Hyperkalemia Detailed Pathophysiology Intracellular Shift And Intake
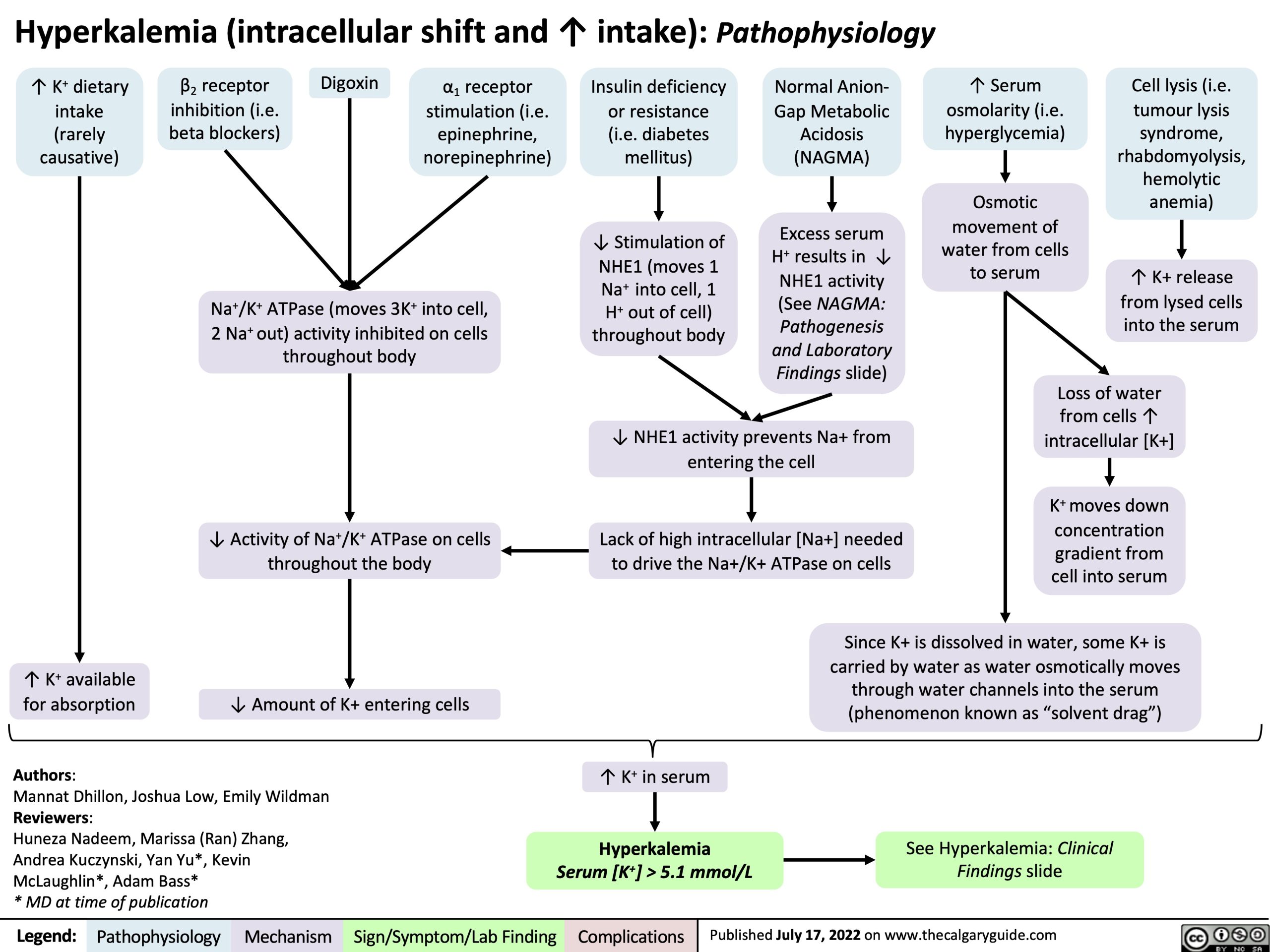
Hyperkalemia Detailed Pathophysiology Intracellular Shift And Intake Hyperkalemia: detailed pathophysiology (intracellular shift and intake) post views: 6,751. Hyperkalemia: pathophysiology, risk factors and.
