Identifying Polygons Identifying Polygons Regular Pol Vrogue Co
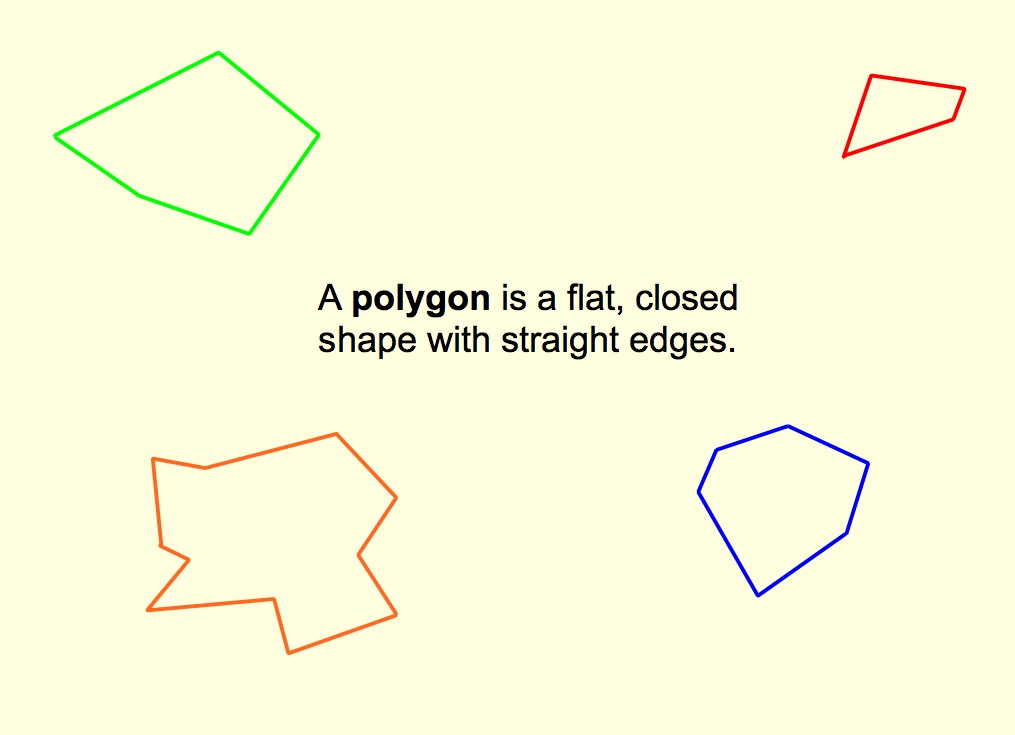
Identifying Polygons Identifying Polygons Regular Pol Vrogue Co Solution for teaching textbooks, geometry, lesson 61, problem 11. learn how to identify a given regular polygon and calculate the measures of the regular pol. The sides of regular polygons are all the same length. in these worksheets, students identify polygons and regular polygons. polygons: worksheet #1. regular polygons: worksheet #2. worksheet #3. similar: types of polygons congruent shapes.
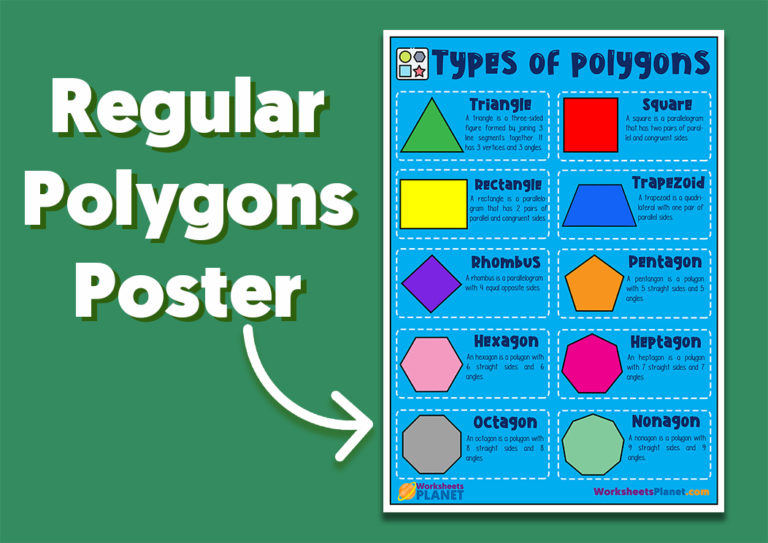
What Is A Regular Polygon Regular Polygons Examples F Vrogue Co For a copy of the notes, vocabulary, and interactive activities, visit me at teacherspayteachers store simplify the middle.this lesson explai. 1. the angles of a regular polygon are all the same size. 2. a regular hexagon has six sides that are different lengths. 3. an irregular pentagon has sides that are the same length. 4. an irregular polygon is one that has one side open. 5. a regular triangle could also be called an equilateral triangle. 6. the side lengths of a regular octagon. A pentagon with all equal sides and angles are regular polygons whereas an irregular pentagon with one or more sides and angles unequal are irregular polygons. q6. is a square a regular polygon? ans. yes, a square is a regular polygon because all its sides are of equal length and all its angles are of equal measure. A regular polygon is a polygon in which all sides are equal and all angles are equal, examples of a regular polygon are the equilateral triangle (3 sides), the square (4 sides), the regular pentagon (5 sides), and the regular hexagon (6 sides). the angles of a regular polygon can easily be found using the methods of section 1.5.
