Identifying Parts Of A Parabola
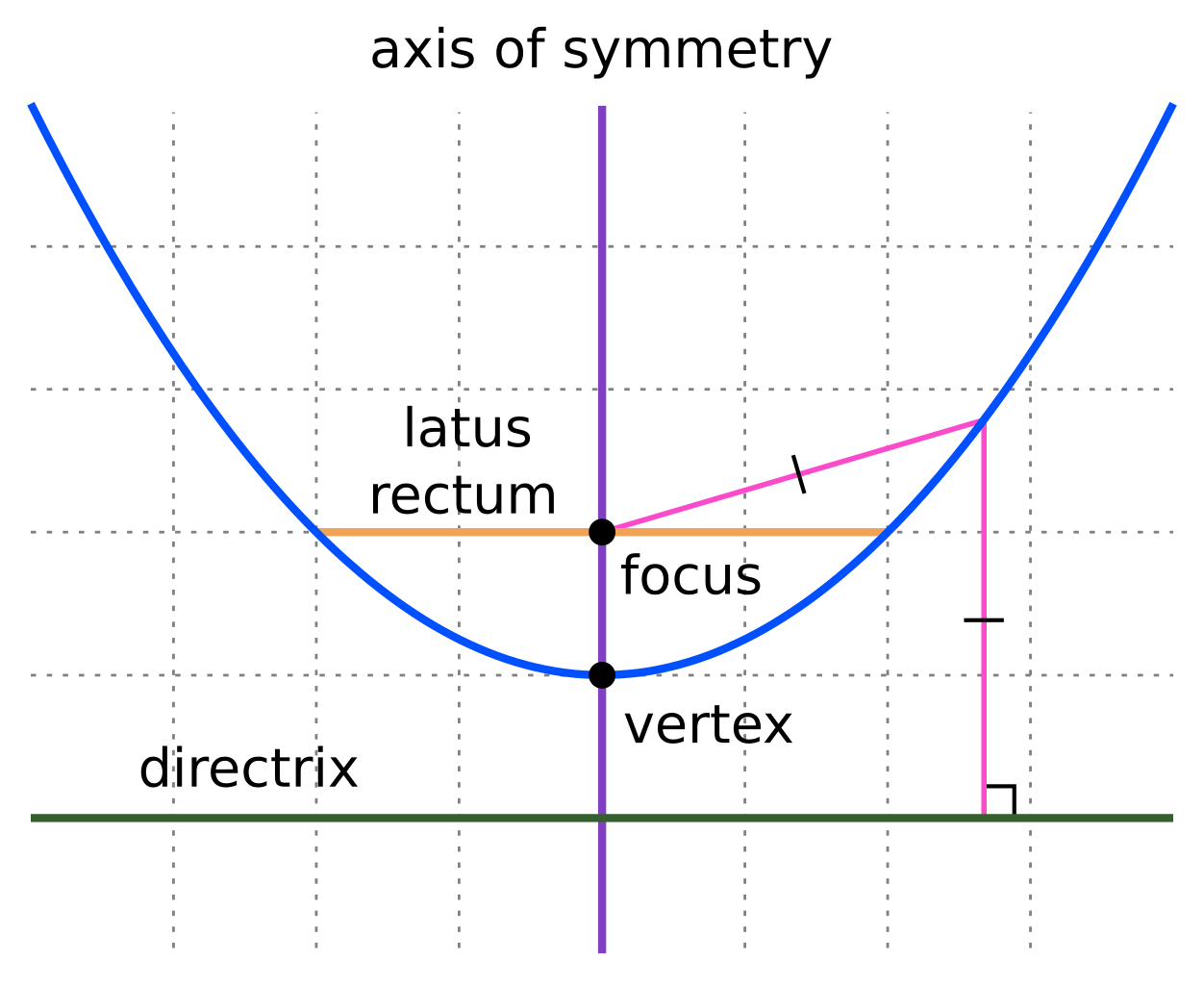
File Parts Of Parabola Svg Wikimedia Commons Learn how to identify the vertex, focus, focal length, latus rectum, directrix and axis of a parabola. see diagrams and examples of different types of parabolas. Learn what a parabola is, how to identify its focus, directrix, vertex, and axis of symmetry, and how to write and graph its equation. find the zeros, eccentricity, and focal length of a parabola and how to sketch it.
