Immunity To Protozoa And Worms Clinical Gate
Immunity To Protozoa And Worms Clinical Gate Chapter 15 immunity to protozoa and worms. summary. • parasites stimulate a variety of immune defense mechanisms. • parasitic infections are often chronic and affect many people. they are generally host specific and most cause chronic infections. many are spread by invertebrate vectors and have complicated life cycles. 1. introduction. host immune responses to parasitic infections are complex. parasites include protozoa, helminths, and insects. previously, the author proposed a framework for all the known host immunological pathways and their roles in the immune responses against four specific types of pathogens and the corresponding four specific types of hypersensitivities [1,2].
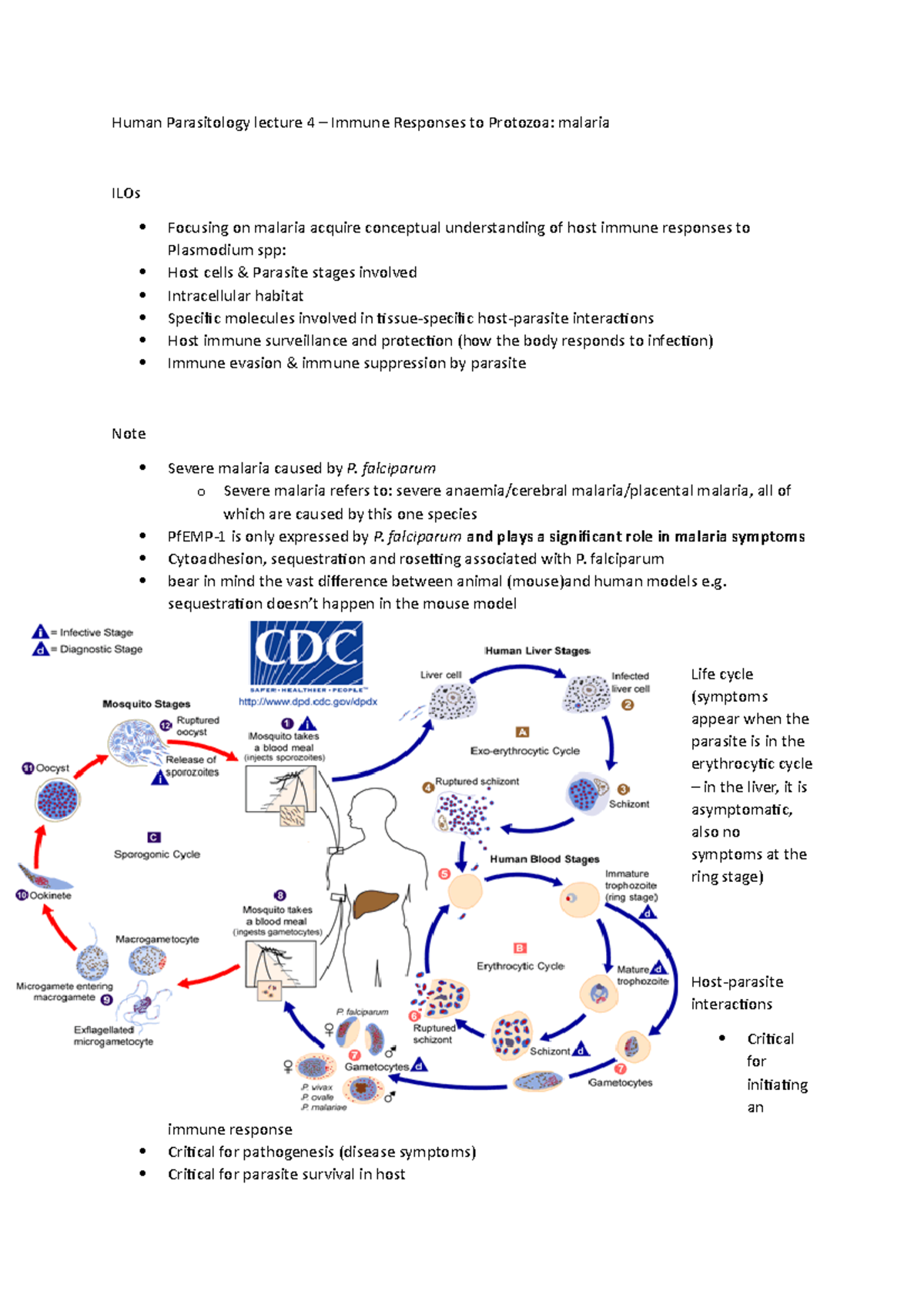
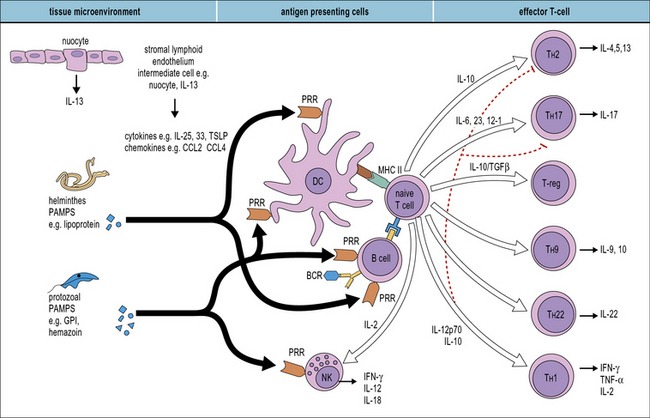
L4 Immune Responses To Protozoa Human Parasitology Lecture 4 Infection of humans is initiated by the bite of an infected mosquito, resulting in the injection of sporozoite stages. the sporozoite enters hepatocytes where asexual reproduction (schizogony. Immunity to protozoa and worms. january 2013; in book: immunology (pp.243 261) immunity against extracellular parasites is depicted for the myxozoans ceratonova shasta and enteromyxum spp. the. Cd4 t cells assist cd8 t cells in mounting an efficient immune response against plasmodium parasites [122, 123]. however, a study has shown that cd4 t cells are critical in providing immunity whereas cd8 t cells are expendable . thus, the coordinated orchestration between t cells is essential for protective immunity against plasmodium. Immunity to protozoan parasites. protozoan parasites cause several diseases, such as malaria, leishmaniasis, and trypanosomiasis, hampering human development worldwide. many protozoa cause infections that often follow chronic courses, owing to coevolution between parasites and host immune system. the survival and transmission of pathogenic.