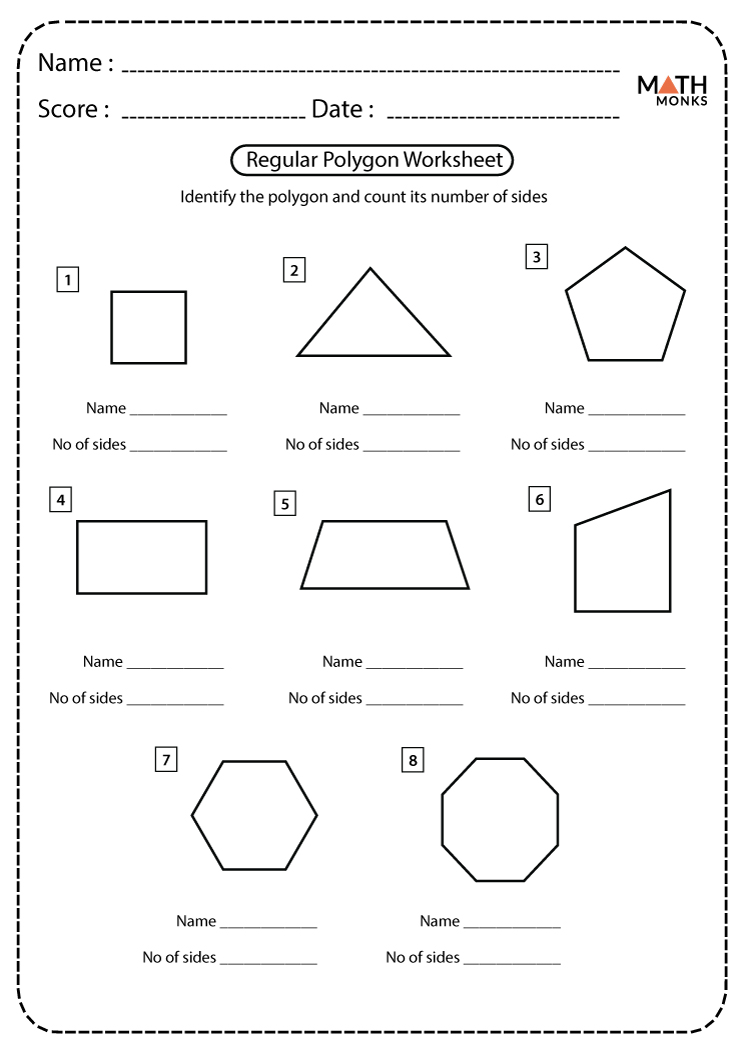
Identifying Polygons Coloring Activity Math Geometry Vrogue Co A pentagon with all equal sides and angles are regular polygons whereas an irregular pentagon with one or more sides and angles unequal are irregular polygons. q6. is a square a regular polygon? ans. yes, a square is a regular polygon because all its sides are of equal length and all its angles are of equal measure. A regular polygon is a polygon in which all sides are equal and all angles are equal, examples of a regular polygon are the equilateral triangle (3 sides), the square (4 sides), the regular pentagon (5 sides), and the regular hexagon (6 sides). the angles of a regular polygon can easily be found using the methods of section 1.5. A polygon is a closed shape. it is made of line segments or straight lines. a polygon is a two dimensional shape (2d shape) that has only two dimensions length and width. a polygon has at least three or more sides. the angles and side lengths of a polygon may be of the same length or of different lengths. The circumference of a circle is found using the formula c = πd, c = π d, where d d is the diameter of the circle, or c = 2πr, c = 2 π r, where r r is the radius. the radius is ½ of the diameter of a circle. the symbol π = 3.141592654 … π = 3.141592654 … is the ratio of the circumference to the diameter.
