How A Blast Furnace Works
Blast Furnace Process Overview Download Scientific Diagram Blast furnace, a vertical shaft furnace that produces liquid metals by the reaction of a flow of air introduced under pressure into the bottom of the furnace with a mixture of metallic ore, coke, and flux fed into the top. blast furnaces are used to produce pig iron from iron ore for subsequent processing into steel, and they are also employed. Blast furnaces operate on the principle of chemical reduction whereby carbon monoxide converts iron oxides to elemental iron. blast furnaces differ from bloomeries and reverberatory furnaces in that in a blast furnace, flue gas is in direct contact with the ore and iron, allowing carbon monoxide to diffuse into the ore and reduce the iron oxide.
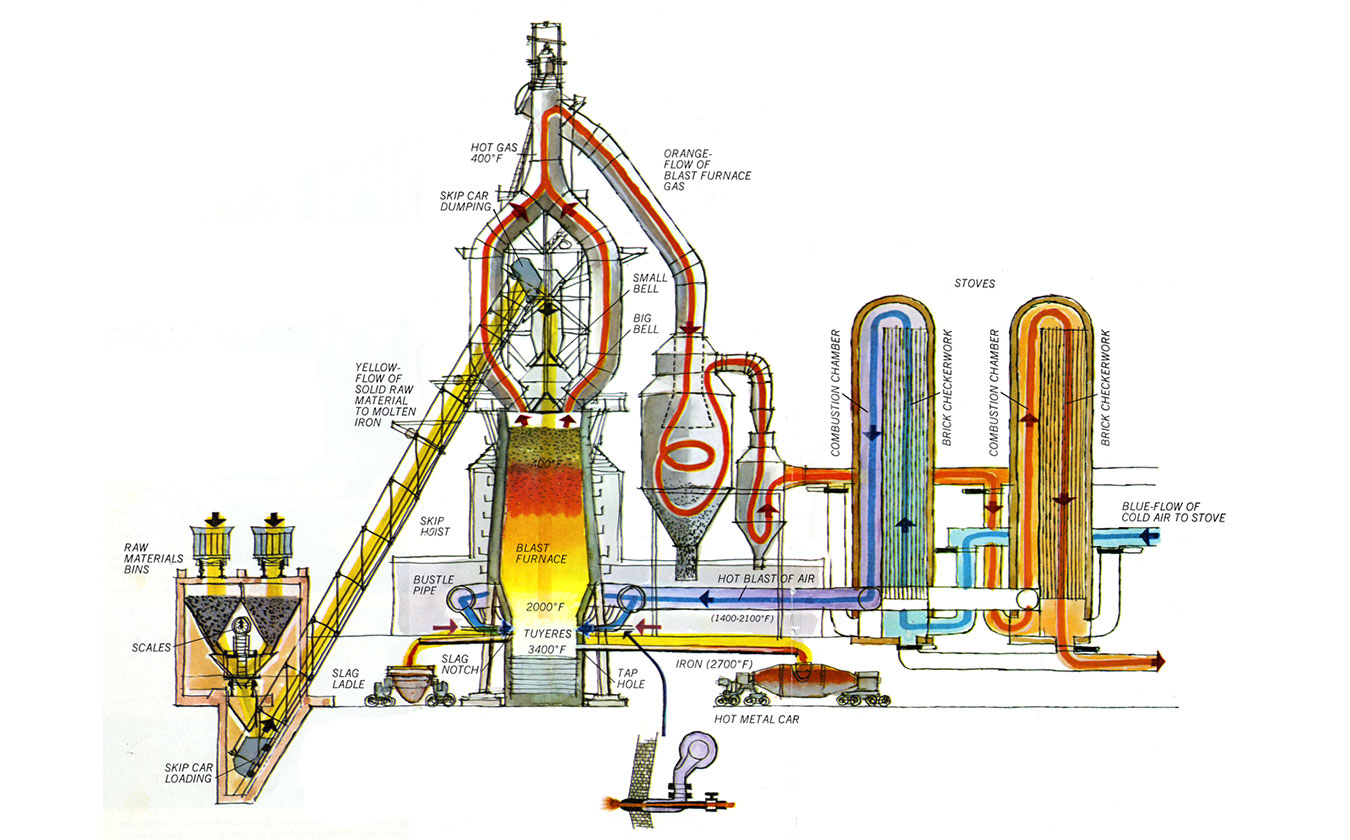
Blast Furnace Process Learn how a blast furnace produces molten iron by heating and reacting iron ore, coke, and limestone. see the chemical reactions, the blast of hot air, and the slag formation in this steel cylinder. Blast furnace construction and working explained in detail blast furnace parts,design,working. the video explains in detail the construction of blast furna. The modern world uses shocking amounts of steel. the input requirements for 16th century blast furnaces were large. though fuel consumption had fallen to roughly the level of the bloomery furnace (initially it used much more fuel than a bloomery), producing a ton of pig iron still required roughly 4.5 5 tons of charcoal, and 5.5 7 tons of iron ore. The blast furnace is the first step in producing steel from iron oxides. the first blast furnaces appeared in the 14th century and produced one ton per day. even though equipment is improved and higher production rates can be achieved, the processes inside the blast furnace remain the same. the blast furnace uses coke, iron ore and limestone to.
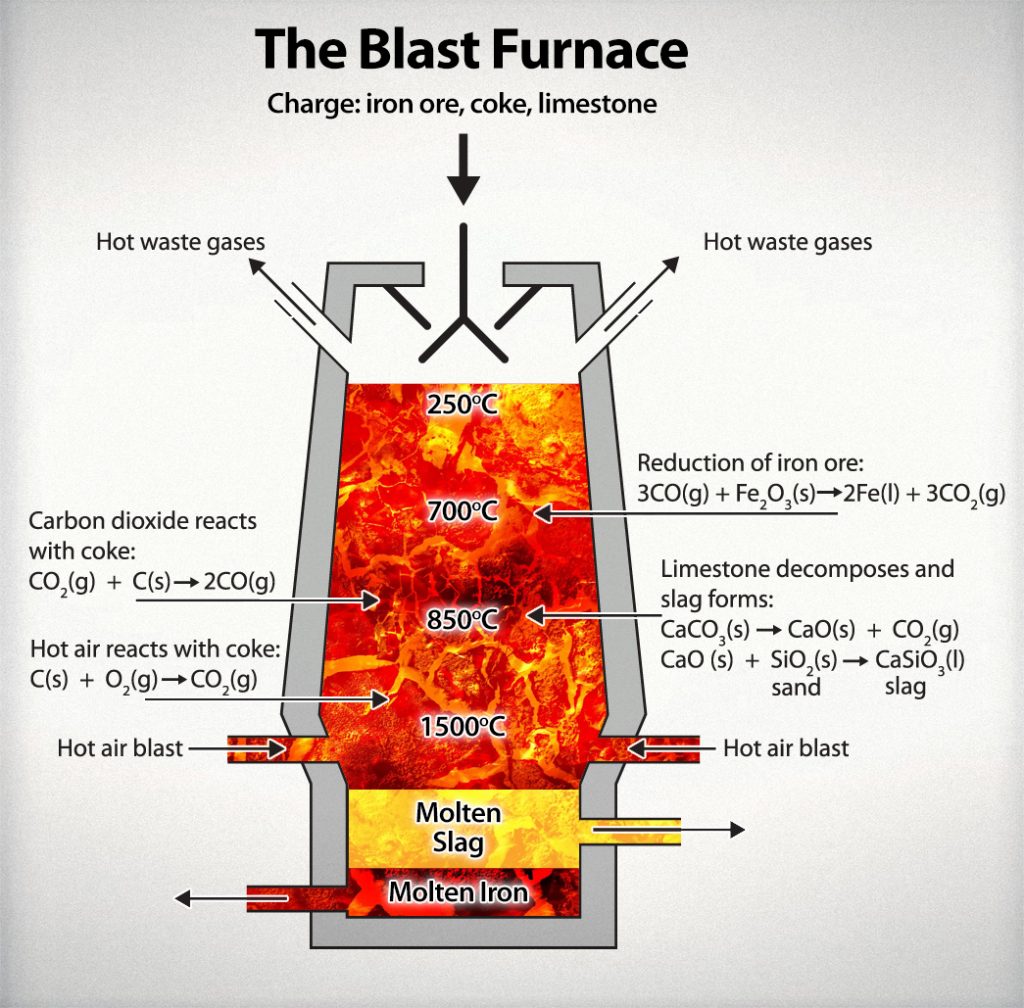
Csma Blast Furnace Diagram Csma The Cementitious Slag Makers The modern world uses shocking amounts of steel. the input requirements for 16th century blast furnaces were large. though fuel consumption had fallen to roughly the level of the bloomery furnace (initially it used much more fuel than a bloomery), producing a ton of pig iron still required roughly 4.5 5 tons of charcoal, and 5.5 7 tons of iron ore. The blast furnace is the first step in producing steel from iron oxides. the first blast furnaces appeared in the 14th century and produced one ton per day. even though equipment is improved and higher production rates can be achieved, the processes inside the blast furnace remain the same. the blast furnace uses coke, iron ore and limestone to. As the mixture of iron ore, coke and limestone heats, the hot waste gases are collected and cleansed. they