Hypertrophy Adaptation Mechanisms Training Guidelines
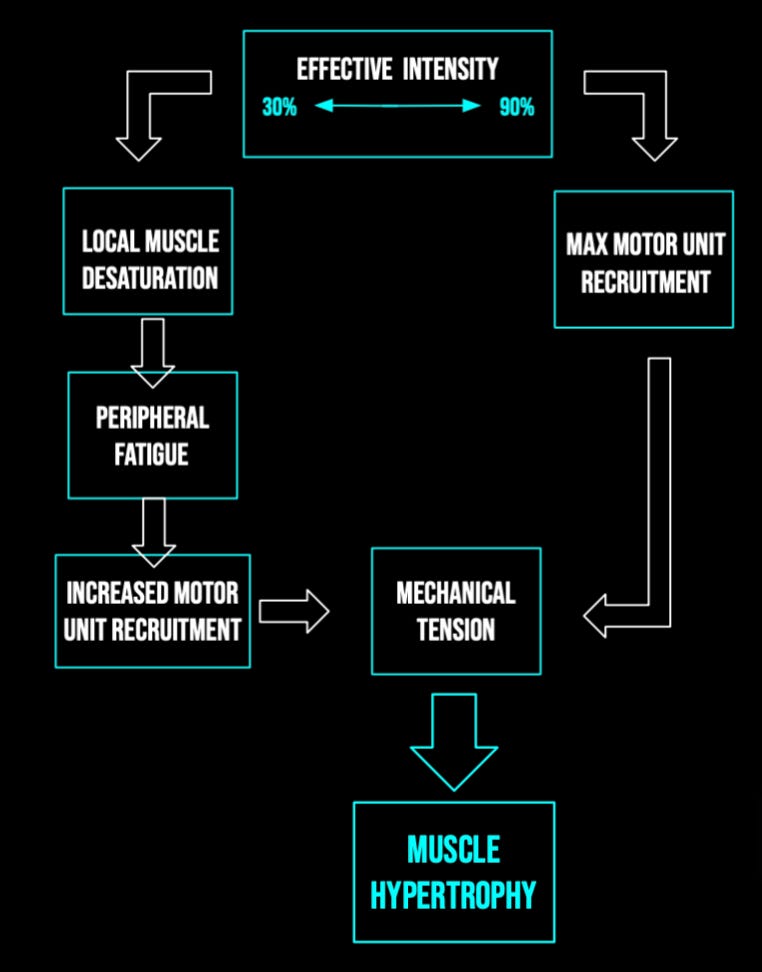
Hypertrophy Adaptation Mechanisms Training Guidelines 1. introduction. resistance training (rt) is a primary exercise intervention used to develop strength and stimulate muscle hypertrophy. increases in muscle mass constitute key components of conditioning in various sports due to the correlation between muscle cross sectional area and muscle strength [1,2]. Hypertrophy: adaptation mechanisms & training guidelines. in many traditional strength training paradigms, there is a dose response relationship ascribed to different rep ranges. they say 1–5 reps are for building strength, 6–10 for functional hypertrophy, 10–15 for non functional hypertrophy, and 15 for muscular endurance.
Hypertrophy Adaptation Mechanisms Training Guidelines The practical implications of this viewpoint are highlighted in the american college of sports medicine rt guidelines, whereby the use of moderate loads is recommended for hypertrophy training . other research papers provide similar loading recommendations when training to maximize muscle development [1,34]. The last adaptation to endurance exercise training that we would like to highlight is muscle hypertrophy and growth (harber et al. 2009b, 2012; konopka and harber 2014). over a 12 wk endurance training program, muscle mass has been reported to increase by 7% to 11% ( konopka et al. 2010 ; trappe et al. 2011 ; harber et al. 2012 ). Evidence based training for muscular strength. strength is measured in a variety of ways but most commonly as a voluntary isotonic (unchanging force throughout a range of motion) maximal lift: the so called one repetition maximum (1rm). other forms might include 3–10 repetitions to fatigue: 3–10rm. tests may also include isometric. Resistance training (rt) is the primary form of exercise that is used to induce gains in muscle mass. the manipulation of rt variables is widely considered an essential strategy to maximize exercise induced muscular adaptations ( 17 ). one rt variable that has received a great deal of attention in this regard, particularly with respect to.

