How To Perform Hands Only Cpr Did You Know That Most Cardiac Arrests
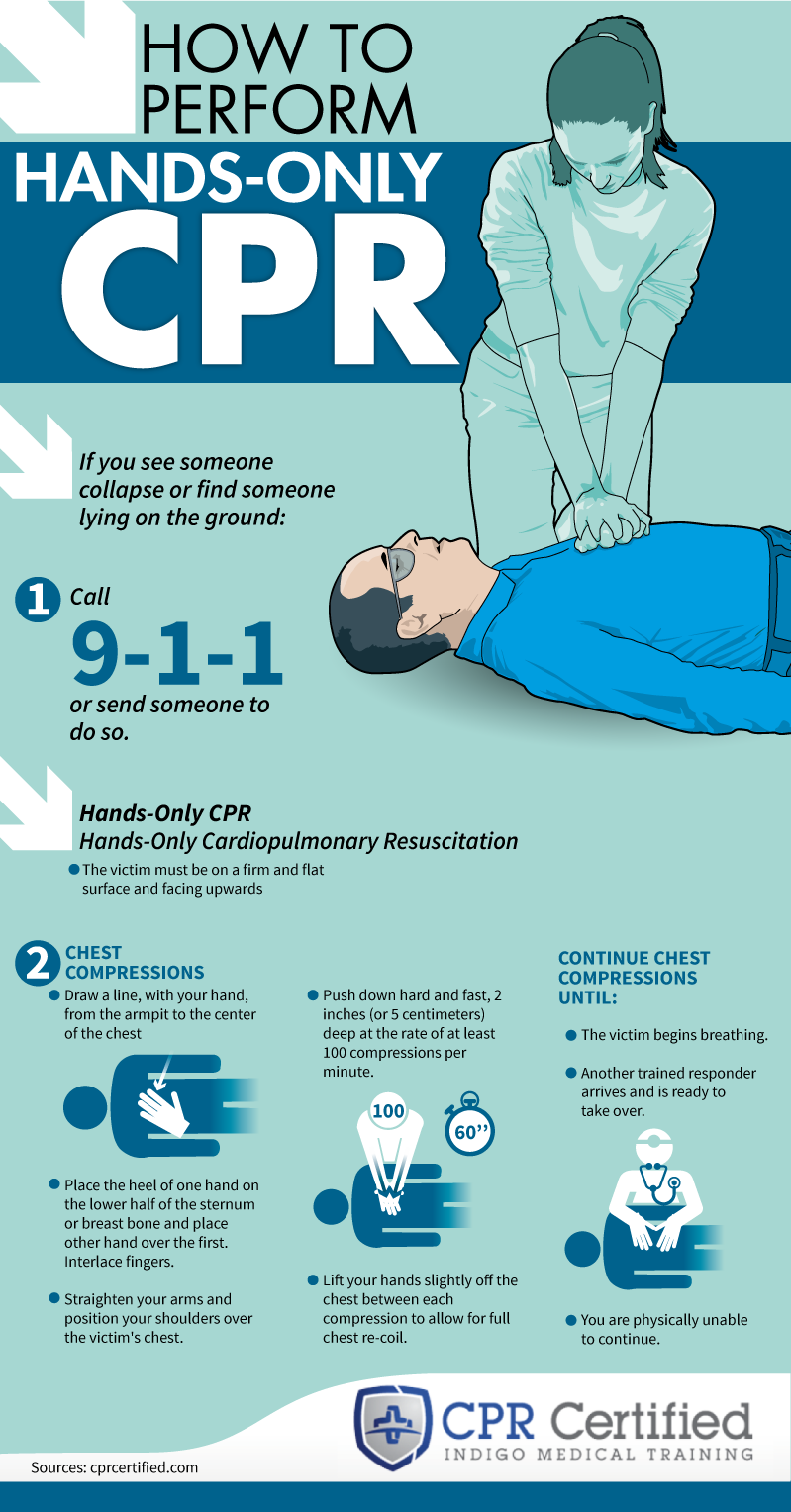
How To Perform Hands Only Cpr Infographic Cardiac arrest – an electrical malfunction in the heart that causes an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) and disrupts the flow of blood to the brain, lungs and other organs – is a leading cause of death. each year, more than 350,000 ems assessed out of hospital cardiac arrests occur in the united states. when a person has a cardiac arrest. Out rescue breaths. if you see a teen or adult collapse, you can perform hands only cpr with. ps:1) call 911 and2) push hard and fast in the center of the chest to the beat of the bee gees’ classic disco song . stayin’ alive.” the song is 100 beats per minute – the minimum rate you should push on the chest du.

Hands Only Cpr Poster вђ Paramedical First Aid Training How to perform hands only cpr. Though immediate cpr can double or even triple their chance of survival, many people can be reluctant to jump into a lifesaving situation. dr. eduardo sanchez talks with professor katie dainty about what gets in the way of bystanders performing cpr, how those obstacles can be overcome. and what you can do to be ready to save a life with hands. 2. push hard and fast in the center of the chest to the beat of a familiar song that has 100 to 120 beats per minute. 1. music can save lives. people feel more confident performing hands only cpr and are more likely to remember the correct rate when trained to the beat of a familiar song. when performing cpr, you should push on the chest at a. Hands only cpr is designed for the untrained lay rescuer or someone who isn't comfortable or confident giving mouth to mouth resuscitation. research suggests that hands only cpr is most effective on adults, as cardiovascular problems are often the cause of their cardiac arrest. whereas, in children, the majority of their cardiac arrest events.

Comments are closed.