How Intermittent Fasting Affects Your Body And Brain The Human Body
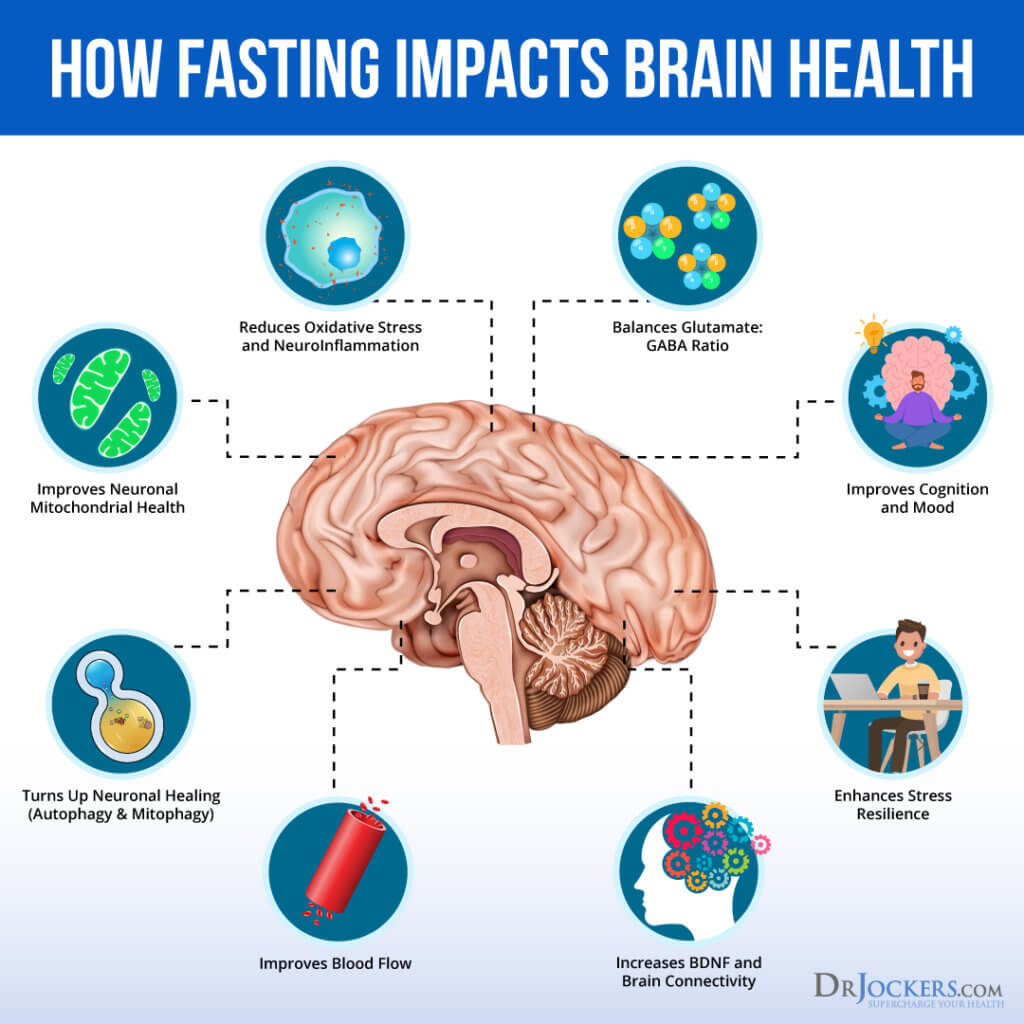
4 Ways Intermittent Fasting Improves Brain Function How does intermittent fasting work? here's wh stars like beyonce and hugh jackman have spoken out about following intermittent fasting plans to get in shape. There are multiple ways by which if can have effects on the brain (i.e., through the vagus nerve, (neuro) metabolites or immune activity). the human body initiates a metabolic switch from glucose to stored lipids after a period of restricted food intake.

This Is Your Body On Intermittent Fasting Prevention In the case of the brain, cognitive function, learning, memory, and alertness are all increased by fasting. and in the body, we recently found that mice maintained on an alternate day fasting diet during a month of treadmill training have better endurance than mice fed every day. so intermittent fasting enhanced the mice’s physical performance. A 2020 review of 27 if trials published in the journal canadian family physician found that people lost anywhere from less than 1% of their body weight to 13%. on average, people lost 4.3% of their body weight when they followed if for periods from two to 12 weeks. some of these studies also compared if to traditional calorie restriction and. Evidence documenting the side effects of intermittent fasting regimens is sparse due to the short duration of assessing intermittent fasting regimens (wks to months). common side effects: hypoglycemia; dizziness; weakness; muscle wasting if protein replacement is not considered during fasting regimes. if is associated with ed symptomatology. Fasting can be classified into short term fasting, such as intermittent fasting (if), and prolonged fasting (>8 days). intermittent fasting (if) is a new type of dietary intervention. during the fasting period, if requires the subjects not to consume any calorie containing food, and “intermittent” highlights the characteristics of an.

Intermittent Fasting The Complete Guide You Need Evidence documenting the side effects of intermittent fasting regimens is sparse due to the short duration of assessing intermittent fasting regimens (wks to months). common side effects: hypoglycemia; dizziness; weakness; muscle wasting if protein replacement is not considered during fasting regimes. if is associated with ed symptomatology. Fasting can be classified into short term fasting, such as intermittent fasting (if), and prolonged fasting (>8 days). intermittent fasting (if) is a new type of dietary intervention. during the fasting period, if requires the subjects not to consume any calorie containing food, and “intermittent” highlights the characteristics of an. There are many types of intermittent fasting, such as the 16:8 and 5:2 methods. numerous studies suggest that it can have powerful benefits for your body and brain. 3.1. fasting and brain metabolism. the human brain represents ~2% of body weight but accounts for ~25% of the body’s resting metabolic rate . most of energy consumption is related to signaling, with the remainder used for essential cellular activities including turnover of proteins, nucleotides, phospholipids and axoplasmic transport.

Effects Of Intermittent Fasting On The Body And Brain Fasting There are many types of intermittent fasting, such as the 16:8 and 5:2 methods. numerous studies suggest that it can have powerful benefits for your body and brain. 3.1. fasting and brain metabolism. the human brain represents ~2% of body weight but accounts for ~25% of the body’s resting metabolic rate . most of energy consumption is related to signaling, with the remainder used for essential cellular activities including turnover of proteins, nucleotides, phospholipids and axoplasmic transport.

Comments are closed.