Hypercalcaemia On Ecg Ecg Disease Patterns Medschool

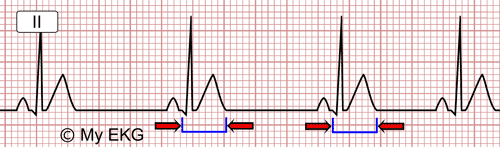
Hypercalcaemia On Ecg Ecg Disease Patterns Medschool Ecg findings in hypercalcaemia. shortened qt interval (due to a shortened st segment) osborn waves (j waves) dome or hump shaped deflections following the j point. qrs prolongation. pr prolongation. severe hypercalcaemia may produce st elevation and t wave inversion that mimics an acute myocardial infarction. next page. The electrocardiographic manifestations of arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia. current cardiology reviews. 2014 aug 1;10 (3):237 45. the electrocardiogram can be used to diagnose a wide variety of cardiac and non cardiac conditions. this section outlines the major findings of conditions that manifest ecg changes.
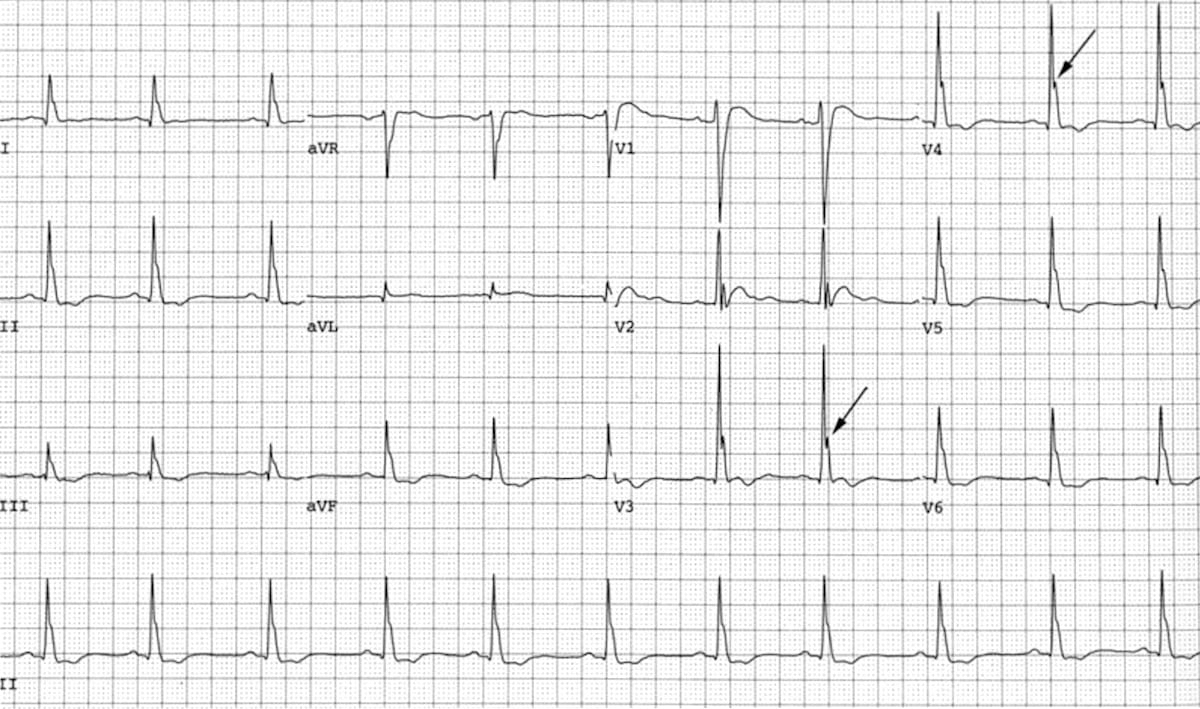
Hypercalcaemia Ecg Changes вђў Litfl вђў Ecg Library Hypercalcaemia ecg library. Ecg changes due to electrolyte imbalance (disorder). Hypothermia refers to a reduction in body temperature below 35 degrees celcius. ecg findings may be seen with profound hypothermia, and particularly below 32 degrees. osborn waves, or j waves, are a classic finding in hypothermia. they may also be seen in hypercalcaemia and early repolarisation syndrome. Additional ecg abnormalities that may occur in patients with severe hypercalcemia include st segment elevation, biphasic t waves, and prominent u waves. 10 changes in t wave morphology, polarity, and amplitude appears with development of hypercalcemia and disappears with normalization of serum calcium level. flattened or biphasic t waves are.

Ekg 1 Ekg Pattern Showing Changes In Hyperkalemia Hypothermia refers to a reduction in body temperature below 35 degrees celcius. ecg findings may be seen with profound hypothermia, and particularly below 32 degrees. osborn waves, or j waves, are a classic finding in hypothermia. they may also be seen in hypercalcaemia and early repolarisation syndrome. Additional ecg abnormalities that may occur in patients with severe hypercalcemia include st segment elevation, biphasic t waves, and prominent u waves. 10 changes in t wave morphology, polarity, and amplitude appears with development of hypercalcemia and disappears with normalization of serum calcium level. flattened or biphasic t waves are. Significant electrolyte imbalances can precipitate cardiac arrest and are potentially reversible etiologies when promptly and appropriately addressed. both venous and arterial blood gases can be utilized for the analysis of electrolyte levels. electrocardiography (ecg) serves as a valuable tool for detecting and assessing the severity of. In summary, electrocardiographic changes are common findings in hypercalcemia and often mimic those of acute myocardial infarction. knowledge of these changes is essential as it helps in improvement of diagnosis and management and significantly, reduces the financial burden on health care system. financial support and sponsorship.
Hypercalcemia Ecg Significant electrolyte imbalances can precipitate cardiac arrest and are potentially reversible etiologies when promptly and appropriately addressed. both venous and arterial blood gases can be utilized for the analysis of electrolyte levels. electrocardiography (ecg) serves as a valuable tool for detecting and assessing the severity of. In summary, electrocardiographic changes are common findings in hypercalcemia and often mimic those of acute myocardial infarction. knowledge of these changes is essential as it helps in improvement of diagnosis and management and significantly, reduces the financial burden on health care system. financial support and sponsorship.

Comments are closed.