How To Calculate Mode And Median Of Grouped Data Haiper
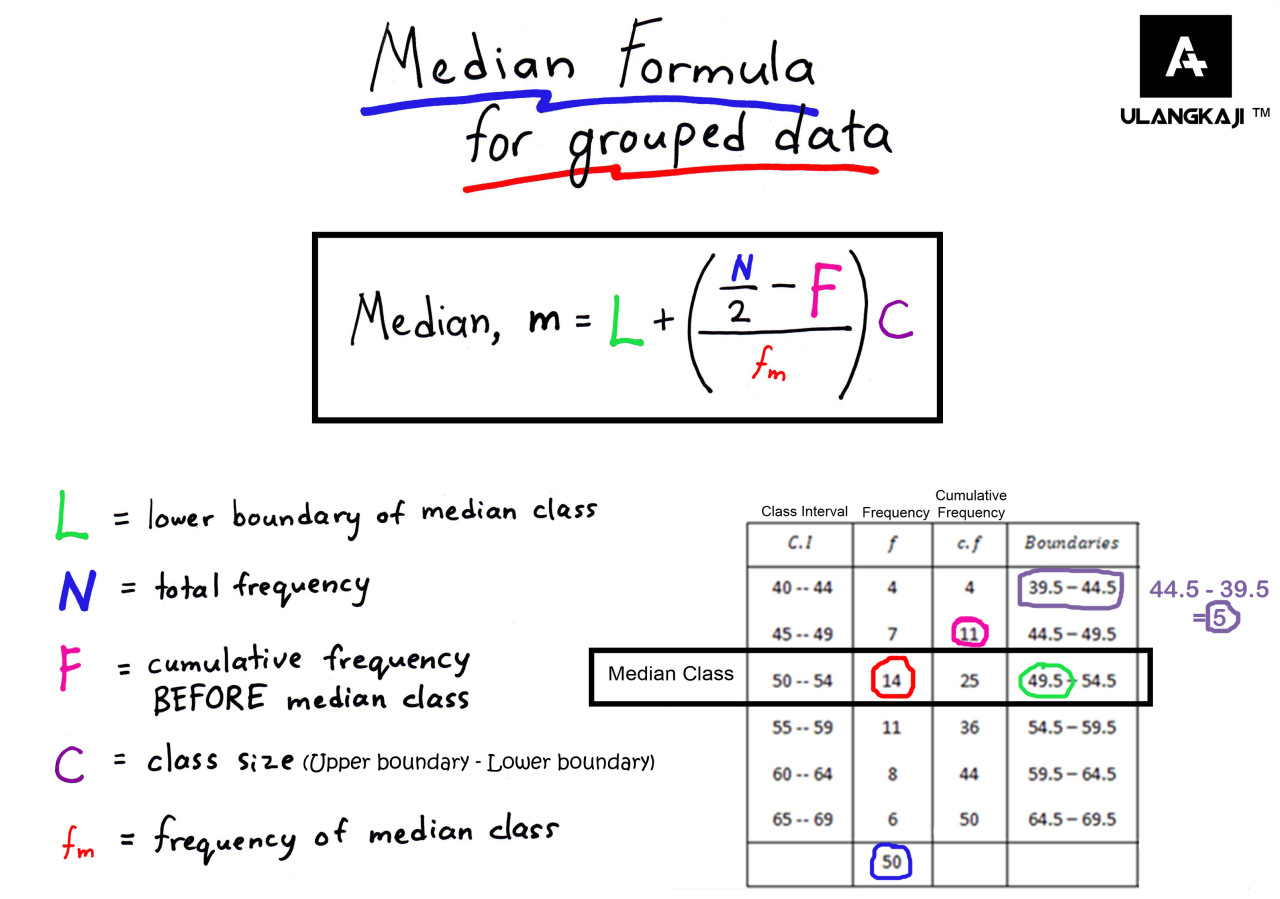
How To Calculate Mode And Median Of Grouped Data Haiper Median of grouped data = l w [ (n 2 – c) f] where: l: lower limit of median class. w: width of median class. n: total frequency. c: cumulative frequency up to median class. f: frequency of median class. note: the median class is the class that contains the value located at n 2. in the example above, there are n = 23 total values. For grouped data, we cannot find the exact mean, median and mode, we can only give estimates. to estimate the mean use the midpoints of the class intervals: estimated mean = sum of (midpoint × frequency) sum of frequency. to estimate the median use: estimated median = l (n 2) − b g × w. where:.
