How To Find Cu And Cc From Gradation Curve
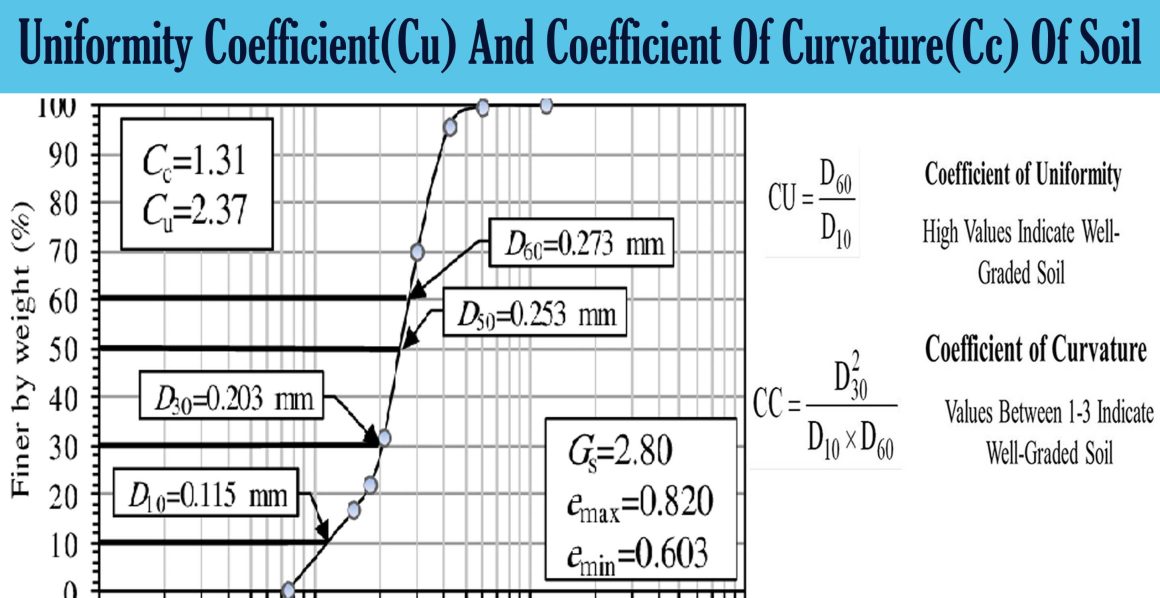
Uniformity Coefficient Cu And Coefficient Of Curvature Cc Of Soil The uniformity coefficient (cu) is defined as the ratio of d60 to d10. a value of cu greater than 4 to 6 classifies the soil as well graded. when cu is less than 4, it is classified as poorly graded or uniformly graded soil. uniformly graded soil has identical particles with cu value approximately equal to 1. a uniformity coefficient value of 2. A higher value of cu indicates that the soil mass consists of soil particles with different size ranges. coefficient of curvature (cc) coefficient of curvature is given by the formula: for the soil to be well graded, the value of cc must range between 1 and 3. for any single sized soil mass, the value of both cu and cc is 1.

How To Find Cu And Cc From Gradation Curve Youtube This animated video describes in detail that how to find:d10d30, andd60 of soil from gradation curve.civil engineeringsoil mechanicsgeotechnical engineeringp. Online calculate the cu and cc. step 1: choose the sheet with the number of sieves used (11,10 or 8) and input the sieve sizes and the mass of soil retained. that’s it. the excel sheet will give the soil cu and cc and the graph. *disclaimer: the author is not responsible for the professional or any use of this calculation sheet. This curve is obtained from the percentage finer results of both coarse and fine grained portions of the soil that is it results from both sieve and hydrometer analysis. this curve is known as particle size distribution curve. it is also called gradation curve. the distribution of particles of different sizes in soil mass is called grading of soil. The coefficient of gradation may he expressed as: where cc is the coefficient of gradation and d30 diameter corresponding to 30% finer. for the particle size distribution curve of soil b shown in figure 2, the values of d10 d30 and d60 are 0.096 mm, 0.16 mm and 0.24 mm, respectively. the uniformity coefficient and coefficient of gradation are:.