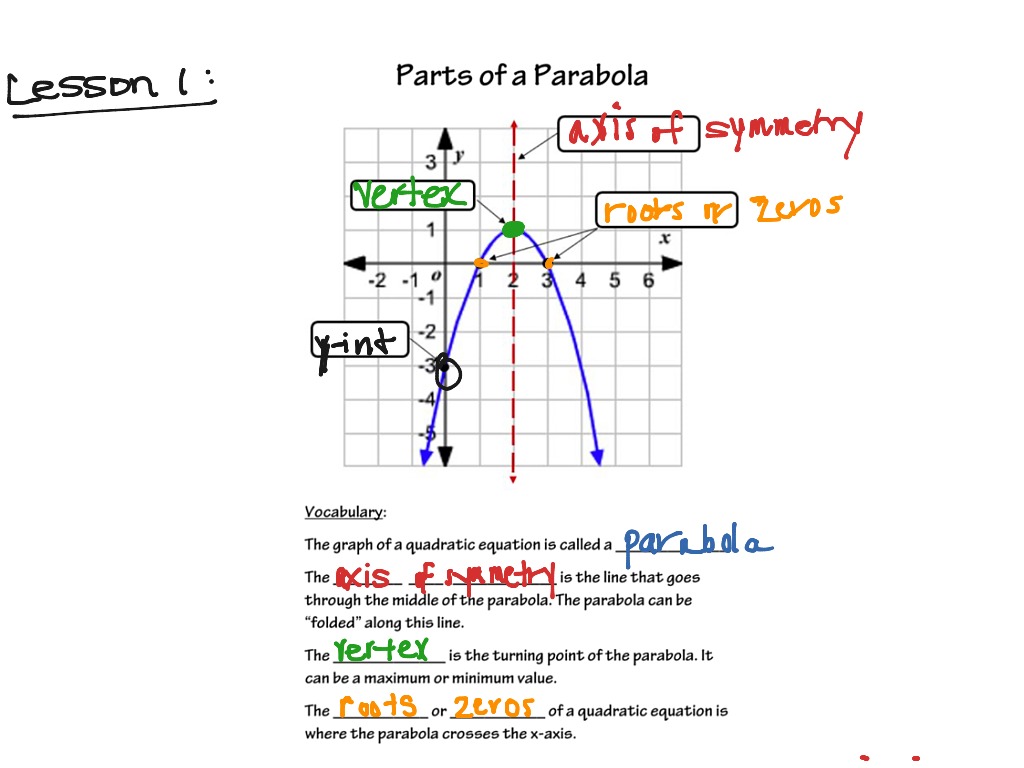
Identifying Parts Of A Parabola Worksheet Pdf Connect the five points to form the parabola. for this parabola, the vertex is the maximum value. if you look at the equation, y = − 1 2x2 − 2x 6, we see that the a value is negative. when a is negative, the sides of the parabola, will point down. finally, let's find the vertex and x − intercepts of y = 2x2 − 5x − 25. Learn what a parabola is, how to draw it, and how to identify its focus, directrix, axis of symmetry and vertex. see how to use equations to find the measurements of a parabolic dish. The general form of a parabola's equation is the quadratic that you're used to: y = ax2 bx c. — unless the quadratic is sideways, in which case the equation will look something like this: x = ay2 by c. the important difference in the two equations is in which variable is squared: for regular (that is, for vertical) parabolas, the x. The key features of a parabola are its vertex, axis of symmetry, focus, directrix, and latus rectum (figure \(\pageindex{5}\)). when given a standard equation for a parabola centered at the origin, we can easily identify the key features to graph the parabola. a line is said to be tangent to a curve if it intersects the curve at exactly one point.

Identifying Parts Of A Parabola Worksheet The general form of a parabola's equation is the quadratic that you're used to: y = ax2 bx c. — unless the quadratic is sideways, in which case the equation will look something like this: x = ay2 by c. the important difference in the two equations is in which variable is squared: for regular (that is, for vertical) parabolas, the x. The key features of a parabola are its vertex, axis of symmetry, focus, directrix, and latus rectum (figure \(\pageindex{5}\)). when given a standard equation for a parabola centered at the origin, we can easily identify the key features to graph the parabola. a line is said to be tangent to a curve if it intersects the curve at exactly one point. Graphs of quadratic functions all have the same shape which we call "parabola." all parabolas have shared characteristics. for example, they are all symmetric about a line that passes through their vertex. this video covers this and other basic facts about parabolas. questions. This includes graphing, knowing the parabola’s different components, and identifying the parabola’s orientation immediately. formal parabola definition. parabolas are curves that contain points where their distances from the focus and their distances from the directrix will always be equal.

Comments are closed.