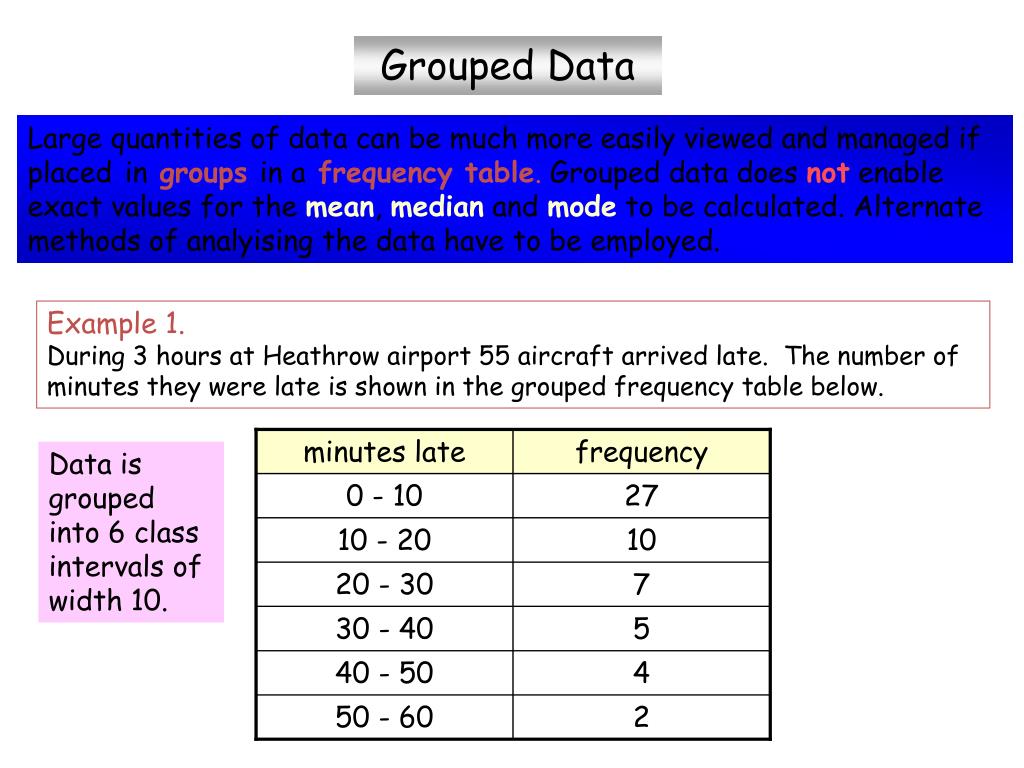
How To Calculate Median Of Grouped Data Haiper For example, suppose we have the following grouped data: while it’s not possible to calculate the exact mode since we don’t know the raw data values, it is possible to estimate the mode using the following formula: mode of grouped data = l w [ (fm – f1) ( (fm f1) (fm – f2) )] where: l: lower limit of modal class. w: width of modal. This statistics tutorial explains how to calculate the mean of grouped data. it also explains how to identify the interval that contains the median and mode. Step 3: now, we note the values of lower limit of median class (l), frequency of the median class (f), cumulative frequency of the class preceding median class (cf), and class size (h). step 4: next, we can substitute these values in the formula to calculate median of grouped data, i.e. median = l ( (n 2 cf) f)×h. The formula to find the median of grouped data is: median = l [ ( (n 2) – cf) f] × h. where l = lower limit of median class, n = number of observations, h = class size, f = frequency of median class, cf = cumulative frequency of class preceding the median class. q5.