Gradation Curves Of The Materials Used In This Study The Uniformity This curve is obtained from the percentage finer results of both coarse and fine grained portions of the soil that is it results from both sieve and hydrometer analysis. this curve is known as particle size distribution curve. it is also called gradation curve. the distribution of particles of different sizes in soil mass is called grading of soil. The coefficient of gradation may he expressed as: where cc is the coefficient of gradation and d30 diameter corresponding to 30% finer. for the particle size distribution curve of soil b shown in figure 2, the values of d10 d30 and d60 are 0.096 mm, 0.16 mm and 0.24 mm, respectively. the uniformity coefficient and coefficient of gradation are:. A simple tutorial about solving for d10, d25, d30, d60, d75.and also coefficient of uniformity cu, coefficient of curvature gradation, and sorting coefficien. Q: how are cu and cc used in foundation design? a: cu and cc are used in foundation design to assess the soil’s bearing capacity and settlement characteristics. by understanding the soil’s uniformity and gradation, engineers can make informed decisions about the type and depth of foundation required for a particular structure. variables.
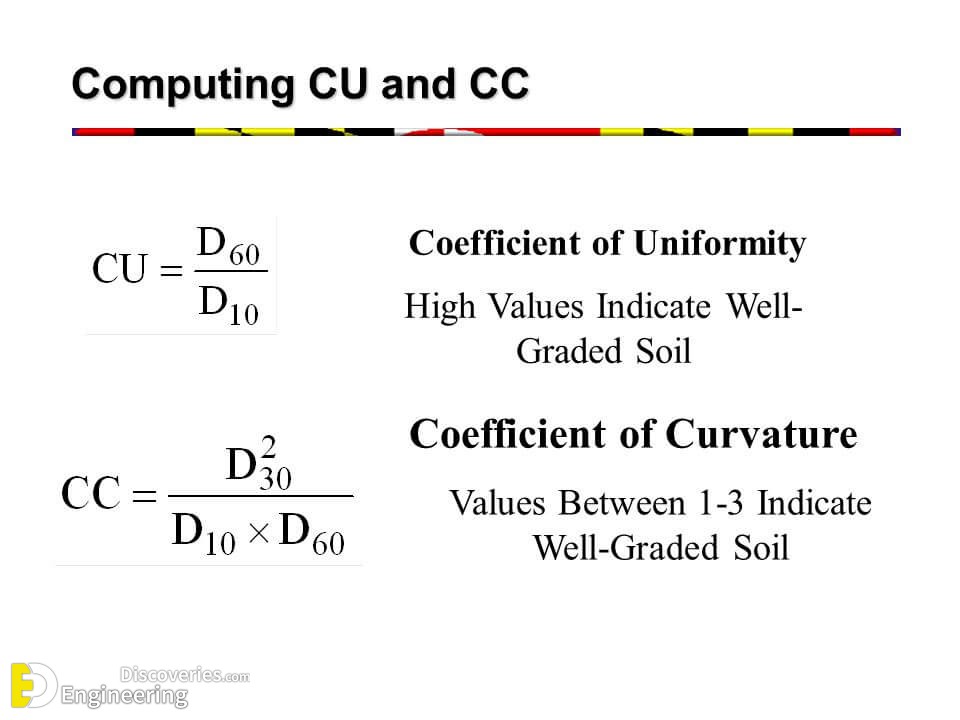
Coeficiente De Curvatura A simple tutorial about solving for d10, d25, d30, d60, d75.and also coefficient of uniformity cu, coefficient of curvature gradation, and sorting coefficien. Q: how are cu and cc used in foundation design? a: cu and cc are used in foundation design to assess the soil’s bearing capacity and settlement characteristics. by understanding the soil’s uniformity and gradation, engineers can make informed decisions about the type and depth of foundation required for a particular structure. variables.
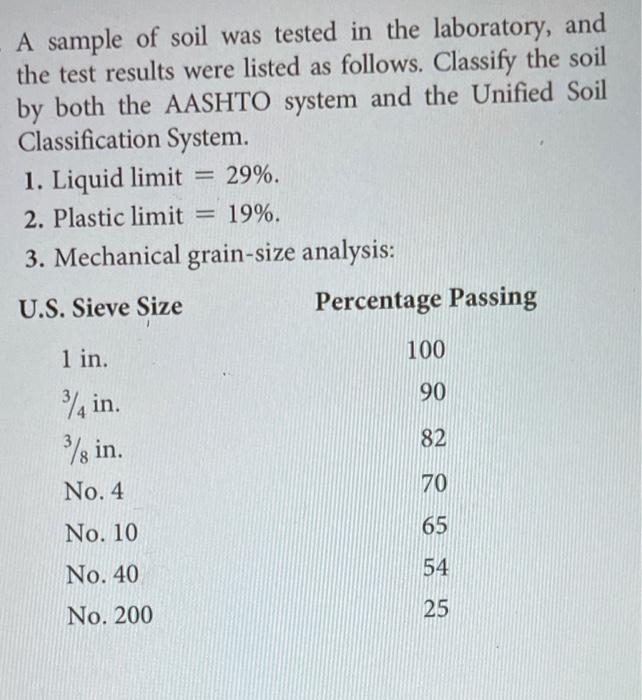
Solved 2 1 Draw A Gradation Curve And Find The Median Size Chegg

Comments are closed.