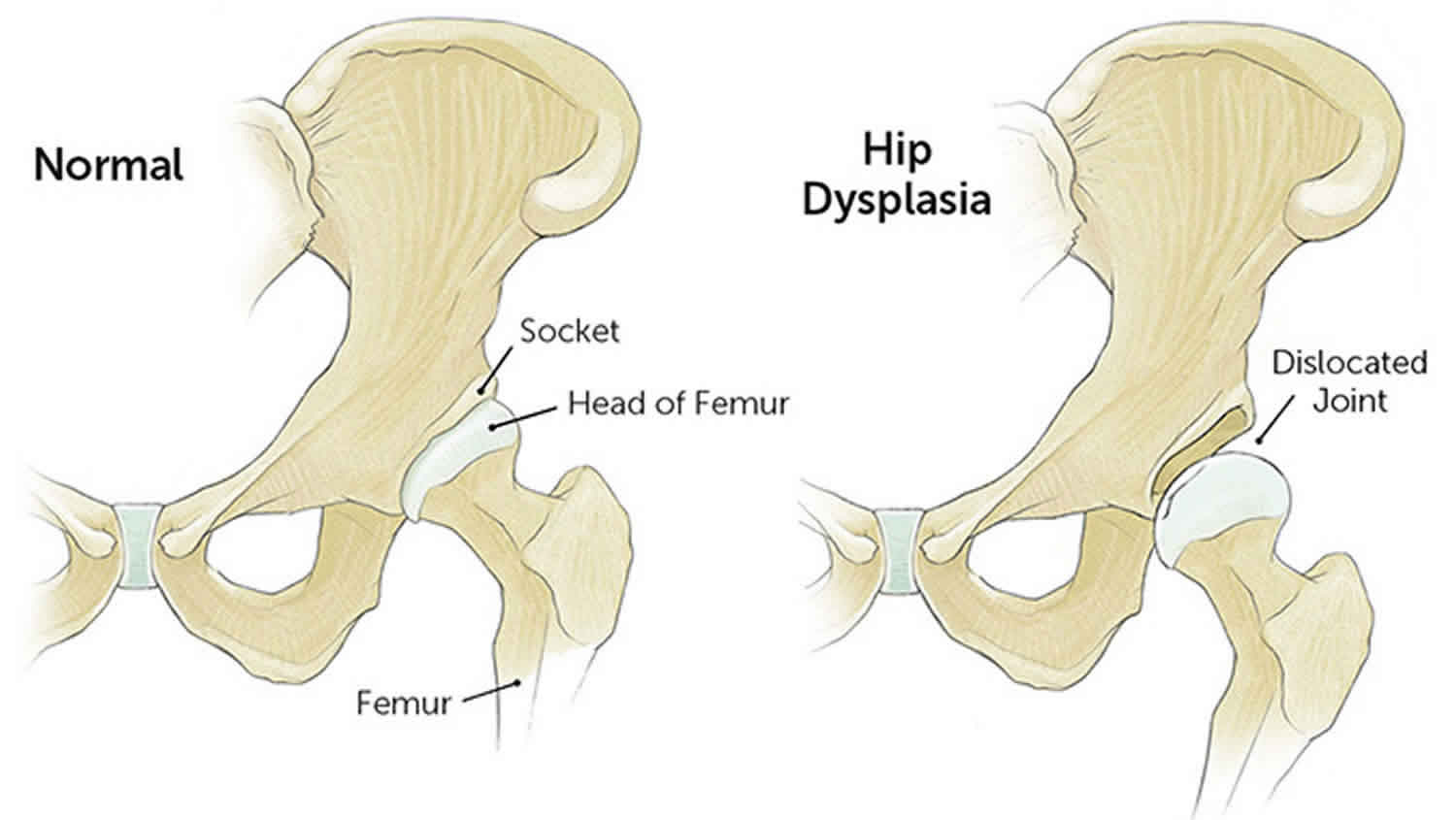
Developmental Dysplasia Of The Hip Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Adolescent hip dysplasia is usually the end result of developmental dysplasia of the hip (ddh), a condition that occurs at birth or in early childhood. although infants are routinely screened for ddh, some cases remain undetected or are mild enough that they are left untreated. these patients may not show symptoms of hip dysplasia until they. Hip dysplasia occurs when the hip joint doesn’t develop normally. it is a condition that may be recognized shortly after birth or later in life, which is then classified as adolescent hip dysplasia (ahd). in a healthy hip joint, the ball of the hip, or top of the femur (thighbone), fits well and is contained within the socket in the pelvis.

Adolescents International Hip Dysplasia Institute What is hip dysplasia? for adolescents and young adults, hip dysplasia is a result of one or more areas of the hip joint not developing properly. it occurs when the ball at the top of the thigh bone (femur) that fits into the hip socket (acetabulum) is loose within the socket, so that the socket’s coverage of the ball (femoral head) is reduced. Hip dysplasia is a common condition. it is the leading cause of hip oa in adults under 60 [16] and is reported as “a significant health concern”. [17] hip dislocations occur in 0.1 0.3% of newborns [18] ddh occurs in 1 3% of newborns [19] 80% of cases are female [18] over 50% of those with ddh have positive family history [20] 92% of young. Hip dysplasia can be seen in a wide age range of patients, but adolescents tend to have more severe dysplasia, as the soft tissues surrounding the joint fail earlier. diagnosis in addition to a thorough physical exam and patient history, orthopedists use x rays , magnetic resonance imaging (mri) , and in some cases, 3 d ct images to confirm a. Description. in patients with hip dysplasia, the acetabulum is shallow, meaning that the ball, or femoral head, cannot firmly fit into the socket. as a result of this abnormality, there is increased stress on a smaller area of the joint, which can result in pain and early degeneration of the hip. the labrum can end up bearing the forces that.

Comments are closed.