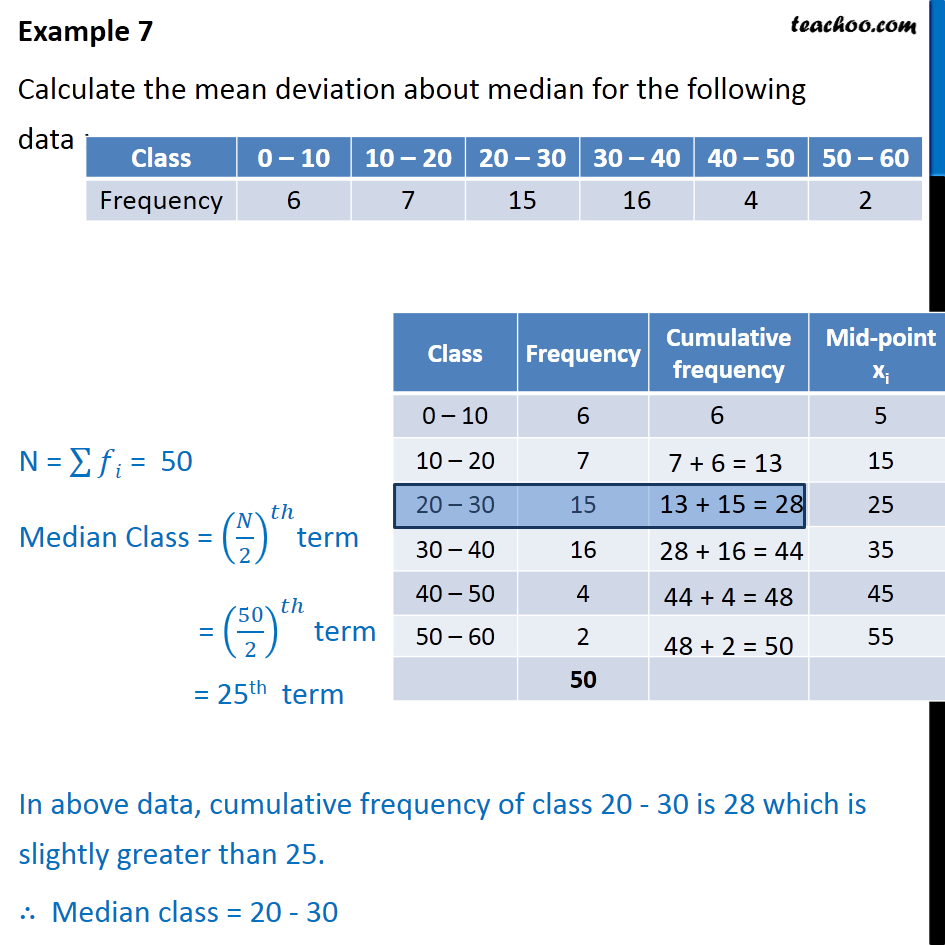
How To Calculate Median And Mode For Grouped Data Haiper Step 3: now, we note the values of lower limit of median class (l), frequency of the median class (f), cumulative frequency of the class preceding median class (cf), and class size (h). step 4: next, we can substitute these values in the formula to calculate median of grouped data, i.e. median = l ( (n 2 cf) f)×h. The formula to find the median of grouped data is: median = l [ ( (n 2) – cf) f] × h. where l = lower limit of median class, n = number of observations, h = class size, f = frequency of median class, cf = cumulative frequency of class preceding the median class. q5. For example, suppose we have the following grouped data: while it’s not possible to calculate the exact median since we don’t know the raw data values, it is possible to estimate the median using the following formula: median of grouped data = l w[(n 2 – c) f] where: l: lower limit of median class; w: width of median class; n: total. To identify the mode in a grouped distribution, follow the steps outlined below: step 1: determine the modal class, which is the class interval with the highest frequency. step 2: determine the modal class’s size. (upper limit – lower limit.) step 3: using the mode formula to compute the mode as described above.

How To Calculate Mode Grouped Data Haiper For example, suppose we have the following grouped data: while it’s not possible to calculate the exact median since we don’t know the raw data values, it is possible to estimate the median using the following formula: median of grouped data = l w[(n 2 – c) f] where: l: lower limit of median class; w: width of median class; n: total. To identify the mode in a grouped distribution, follow the steps outlined below: step 1: determine the modal class, which is the class interval with the highest frequency. step 2: determine the modal class’s size. (upper limit – lower limit.) step 3: using the mode formula to compute the mode as described above.

Comments are closed.