Hypersensitivity Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
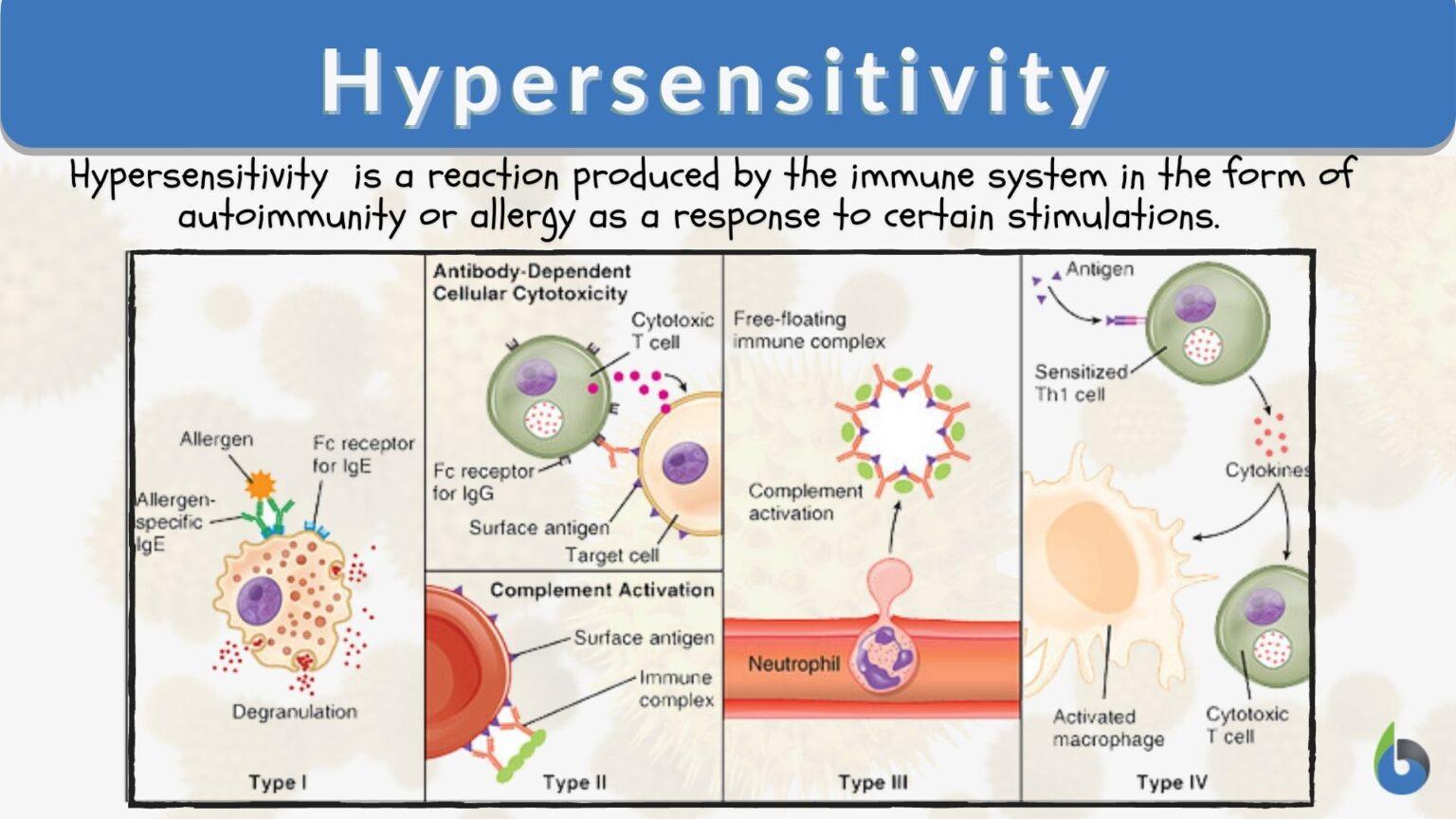
Hypersensitivity Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Reflux hypersensitivity: is a disorder of the esophagus. the main symptoms are heartburn, esophagitis, and chest pain. biology definition: hypersensitivity is a state of altered reactivity in which the body reacts with an exaggerated immune response to a foreign substance. hypersensitivity reactions are classified as immediate or delayed (type. Hypersensitive, also known as hypersensitive reaction or intolerance, is an abnormal physiological condition in which the body’s immune system reacts negatively to an antigen. it reflects an immune system malfunction that can lead to immunological disorders such as allergies and autoimmunity. various particles and chemicals from the external.
