How To Convert Units In Chemistry

Chemistry Units Conversion Chart Practice Here is what we would have gotten: 3.55 m × 1 m 100 cm = 0.0355m2 cm 3.55 m × 1 m 100 c m = 0.0355 m 2 c m. for the answer to be meaningful, we have to construct the conversion factor in a form that causes the original unit to cancel out. figure 1.7.1 1.7. 1 shows a concept map for constructing a proper conversion. If unit conversion has never made sense to you then please watch this video. i'll explain the concept of unit conversion and do multiple examples explaining.
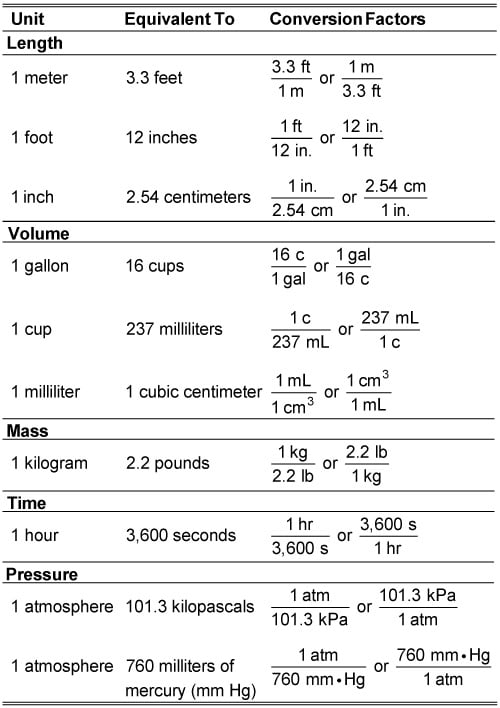
How To Convert Units Using Conversion Factors Dummies Dimensional analysis (unit conversions) involves the use of conversion factors that will cancel unwanted units and produce the appropriate units. 2.6: problem solving and unit conversions is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by marisa alviar agnew & henry agnew. during your studies of chemistry (and physics also. Suppose you wish to convert pressure of 14 lb in 2 to g cm 2. when setting up the conversion, worry about one unit at a time, for example, convert the pound units to gram units, first: next, convert in 2 to cm 2. set up the conversion without the exponent first, using the conversion factor, 1 in = 2.54 cm. A unit is a frequently arbitrary designation we have given to something to convey a definite magnitude of a physical quantity and every quantity can be expre. Unit conversions work the same way, except "1" is expressed in the form of a conversion factor or ratio. consider the unit conversion: 1 g = 1000 mg. this could be written as: 1g 1000 mg = 1 or 1000 mg 1 g = 1. if you multiply a value times either of these fractions, its value will be unchanged.

Conversion Chart Chemistry Units A unit is a frequently arbitrary designation we have given to something to convey a definite magnitude of a physical quantity and every quantity can be expre. Unit conversions work the same way, except "1" is expressed in the form of a conversion factor or ratio. consider the unit conversion: 1 g = 1000 mg. this could be written as: 1g 1000 mg = 1 or 1000 mg 1 g = 1. if you multiply a value times either of these fractions, its value will be unchanged. Cancelling units and performing the mathematics, we get: 14.66 m × 1000 mm 1 m = 14,660 mm 14.66 m × 1000 mm 1 m = 14, 660 mm. note how m cancels, leaving mm, which is the unit of interest. the ability to construct and apply proper conversion factors is a very powerful mathematical technique in chemistry. Certain systems, such as the si system of units, have different units for describing the same features, such as the meter and millimeter, which are both units of distance. if a measurement is given in one unit, it can be converted into another unit describing the same property, such as length. a conversion factor can be used, such as a meter being 1000 times more than a millimeter.

