How To Make The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22 Does The Molecule Exist
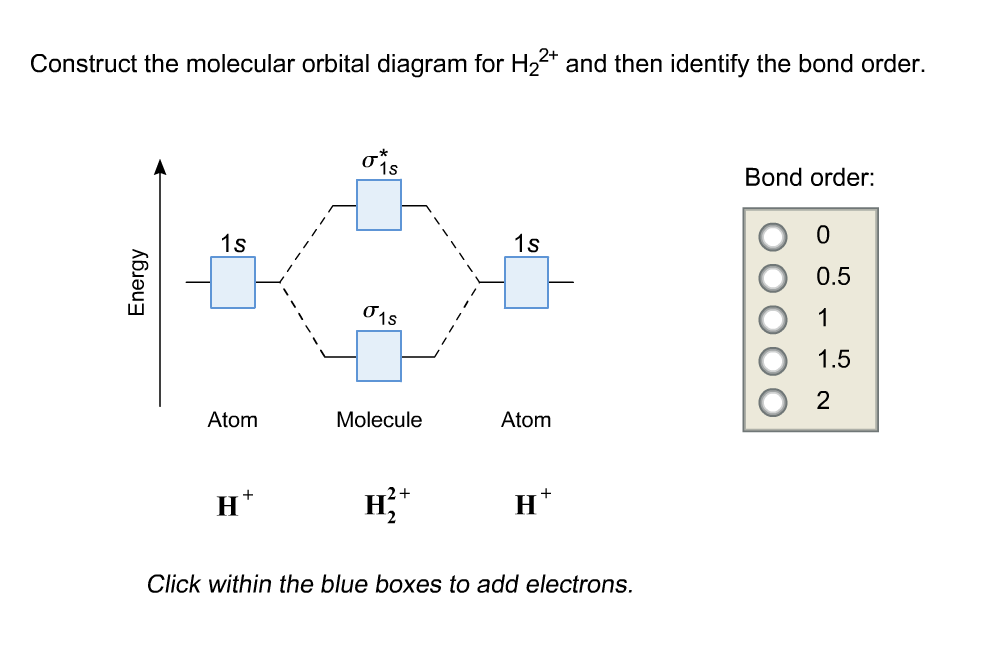
Solved Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22 And Chegg This video discusses how to draw the molecular orbital (mo) diagram for the h2(2 ) molecule. the bond order of h2(2 ) is calculated and the meaning of this n. For the ion h22 :a) draw the molecular orbital diagram.b) calculate the bond order.c) would this ion exist?d) write the electron configuration of the ion.
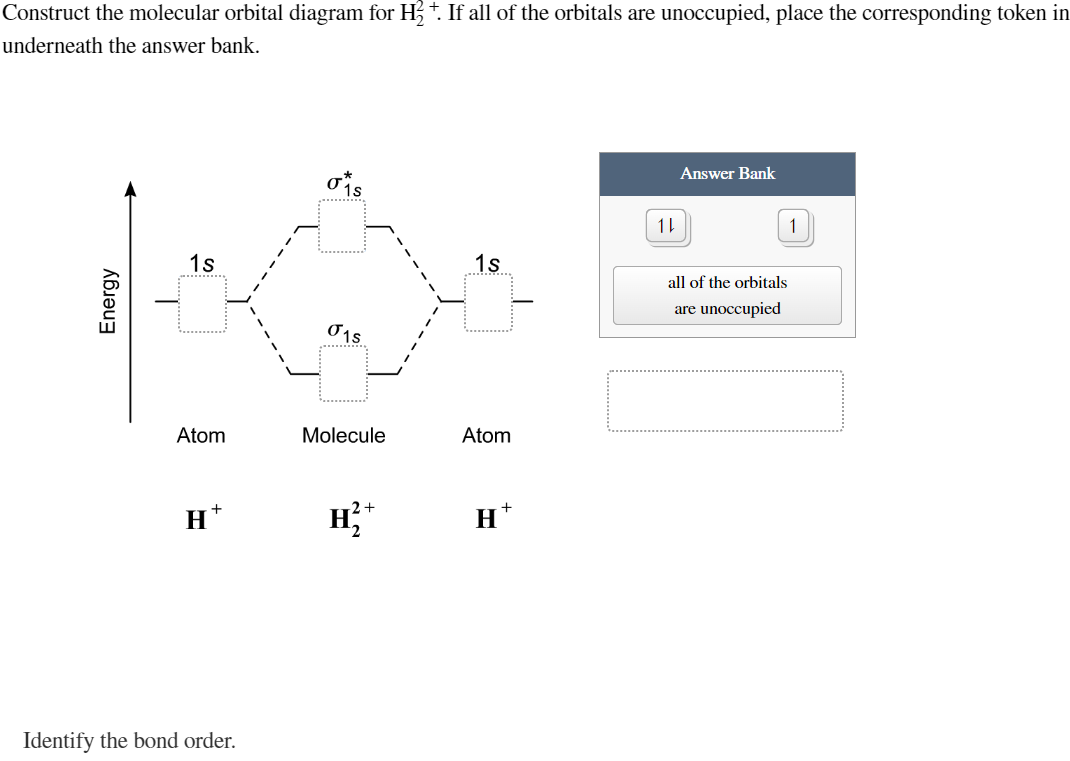
Solved Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22 If Chegg Sidra ayub (ucd) 7.3: how to build molecular orbitals is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. the molecular orbital (mo) theory is a powerful and extensive approach which describes electrons as delocalized moieties over adjacent atoms. the applications of the mo theory extend beyond the …. 9.7: molecular orbitals is shared under a license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by libretexts. a molecular orbital is an allowed spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular orbital energy. unlike an atomic orbital, which is centered on a single atom, a …. Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals ( σ σ, σ σ *, π π, π π *) forms σ or.
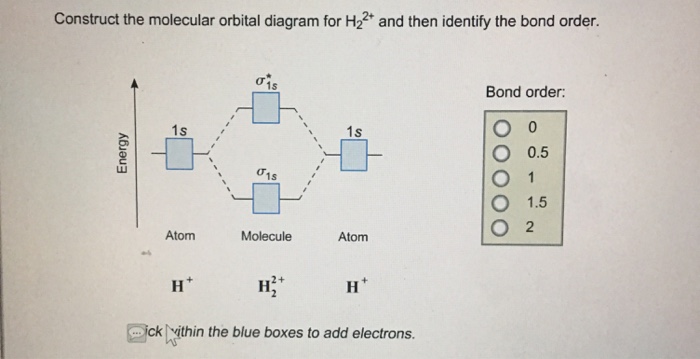
Solved Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22 And Chegg Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals (s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals (sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals (σ, σ*, π, π*) forms σ or π bonds. Molecular