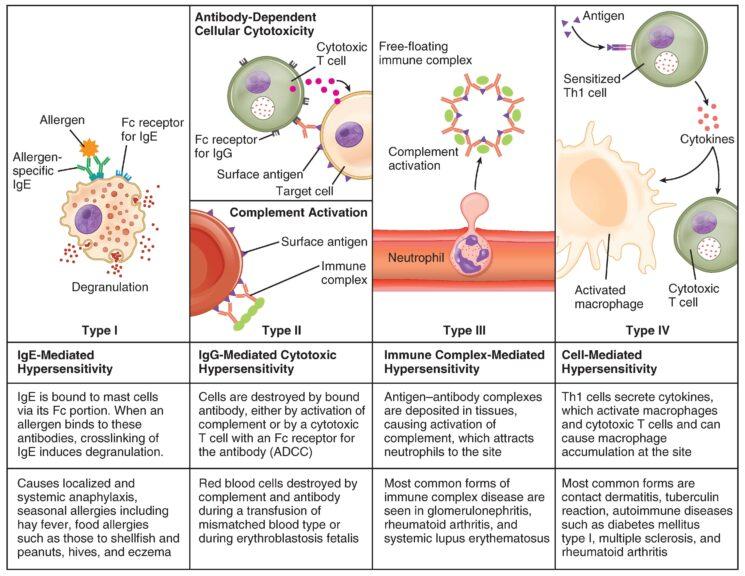
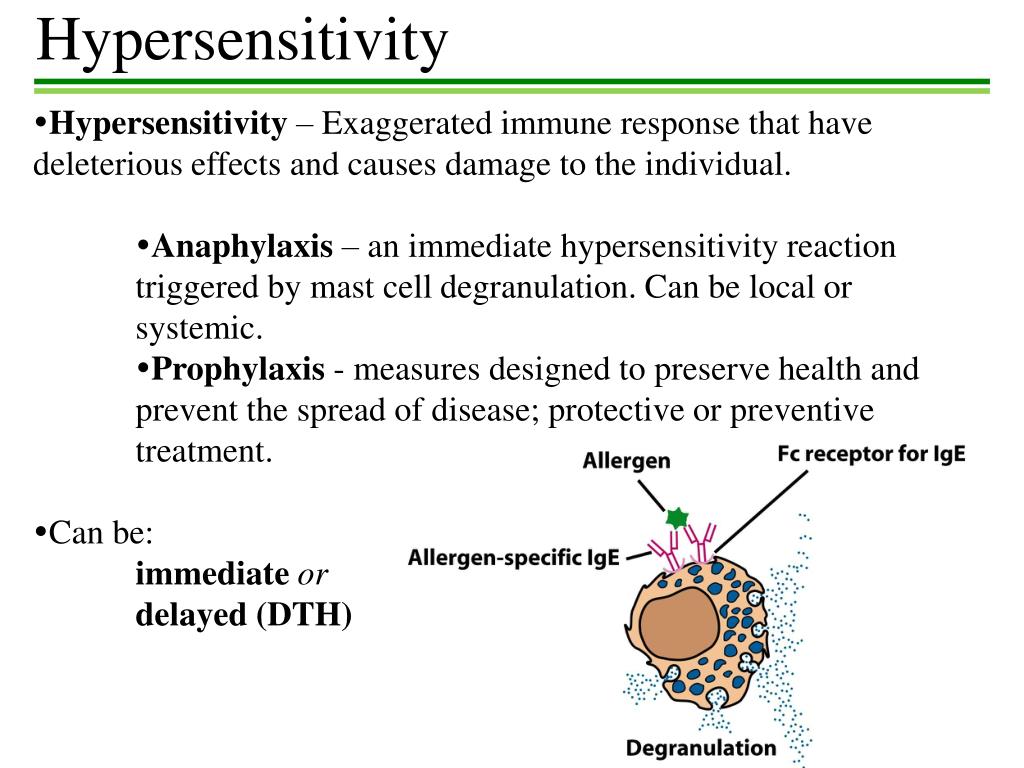
Hypersensitivity Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary Allergy. 1. (science: immunology) a state of hypersensitivity induced by exposure to a particular antigen (allergen) resulting in harmful immunologic reactions on subsequent exposures, the term is usually used to refer to hypersensitivity to an environmental antigen (atopic allergy or contact dermatitis) or to drug allergy. the original meaning. Hypersensitivity definition, causes, mechanism, types,. Acquired sensitivity –> allergy 1. (science: immunology) a state of hypersensitivity induced by exposure to a particular antigen (allergen) resulting in harmful immunologic reactions on subsequent exposures, the term is usually used to refer to hypersensitivity to an environmental antigen (atopic allergy or contact dermatitis) or to drug allergy. Allergic conjunctivitis is an example of this type of hypersensitivity. type 2 h . (cytotoxic h.) is caused by an interaction of antibody and antigens on cell surfaces. examples: graves' disease, myasthenia gravis. type 3 h. (immune complex mediated h.) is mediated by a combination of antigen antibody. example: systemic lupus erythematosus.