Si Unit Conversion Chart Cancelling units and performing the mathematics, we get: 14.66 m × 1000 mm 1 m = 14,660 mm 14.66 m × 1000 mm 1 m = 14, 660 mm. note how m cancels, leaving mm, which is the unit of interest. the ability to construct and apply proper conversion factors is a very powerful mathematical technique in chemistry. Certain systems, such as the si system of units, have different units for describing the same features, such as the meter and millimeter, which are both units of distance. if a measurement is given in one unit, it can be converted into another unit describing the same property, such as length. a conversion factor can be used, such as a meter being 1000 times more than a millimeter.
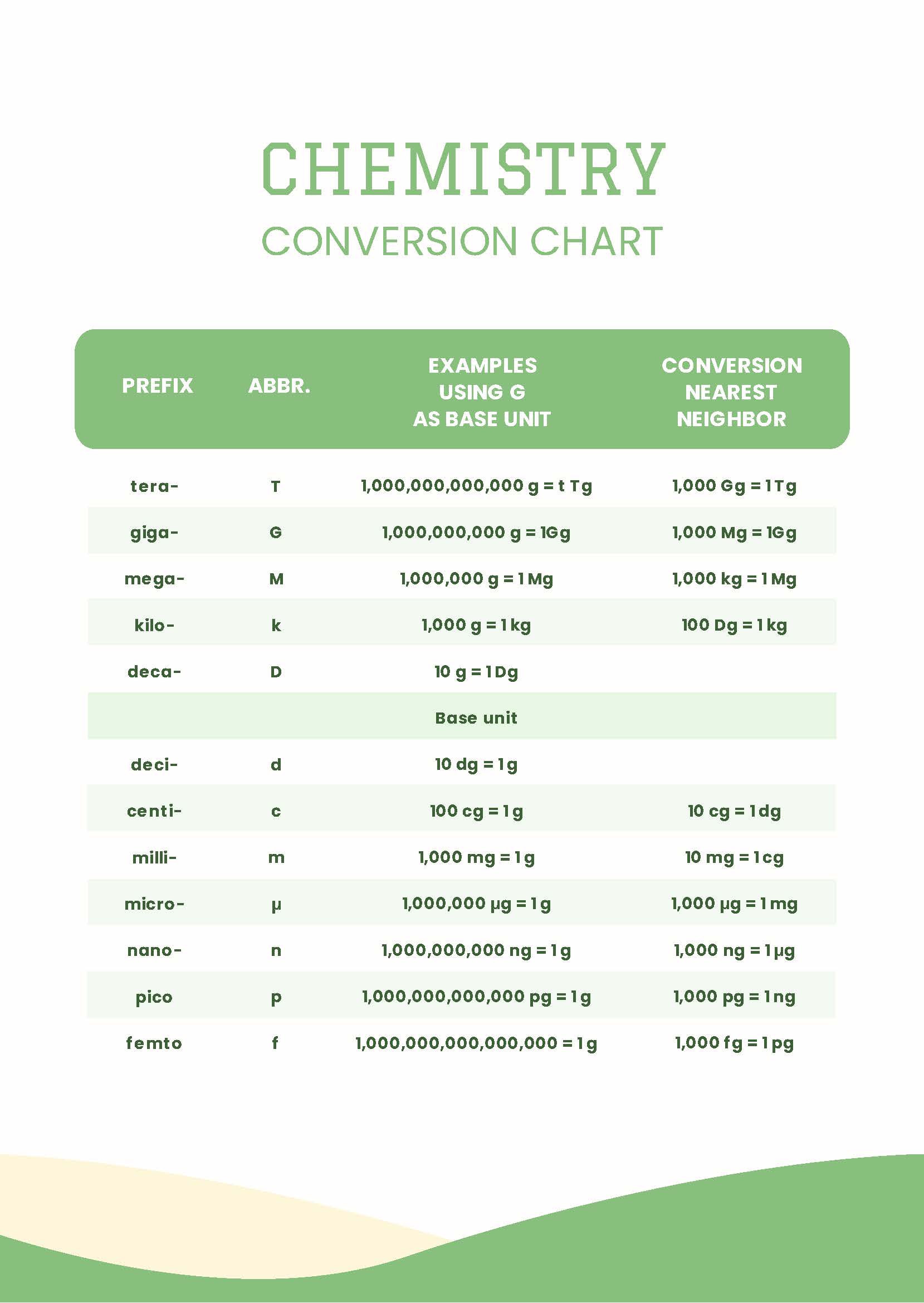
Printable Chemistry Conversion Chart

Comments are closed.