Hypercalcemia Differential Diagnosis Algorithm Elevated Grepmed
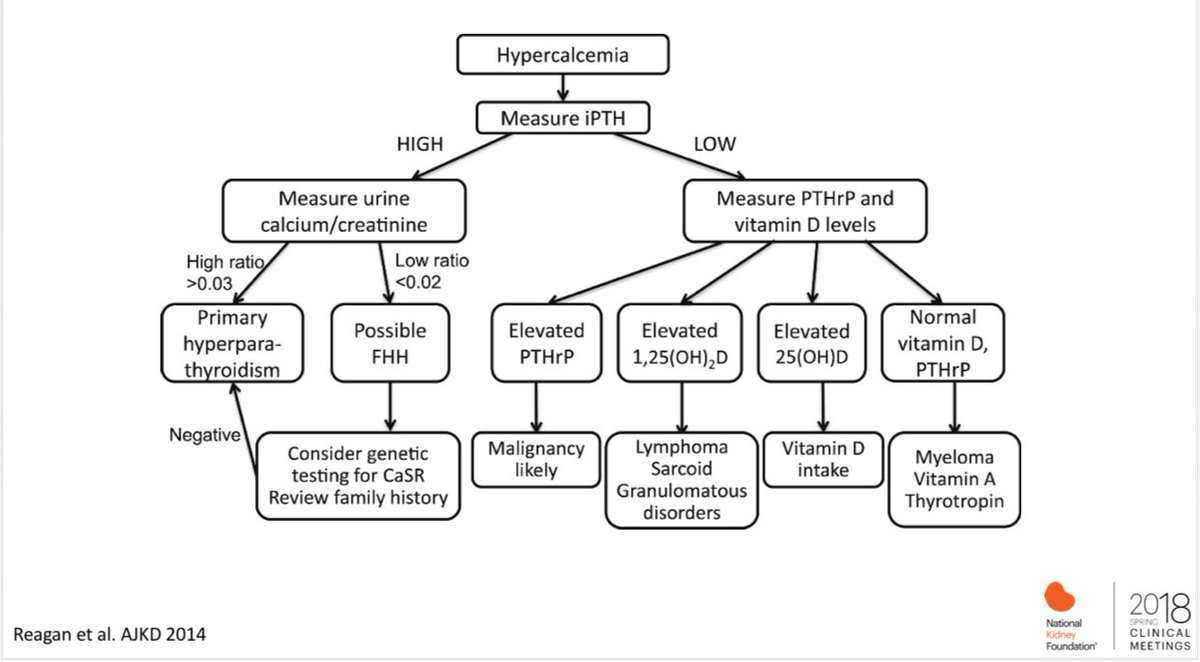
Diagnostic Algorithm For The Workup Of Hypercalcemia Grepmed Diagnostic approach to hypercalcemia uptodate. Workup of hypercalcemia differential diagnosis algorithm high or normal pth: • hyperparathyroidism: parathyroid adenoma, parathyroid hyperplasia, parathyroid carcinoma, lithium • familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia low pth: • high pthrp: malignancy • normal pthrp: low 25 vitd: multiple myeloma, skeletal metastatic disease, milk alkali syndrome, immobilization, drugs, endocrine.

Hypercalcemia Differential Diagnosis Algorithm Elevated Grepmed Hypercalcemia statpearls. A practical approach to hypercalcemia. A reduction in serum calcium can stimulate parathyroid hormone (pth) release which may then increase bone resorption, enhance renal calcium reabsorption, and stimulate renal conversion of 25 hydroxyvitamin d, to the active moiety 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin d [1,25(oh)2d] which then will enhance intestinal calcium absorption. these mechanisms restore the serum calcium to normal and inhibit further. Hypercalcemia may be mild and occur without symptoms. history may also identify symptoms of high calcium such as renal stones (typical of hyperparathyroidism), lethargy, easy fatigue, confusion, depression, irritability, constipation, and polyuria and polydipsia. [2] chronic symptoms are more consistent with hyperparathyroidism, whereas more.

Algorithmic Approach And Differential Diagnosis Hypercalcemia A reduction in serum calcium can stimulate parathyroid hormone (pth) release which may then increase bone resorption, enhance renal calcium reabsorption, and stimulate renal conversion of 25 hydroxyvitamin d, to the active moiety 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin d [1,25(oh)2d] which then will enhance intestinal calcium absorption. these mechanisms restore the serum calcium to normal and inhibit further. Hypercalcemia may be mild and occur without symptoms. history may also identify symptoms of high calcium such as renal stones (typical of hyperparathyroidism), lethargy, easy fatigue, confusion, depression, irritability, constipation, and polyuria and polydipsia. [2] chronic symptoms are more consistent with hyperparathyroidism, whereas more. Only the ionized calcium is metabolically active i.e. subject to transport into cells, but most laboratories report total serum calcium concentrations. hypercalcemia is therefore often defined as a total serum calcium (bound plus ionized) greater than 10.6 mg dl (2.65 mm) or an ionized serum calcium greater than 5.3 mg dl (1.3 mm) but values may vary between laboratories. Hypercalcemia (defined as a serum calcium level >10.5 mg dl or 2.5 mmol l) is an important clinical problem [1]. among the causes of hypercalcemia, primary hyperparathyroidism (phpt) and malignancy are most common, accounting for 80–90% of cases. phpt is the major cause of hypercalcemia in the ambulatory population, comprising up to 60% of.

Comments are closed.