How The Brain Develops Grows And Learns Throughout Our Lives

How The Brain Develops Grows And Learns Throughout Our Lives A two minute animated introduction to brain development script by nora raschle and sabine gysivideo produced by kurzgesagt for bold – blog on learning and de. Brain volume continues growing in the second year (an estimated 15 percent). developmental peaks in childhood: the brain grows more gradually, with brain size peaking around age 10 for girls and.

Learn How The Brain Develops How It Transmits Messages Throughout The The use of particular brain pathways strengthens those pathways. this is thought to be the major way that the brain learns, by adapting and changing connections with experience. the story of einstein’s brain. when albert einstein died in 1955 his brain was removed during autopsy, photographed, and then dissected into many parts and preserved. But, unlike a static mechanical machine — like a car or a dishwasher — the brain is an organ that grows, changes, and learns. to get “under the hood,” scientists need to go back to the brain’s infancy and explore how it develops. click on the targets below to learn how the brain grows, changes, and adapts to its environment through. The brain is the ultimate organ of adaptation. it takes in information and orchestrates complex behavioral repertoires that allow human beings to act in sometimes marvelous, sometimes terrible ways. most of what people think of as the “self”—what we think, what we remember, what we can do, how we feel—is acquired by the brain from the experiences that occur after birth. some of this. Your brain on learning. according to neurologist and educator judy willis (and suggested by a research rich chapter in the second edition of developmental psychopathology, among many other publications), neuroplasticity is defined as the selective organizing of connections between neurons in our brains. this means that when people repeatedly.
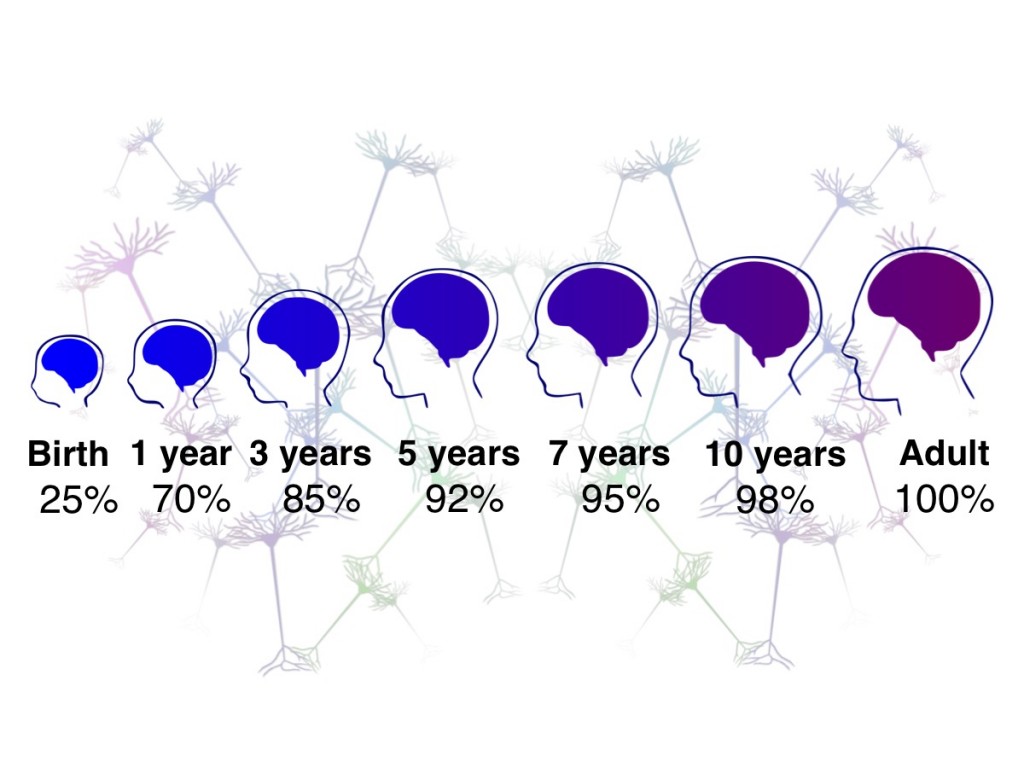
Brain Growth In The First Five Years Of Life Institute For Learning The brain is the ultimate organ of adaptation. it takes in information and orchestrates complex behavioral repertoires that allow human beings to act in sometimes marvelous, sometimes terrible ways. most of what people think of as the “self”—what we think, what we remember, what we can do, how we feel—is acquired by the brain from the experiences that occur after birth. some of this. Your brain on learning. according to neurologist and educator judy willis (and suggested by a research rich chapter in the second edition of developmental psychopathology, among many other publications), neuroplasticity is defined as the selective organizing of connections between neurons in our brains. this means that when people repeatedly. Each individual learner functions within a complex developmental, cognitive, physical, social, and cultural system. learning also changes the brain throughout the life span. at the same time, the brain develops in ways that impact learning and are in turn shaped by the learner’s context and cultural influences. During these times, sensory stimulation, motor activity, and even emotions shape the brain as it grows, wires, and learns. the period shortly after birth is one such window. a baby’s early life experiences — seeing parents’ faces, hearing their voices, and being held — provide important sensory information that guides its developing.

Brain Science Proves The Value Of Early Learning вђ Kids Co Each individual learner functions within a complex developmental, cognitive, physical, social, and cultural system. learning also changes the brain throughout the life span. at the same time, the brain develops in ways that impact learning and are in turn shaped by the learner’s context and cultural influences. During these times, sensory stimulation, motor activity, and even emotions shape the brain as it grows, wires, and learns. the period shortly after birth is one such window. a baby’s early life experiences — seeing parents’ faces, hearing their voices, and being held — provide important sensory information that guides its developing.

Comments are closed.