orbital theory. considers bonds as localized between one pair of atoms. considers electrons delocalized throughout the entire molecule. creates bonds from overlap of atomic orbitals ( s, p, d …) and hybrid orbitals ( sp, sp2, sp3 …) combines atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals ( σ σ, σ σ *, π π, π π *) forms σ or. A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. mo diagrams can be used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule and how they change with ionization. they also give insight to the bond order of the molecule, how many bonds are shared between the two atoms. [12]. Mo diagrams and bond orders of h2 , h2–, h22 and h22 . h2 represents a cation of h 2, carrying a positive 1 charge which means it is formed by the loss of 1 valence electron from one of the two neutral h atoms. an h ion (proton) is produced by removing the single valence electron possessed by an h atom.
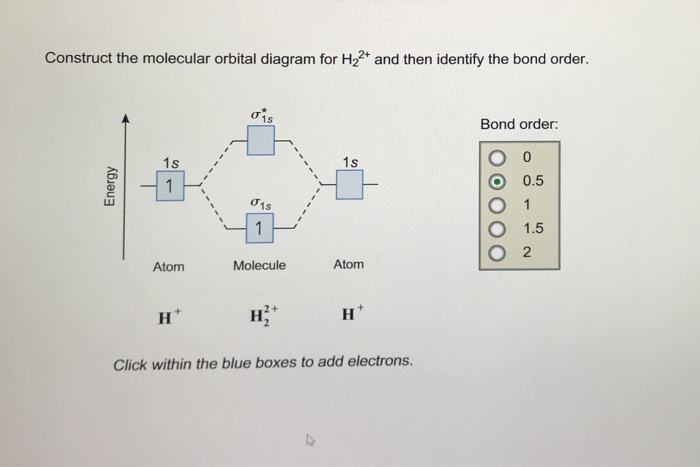
Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H2 And Then Identify The A diatomic molecular orbital diagram is used to understand the bonding of a diatomic molecule. mo diagrams can be used to deduce magnetic properties of a molecule and how they change with ionization. they also give insight to the bond order of the molecule, how many bonds are shared between the two atoms. [12]. Mo diagrams and bond orders of h2 , h2–, h22 and h22 . h2 represents a cation of h 2, carrying a positive 1 charge which means it is formed by the loss of 1 valence electron from one of the two neutral h atoms. an h ion (proton) is produced by removing the single valence electron possessed by an h atom.