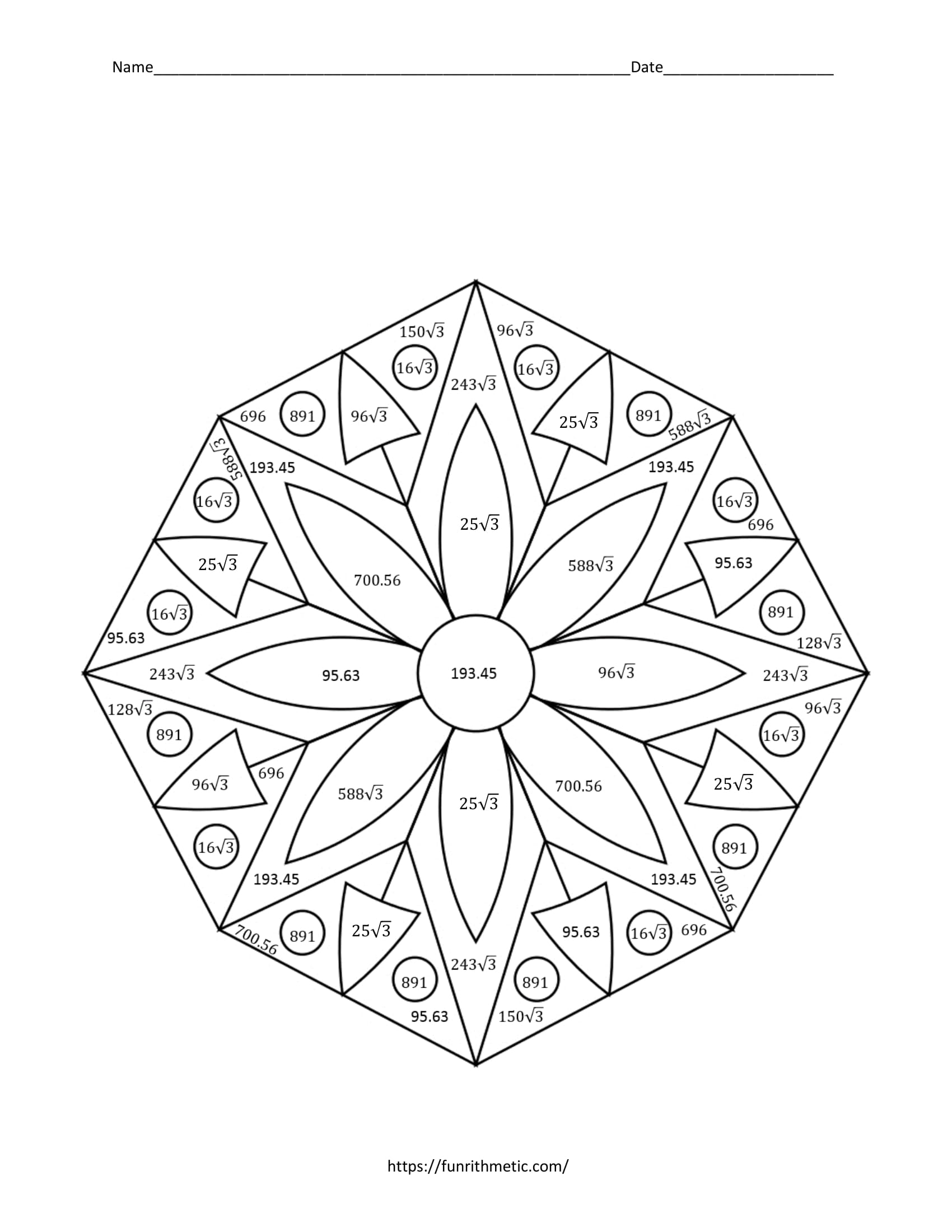
Identifying Polygons Coloring Activity Math Geometry Vrogue Co A polygon is a closed shape. it is made of line segments or straight lines. a polygon is a two dimensional shape (2d shape) that has only two dimensions length and width. a polygon has at least three or more sides. the angles and side lengths of a polygon may be of the same length or of different lengths. The circumference of a circle is found using the formula c = πd, c = π d, where d d is the diameter of the circle, or c = 2πr, c = 2 π r, where r r is the radius. the radius is ½ of the diameter of a circle. the symbol π = 3.141592654 … π = 3.141592654 … is the ratio of the circumference to the diameter.

Comments are closed.