Histology Of Thymus And Lymph Node Step By Step Guide With Brief Description

Histology Of Thymus And Lymph Node Step By Step Guide W About press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. Thymus. thymus is an encapsulated organ where t cells proliferate and mature behind the blood thymus barrier. this slide has good examples of macrophages. thin connective tissue surrounding the thymus that extends trabeculae inward forming incomplete lobules. outer darker, region of small lymphocytes.

Thymus Histology Labeled Summary. the thymus is a flat encapsulated lymphoid organ located behind the sternum. it's most active during childhood and slowly involutes in adulthood, with fatty infiltrates and decreased thymic tissue. the thymus gland has two lobes, each of which has an outer cortex that's very basophilic and stains dark purple, whereas the inner medulla. Thymus (anterior view) the thymus is a primary lymphoid organ located in the mediastinum. it consists of two lobes connected by an isthmus. histologically, the thymus is divided into lobules, each one consisting of a central medulla and a peripheral cortex. the thymus is an essential component of our immune systems. Mediastinum is the centrally located portion of thorax, which notably contains the heart, aorta, vena cava, esophagus, trachea, thymus, thoracic duct, sympathetic trunk, phrenic and vagus nerves, internal thoracic arteries, azygos and hemiazygos veins. mediastinum can be divided into 4 regions: superior, anterior, middle and posterior. The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ found within the superior mediatinum, behind the upper part of the sternum. this organ is active in children, but at the start of puberty, until old age, it starts to atrophy, producing fewer t cells. the thymus also produces thymic hormones that support the growth and differentiation of t cell progenitors.
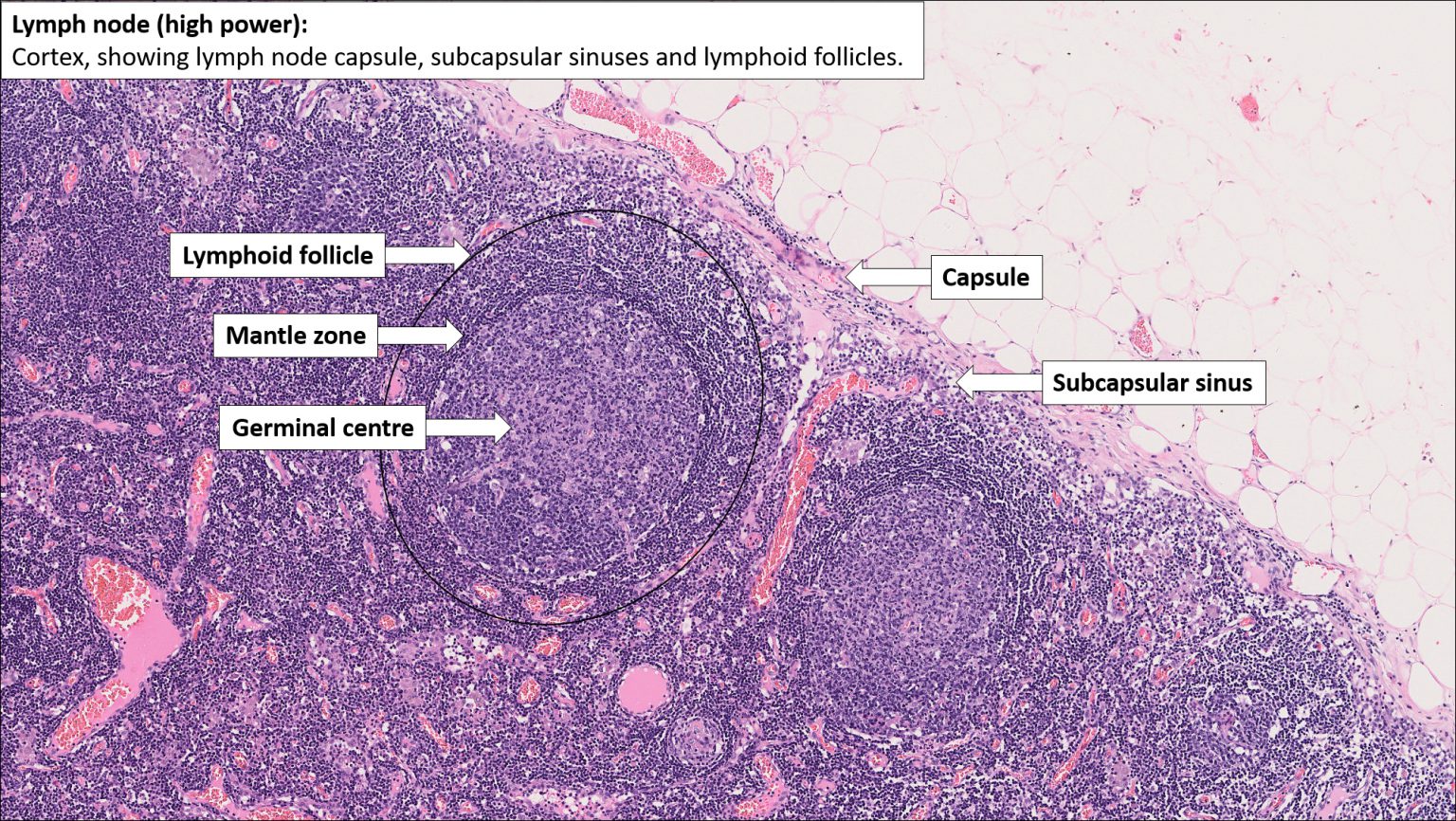
Lymph Node вђ Normal Histology вђ Nus Pathweb Nus Pathweb Mediastinum is the centrally located portion of thorax, which notably contains the heart, aorta, vena cava, esophagus, trachea, thymus, thoracic duct, sympathetic trunk, phrenic and vagus nerves, internal thoracic arteries, azygos and hemiazygos veins. mediastinum can be divided into 4 regions: superior, anterior, middle and posterior. The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ found within the superior mediatinum, behind the upper part of the sternum. this organ is active in children, but at the start of puberty, until old age, it starts to atrophy, producing fewer t cells. the thymus also produces thymic hormones that support the growth and differentiation of t cell progenitors. Lymph nodes are small organs interposed along lymphatic vessels that immunologically monitor lymph. dense connective tissue enclosing the node. space underneath the capsule that receives lymph from afferent lymphatic vessels. connective tissue that extends inward from the capsule. Chapter 10 lymphoid system. the main function of the lymphoid system is to protect the body from pathogens (e.g., bacteria, virus, and parasites) and diseased cells (e.g., virus infected or tumor cells). the immune system is organized into organs and tissues that are functionally unified via blood and lymph vascular systems.

Thymus вђ Tutorial вђ Histology Atlas For Anatomy And Physiology Lymph nodes are small organs interposed along lymphatic vessels that immunologically monitor lymph. dense connective tissue enclosing the node. space underneath the capsule that receives lymph from afferent lymphatic vessels. connective tissue that extends inward from the capsule. Chapter 10 lymphoid system. the main function of the lymphoid system is to protect the body from pathogens (e.g., bacteria, virus, and parasites) and diseased cells (e.g., virus infected or tumor cells). the immune system is organized into organs and tissues that are functionally unified via blood and lymph vascular systems.

Thymus вђ Tutorial вђ Histology Atlas For Anatomy And Physiology

Comments are closed.