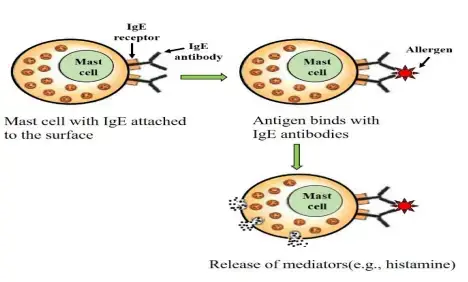
Hypersensitivity Definition Types Mechanisms Examples Biology Acquired sensitivity –> allergy 1. (science: immunology) a state of hypersensitivity induced by exposure to a particular antigen (allergen) resulting in harmful immunologic reactions on subsequent exposures, the term is usually used to refer to hypersensitivity to an environmental antigen (atopic allergy or contact dermatitis) or to drug allergy. Allergic conjunctivitis is an example of this type of hypersensitivity. type 2 h . (cytotoxic h.) is caused by an interaction of antibody and antigens on cell surfaces. examples: graves' disease, myasthenia gravis. type 3 h. (immune complex mediated h.) is mediated by a combination of antigen antibody. example: systemic lupus erythematosus. Hypersensitivity refers to an exaggerated or unnecessary reaction produced by the host immune system. it is an immunological dysfunction, mainly targeted at innocuous antigens with consequent tissue damage. the human immune system protects body from damage by fighting invasive substances and infections. sometimes, however, it can ‘ overreact. Type iii hypersensitivity is classified as an immunoglobulin mediated or immediate hypersensitivity reaction, where the destruction of cells is mediated by antigen antibody complexes. when antibodies combine with their specific antigens, immune complexes are formed. normally, these complexes are promptly removed from the body.
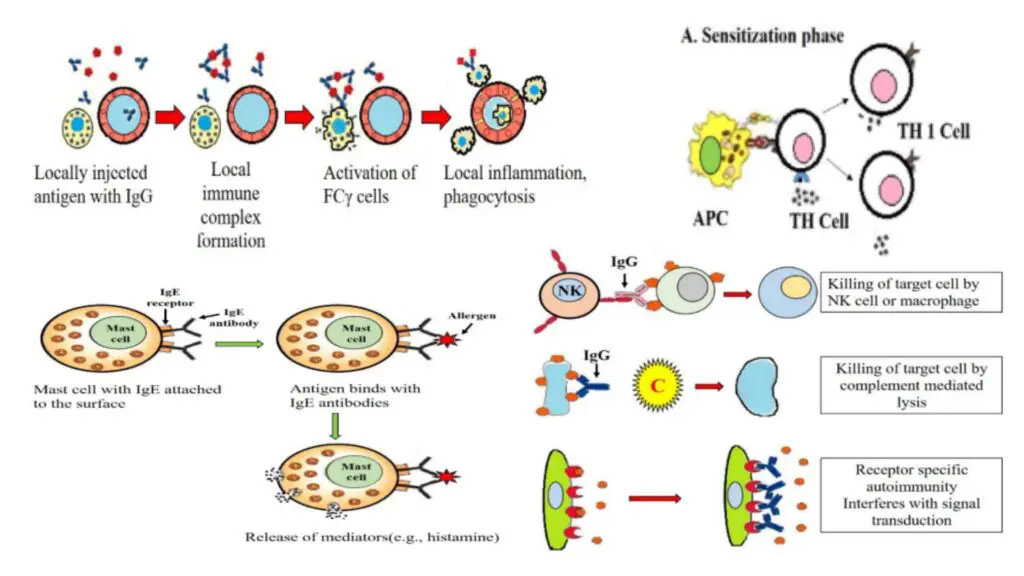
Hypersensitivity Definition Types Mechanisms Examples Biology Hypersensitivity refers to an exaggerated or unnecessary reaction produced by the host immune system. it is an immunological dysfunction, mainly targeted at innocuous antigens with consequent tissue damage. the human immune system protects body from damage by fighting invasive substances and infections. sometimes, however, it can ‘ overreact. Type iii hypersensitivity is classified as an immunoglobulin mediated or immediate hypersensitivity reaction, where the destruction of cells is mediated by antigen antibody complexes. when antibodies combine with their specific antigens, immune complexes are formed. normally, these complexes are promptly removed from the body.
Hypersensitivity Introduction Causes Mechanism And Ty Vrogue Co

Comments are closed.