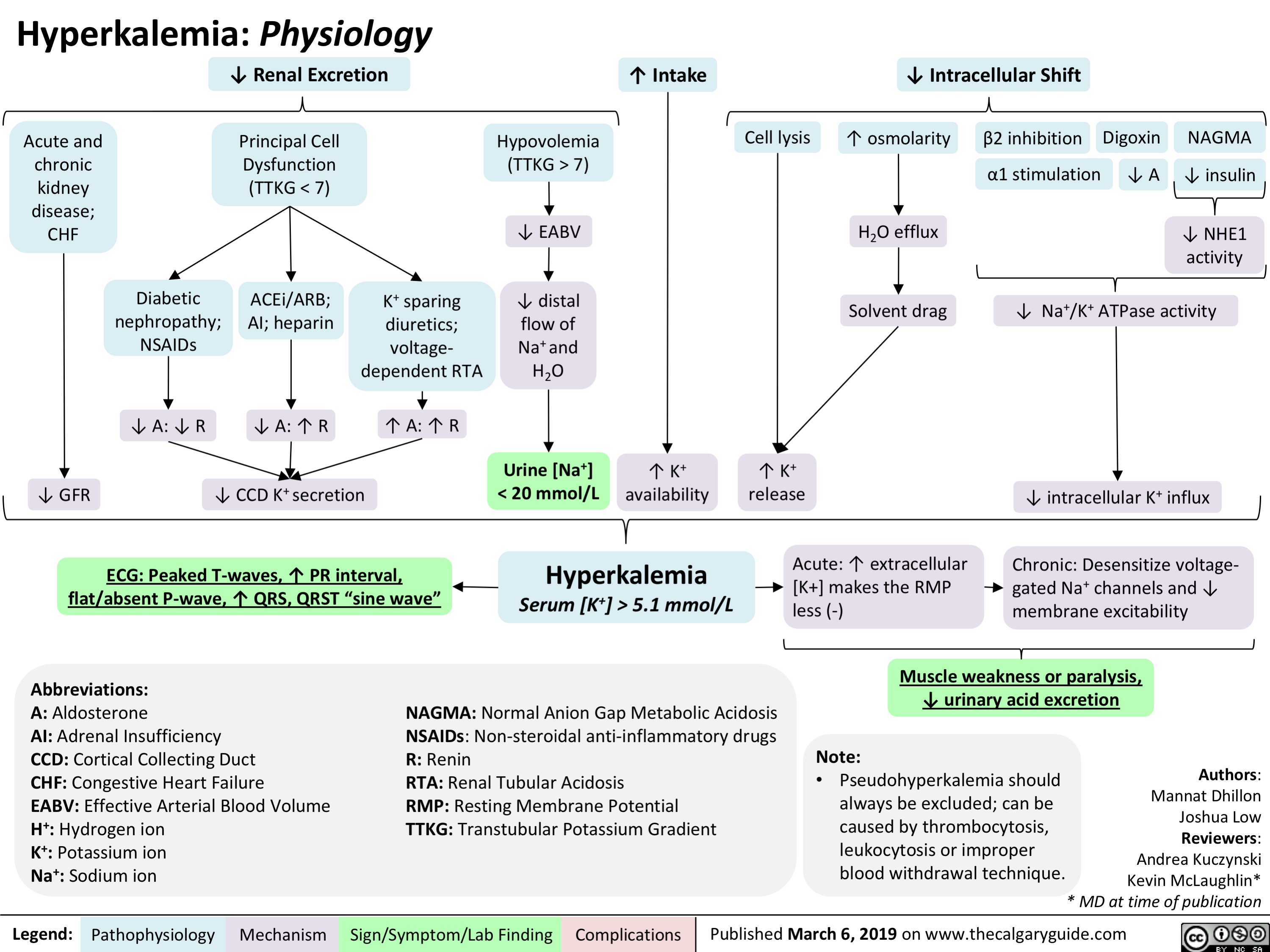
Hyperkalemia Physiology Overview Calgary Guide Hyperkalemia (intracellular shift and ↑ intake): pathophysiology ↑ k dietary intake (rarely causative) β2 receptor inhibition (i.e. beta blockers) digoxin α1 receptor stimulation (i.e. epinephrine, norepinephrine) insulin deficiency or resistance (i.e. diabetes mellitus) ↓ stimulation of nhe1 (moves 1 na into cell, 1 h out of cell) throughout body normal anion gap metabolic. Tissue damage (eg, rhabdomyolysis, trauma, massive hemolysis, and tumor lysis) are common causes of hyperkalemia resulting from cell shift. these conditions can cause sudden and severe hyperkalemia because only a 2% shift of intracellular k to the extracellular space can double the normal extracellular k concentration. Hyperkalemia statpearls. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of hyperkalemia.
