How To Find The Reference Angle 16 Examples
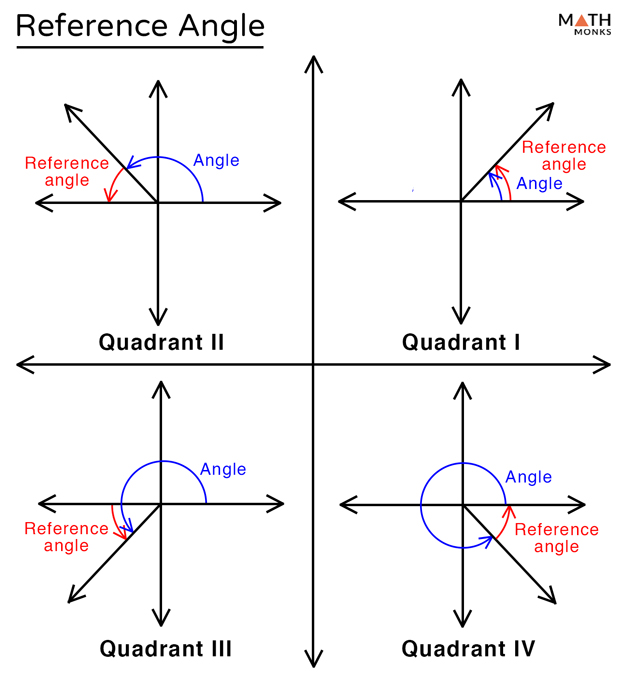
Reference Angle вђ Definition And Formulas With Examples I make short, to the point online math tutorials. i struggled with math growing up and have been able to use those experiences to help students improve in ma. 180° 120° = 60°. the reference angle is. θ 1 {\displaystyle {\theta }^ {1}} = 60°. 4. if the given angle is in quadrant 3, subtract 180° from the angle. when the angle given to you is in the third quadrant, you subtract 180° from the angle to get the reference angle, or .
Evaluating Trigonometric Functions Using The Reference Angle Solutions Find reference angle. the reference angle is the positive acute angle that can represent an angle of any measure. the reference angle must be <90∘ must be <90 ∘. in radian measure, the reference angle must be <π 2 must be <π 2. basically, any angle on the x y plane has a reference angle, which is always between 0 and 90 degrees. Reference angle – definition and formulas with examples. Now, the sign of the function value is positive or negative depending on the quadrant of the terminal side, but the numerical value of the trig function is the same! a reference angle is a positive, acute angle determined by the x axis and the terminal side of a given angle. in other words, it’s always found inside our reference triangle. Example 1: find the reference angle of 8π 3 in radians. solution: the given angle is greater than 2π. step 1: finding co terminal angle: we find its co terminal angle by subtracting 2π from it. 8π 3 2π = 2π 3. this angle does not lie between 0 and π 2. hence, it is not the reference angle of the given angle.

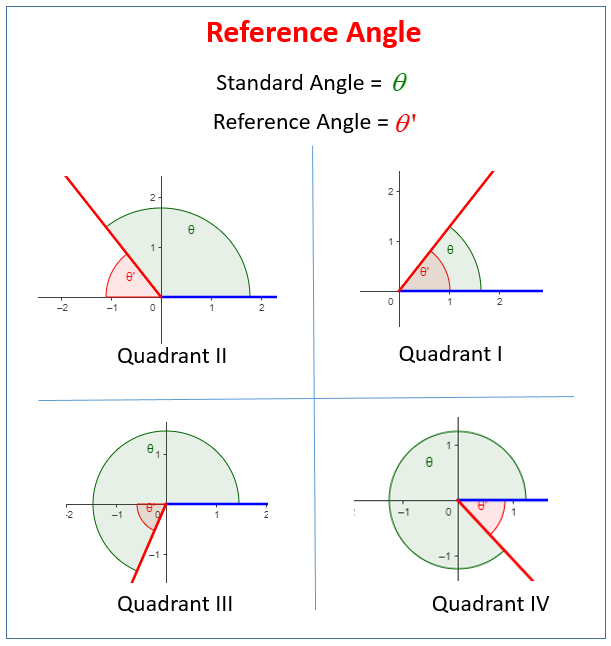
How To Find The Reference Angle In Radians And Degrees Trigonometry Now, the sign of the function value is positive or negative depending on the quadrant of the terminal side, but the numerical value of the trig function is the same! a reference angle is a positive, acute angle determined by the x axis and the terminal side of a given angle. in other words, it’s always found inside our reference triangle. Example 1: find the reference angle of 8π 3 in radians. solution: the given angle is greater than 2π. step 1: finding co terminal angle: we find its co terminal angle by subtracting 2π from it. 8π 3 2π = 2π 3. this angle does not lie between 0 and π 2. hence, it is not the reference angle of the given angle. A reference angle is the acute angle formed by the terminal side of the given angle and the x axis. how to find the reference angle? step 1: sketch the given angle. step 2: drop a perpendicular to the x axis. step 3: determine the angle measure of the triangle formed. how to use reference angles to find the sine, cosine and tangent of non acute. An angle’s reference angle is the measure of the smallest, positive, acute angle t t formed by the terminal side of the angle t t and the horizontal axis. thus positive reference angles have terminal sides that lie in the first quadrant and can be used as models for angles in other quadrants. see figure 1 for examples of reference angles for.

Comments are closed.