Immunity To Protozoa And Worms Primary Immunodeficiency Ppt Download Cd4 t cells assist cd8 t cells in mounting an efficient immune response against plasmodium parasites [122, 123]. however, a study has shown that cd4 t cells are critical in providing immunity whereas cd8 t cells are expendable . thus, the coordinated orchestration between t cells is essential for protective immunity against plasmodium. Immunity to protozoan parasites. protozoan parasites cause several diseases, such as malaria, leishmaniasis, and trypanosomiasis, hampering human development worldwide. many protozoa cause infections that often follow chronic courses, owing to coevolution between parasites and host immune system. the survival and transmission of pathogenic. Dianna lydick. kyle burks. donna doherty. request pdf | on jan 1, 2006, david male and others published immunity to protozoa and worms | find, read and cite all the research you need on researchgate. Together, our model mimics components of the intestinal tissue including the epithelium, adjacent blood vessels, and immune cell components that could provide insight into human innate immune response during infection by protozoan parasites in a more physiologically relevant context.

Overview Of The Intestinal Immune System Innate Immunity Intestinal Dianna lydick. kyle burks. donna doherty. request pdf | on jan 1, 2006, david male and others published immunity to protozoa and worms | find, read and cite all the research you need on researchgate. Together, our model mimics components of the intestinal tissue including the epithelium, adjacent blood vessels, and immune cell components that could provide insight into human innate immune response during infection by protozoan parasites in a more physiologically relevant context.

Comments are closed.