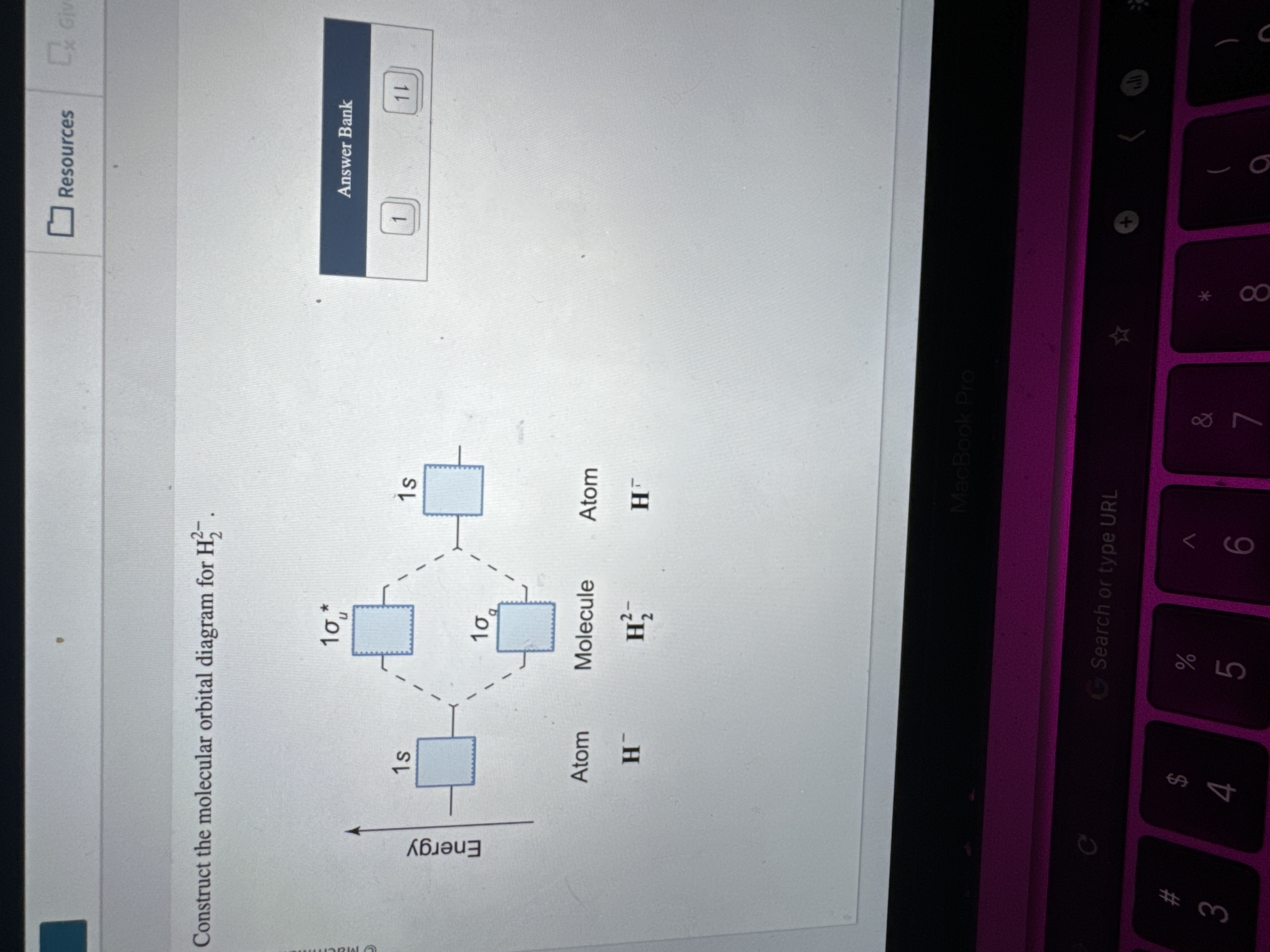
Solved Construct The Molecular Orbital Diagram For H22в Chegg

Comments are closed.