Hyperkalemia Hypokalemia Made Easy With Mnemonics Visuals In 5 Mins

Hyperkalemia Hypokalemia Made Easy With Mnemonics Visuals In Hi friends. this is a video on hyperkalemia & hypokalemia. this is a very important topic for all the medicos. i have explained the signs & symptoms, causes. Kal = root word for potassium. emia =blood. meaning of hyperkalemia: e xcessive potassium in the blood. normal potassium is 3.5 to 5.1. anything higher 7.0 or higher is very dangerous! most of the body’s potassium is found in the intracellular part of the cell compared to the extracellular which is where sodium is mainly found.
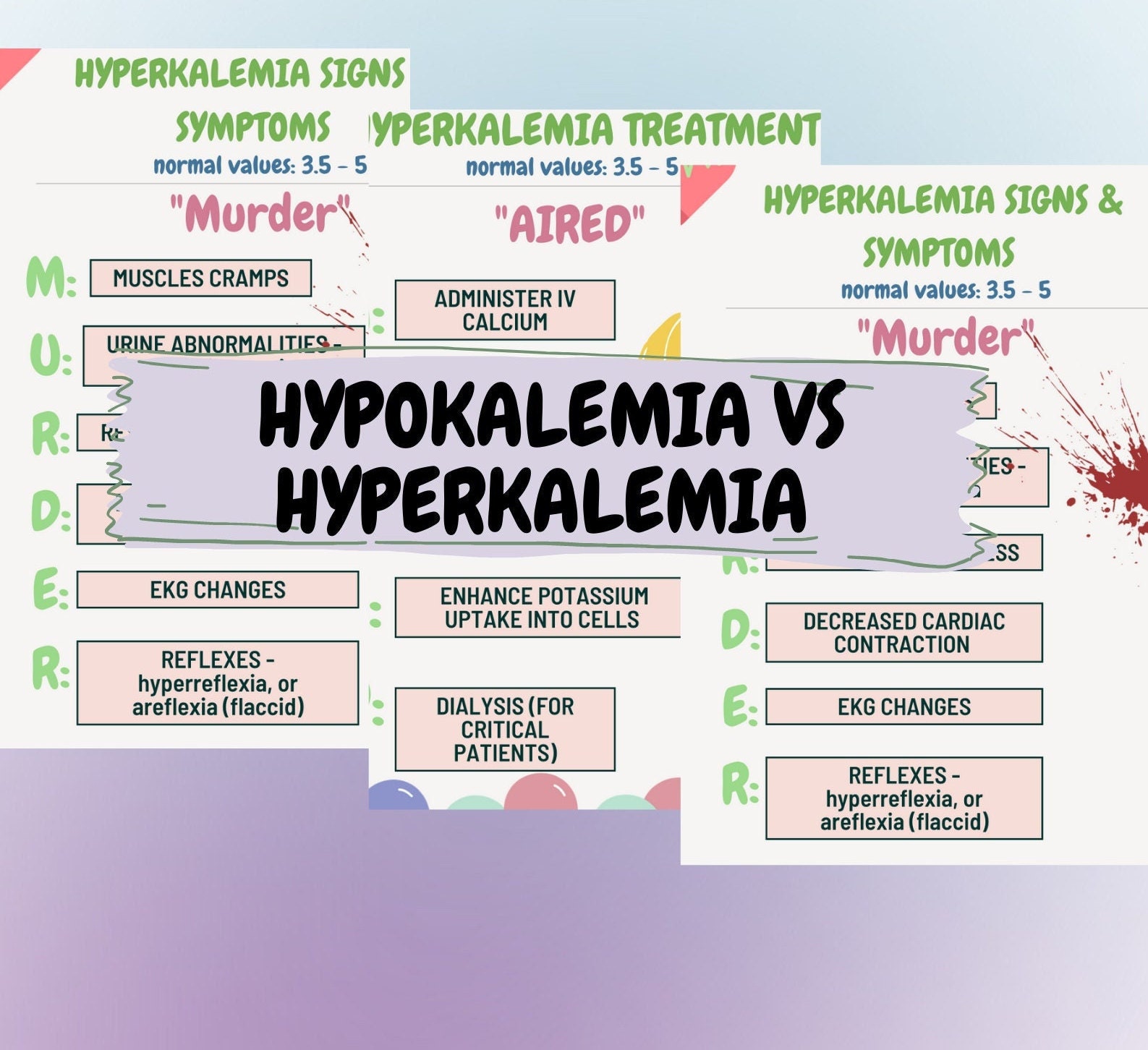
Hyperkalemia Mnemonic Pulling out of hair had commenced! so…in order to hopefully make your life a little easier, i have compiled some of the mnemonics regarding hyperkalemia and hypokalemia. causes of hyperkalemia m a c h i n e m eds (acei, beta blockers) a cidosis c ellular destruction h ypoaldosteronism, hemolysis i ntake, excessive n ephrons, renal failure e. It is generally accepted that calcium should be given when there are ecg changes associated with hyperkalaemia. calcium gluconate 10% 10 30 ml iv (1 3 gm) over 5 10 minutes (can be repeated after 5 minutes if ecg changes persistent) 0.5 ml kg in children. onsent of action: immediate. duration of action: 30 60 minutes. Hypokalemia. this osmosis high yield note provides an overview of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia essentials. all osmosis notes are clearly laid out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. find more information about hyperkalemia and hypokalemia:. It helps with the electrical impulses, acid base balance, and it's the main intracellular cation, or positively charged ion hypokalemia is less than 3.5. think hypokalemia, hypoactive, and we really want to replace our potassium. hyperkalemia is greater than 5. think hyperkalemia, hyperactive. we want to restrict and reduce our potassium.

Hyperkalemia Mnemonic Hypokalemia. this osmosis high yield note provides an overview of hyperkalemia and hypokalemia essentials. all osmosis notes are clearly laid out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. find more information about hyperkalemia and hypokalemia:. It helps with the electrical impulses, acid base balance, and it's the main intracellular cation, or positively charged ion hypokalemia is less than 3.5. think hypokalemia, hypoactive, and we really want to replace our potassium. hyperkalemia is greater than 5. think hyperkalemia, hyperactive. we want to restrict and reduce our potassium. Hyperkalemia may result in a progression of ekg changes including peaked t waves and qt interval shortening, pr and qrs interval prolongation, and finally a sine wave appearance. after obtaining an ekg, the approach to hyperkalemia management can be remembered with the mnemonic “c big k di” (i.e. if you see a big k, the patient could die!):. This is a nclex quiz for fluid and electrolytes on hyperkalemia and hypokalemia. 1. a patient has a potassium level of 9.0. which nursing intervention is priority? a. prepare the patient for dialysis and place the patient on a cardiac monitor. b. administer spironolactone. c. place patient on a potassium restrictive diet. d. administer a laxative.

Hyperkalemia Treatment Mnemonic Hyperkalemia may result in a progression of ekg changes including peaked t waves and qt interval shortening, pr and qrs interval prolongation, and finally a sine wave appearance. after obtaining an ekg, the approach to hyperkalemia management can be remembered with the mnemonic “c big k di” (i.e. if you see a big k, the patient could die!):. This is a nclex quiz for fluid and electrolytes on hyperkalemia and hypokalemia. 1. a patient has a potassium level of 9.0. which nursing intervention is priority? a. prepare the patient for dialysis and place the patient on a cardiac monitor. b. administer spironolactone. c. place patient on a potassium restrictive diet. d. administer a laxative.

Hyperkalemia Mnemonic

Comments are closed.