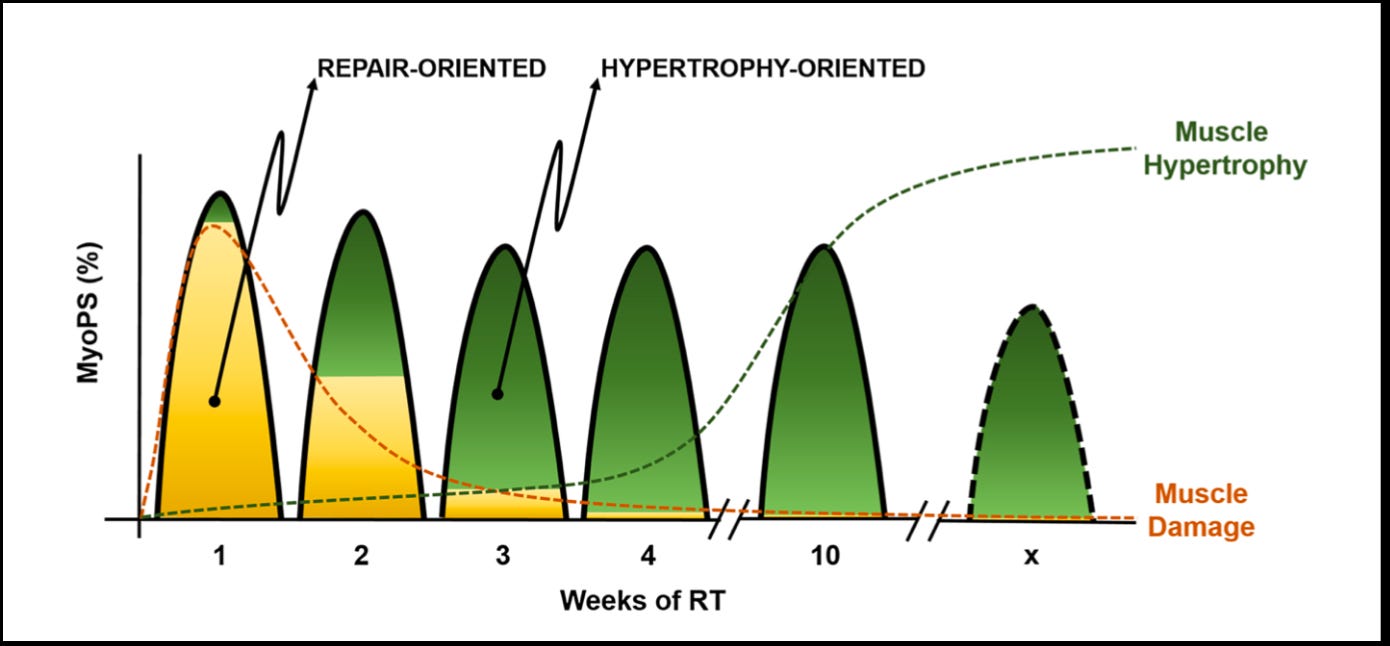
Hypertrophy Adaptation Mechanisms Training Guidelines Evidence based training for muscular strength. strength is measured in a variety of ways but most commonly as a voluntary isotonic (unchanging force throughout a range of motion) maximal lift: the so called one repetition maximum (1rm). other forms might include 3–10 repetitions to fatigue: 3–10rm. tests may also include isometric. Resistance training (rt) is the primary form of exercise that is used to induce gains in muscle mass. the manipulation of rt variables is widely considered an essential strategy to maximize exercise induced muscular adaptations ( 17 ). one rt variable that has received a great deal of attention in this regard, particularly with respect to. Cause continual positive adaptations, a training program needs (2010, october). the mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application to resistance training. Key points. mechanical tension and metabolic stress contribute to training related muscle hypertrophy and increase in maximal strength. as the magnitude of the neural adaptations after low load exercise with blood flow restriction is less than that elicited by high load strength training and this method is difficult for some individuals and insufficient for well trained athletes, we suggest.

Complete Technique Guidelines For Hypertrophy Training Youtube Cause continual positive adaptations, a training program needs (2010, october). the mechanisms of muscle hypertrophy and their application to resistance training. Key points. mechanical tension and metabolic stress contribute to training related muscle hypertrophy and increase in maximal strength. as the magnitude of the neural adaptations after low load exercise with blood flow restriction is less than that elicited by high load strength training and this method is difficult for some individuals and insufficient for well trained athletes, we suggest.

Comments are closed.