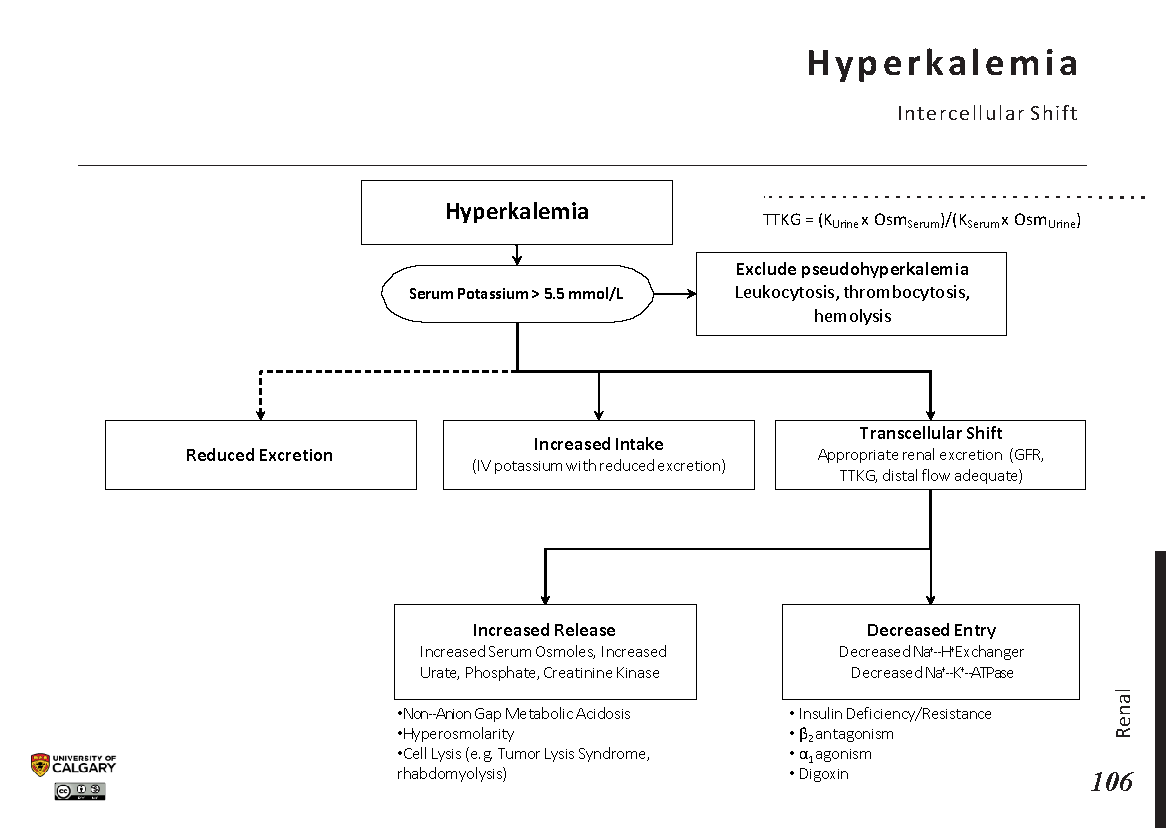
Hyperkalemia Detailed Pathophysiology Intracellular S Vrogue Co Hyperkalemia statpearls. Pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of hyperkalemia. Insulin lowers the plasma potassium con centration by promoting its entry into cells. to avoid hypoglycemia, 10 units of short act ing insulin should be accompanied by a 50 g infusion of glucose, increased to 60 g if 20 units of insulin are given.24. beta 2 receptor agonists produce a similar effect. This is an overview of the pathophysiology of hyperkalemia. for details of the underlying mechanism, please see the accompanying two slides on reduced intracellular shift and reduced renal excretion. for a full explanation of the signs symptoms of hyperkalemia, please see our slide on hyperkalemia: clinical findings. post views: 23,838.

Comments are closed.