I Biologyi I Notesi Mitosis Studygram A A A A A A A A Follow Motivation2study

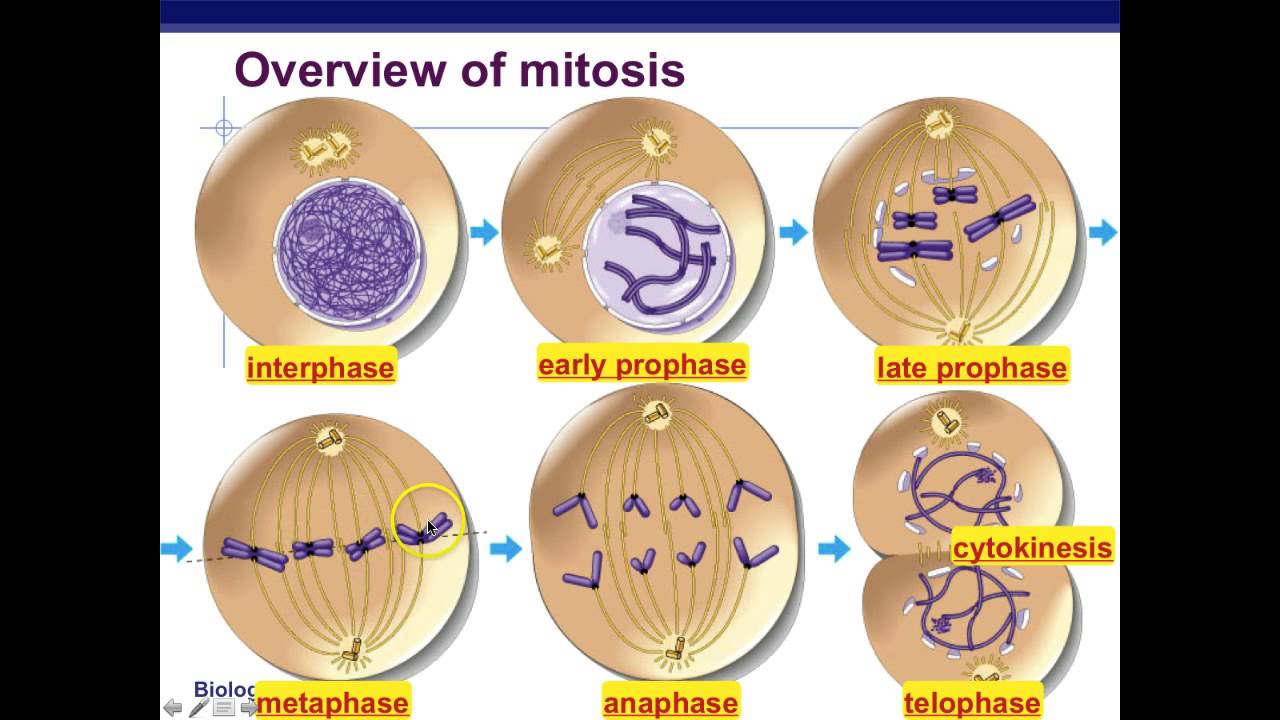
ççbiology çü ççnotes çü ççmitosis çü ççstudygram çü ôÿà à à à àôÿà ççfollow çü ççmotivation2study ç Although mitosis is, in reality, one continuous process, it can be divided into four main stages. these stages are: prophase. metaphase. anaphase. telophase. most organisms contain many chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells (eg. humans have 46) but the diagrams below show mitosis of an animal cell with only four chromosomes, for simplicity. Cytokinesis is the final step of mitosis. in this step, the cell will completely divide in to two daughter cells as the cytoplasm and cell membrane separates. each daughter cell will be identical to each other and their parent cell. each daughter will have one nucleus, a complete set of dna, and a set of organelles and the same amount of.

Mitosis And The Cell Cycle Biology Lessons Biology College Study Mitosis is the process of nuclear division by which two genetically identical daughter nuclei are produced that are also genetically identical to the parent cell nucleus (they have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell) although mitosis is, in reality, one continuous process, it can be divided into four main stages. these stages are:. The cell cycle has three phases: interphase. nuclear division (mitosis) cell division (cytokinesis) the length of the cell cycle is very variable depending on environmental conditions, the cell type and the organism. for example, onion root tip cells divide once every 20 hours (roughly) but human intestine epithelial cells divide once every 10. Find and save ideas about biology notes layout on pinterest. The purpose of mitosis is to produce more cells. after the first round of mitosis, there are only two cells. these cells both undergo mitosis, and there are 4 cells. pretty soon, a small, hollow ball of cells is formed, called the blastula. this ball folds in on itself as more and more cells are created.
Mitosis Mitotic Cell Division Stages And Significance Online Find and save ideas about biology notes layout on pinterest. The purpose of mitosis is to produce more cells. after the first round of mitosis, there are only two cells. these cells both undergo mitosis, and there are 4 cells. pretty soon, a small, hollow ball of cells is formed, called the blastula. this ball folds in on itself as more and more cells are created. Outcome. while mitosis yields two daughter cells that are genetically identical (2n) to the parent cell, meiosis produces four haploid (n) cells that are genetically different from the parent cell. mitosis: two identical daughter cells. meiosis: four non identical daughter cells with half the chromosome number. Enhance your understanding of mitosis and meiosis with these beautifully designed aesthetic notes. explore the key concepts and processes in a visually appealing way to make your learning experience more enjoyable.

Comments are closed.