are then used to help heat the air blast, required if blast furnace is to reach the high temperatures needed to produce molten iron. the stock level is constantly ‘topped up’. molten iron ore is ‘tapped’ at the bottom of the blast. 1 blast furnace process. the blast furnace is a tall, vertical shaft furnace which has the purpose of heating and reducing iron oxides (hematite and magnetite) into hot metal which is basically a carbon saturated silicon and manganese iron alloy with residual amounts of sulfur and phosphorus. a schematic representation of a blast furnace and.
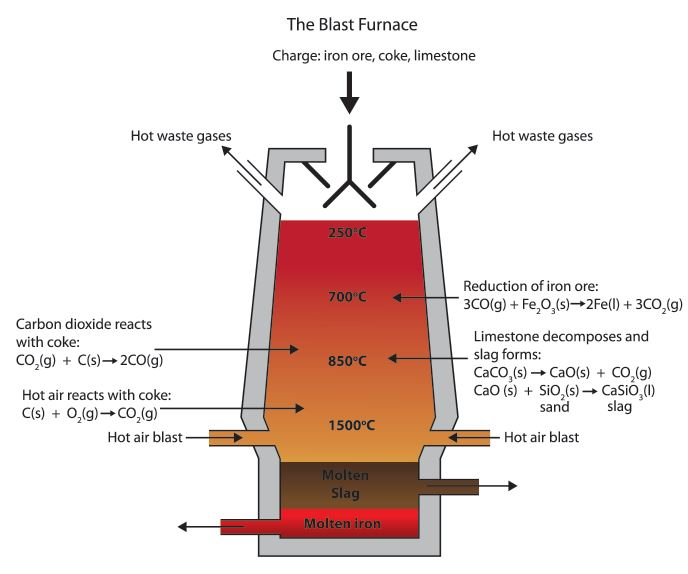
Draw A Neat Diagram Of The Blast Furnace Used In The Extraction Of Iron As the mixture of iron ore, coke and limestone heats, the hot waste gases are collected and cleansed. they are then used to help heat the air blast, required if blast furnace is to reach the high temperatures needed to produce molten iron. the stock level is constantly ‘topped up’. molten iron ore is ‘tapped’ at the bottom of the blast. 1 blast furnace process. the blast furnace is a tall, vertical shaft furnace which has the purpose of heating and reducing iron oxides (hematite and magnetite) into hot metal which is basically a carbon saturated silicon and manganese iron alloy with residual amounts of sulfur and phosphorus. a schematic representation of a blast furnace and.

Comments are closed.