How Does Human Memory Work

An Overview Of How Human Memory Works How memory works. memory is a continually unfolding process. initial details of an experience take shape in memory; the brain’s representation of that information then changes over time. with. Learn how memory operates according to a dual process theory, where system 1 and system 2 cognitive processes interact. explore the three main processes of memory: encoding, storage, and retrieval, and how they relate to teaching and learning.
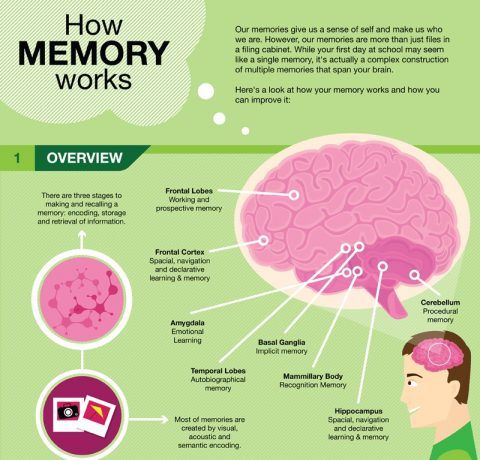
Memory Infographic Archives E Learning Infographics Approximate number system. parallel individuation system. v. t. e. overview of the forms and functions of memory. memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. it is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. [1]. The process of memory begins with encoding, then proceeds to storage and, eventually, retrieval. on the next page, you'll learn how encoding works and the brain activity involved in retrieving a memory. richard c. mohs "how human memory works" 1 january 1970. human memory is a complex, brain wide process that is essential to who we are. The three main processes that describe how memory works are encoding, storage, and retrieval. three main processes characterize how memory works. encoding is the first type and refers to how. Dementia (di men sha): a loss of brain function that can be caused by a variety of disorders affecting the brain. symptoms include forgetfulness, impaired thinking and judgment, personality changes, agitation and loss of emotional control. alzheimer’s disease, huntington’s disease and inadequate blood flow to the brain can all cause dementia.

Comments are closed.