In This Video You Will Learn All About Blast Furnace And Its Uses
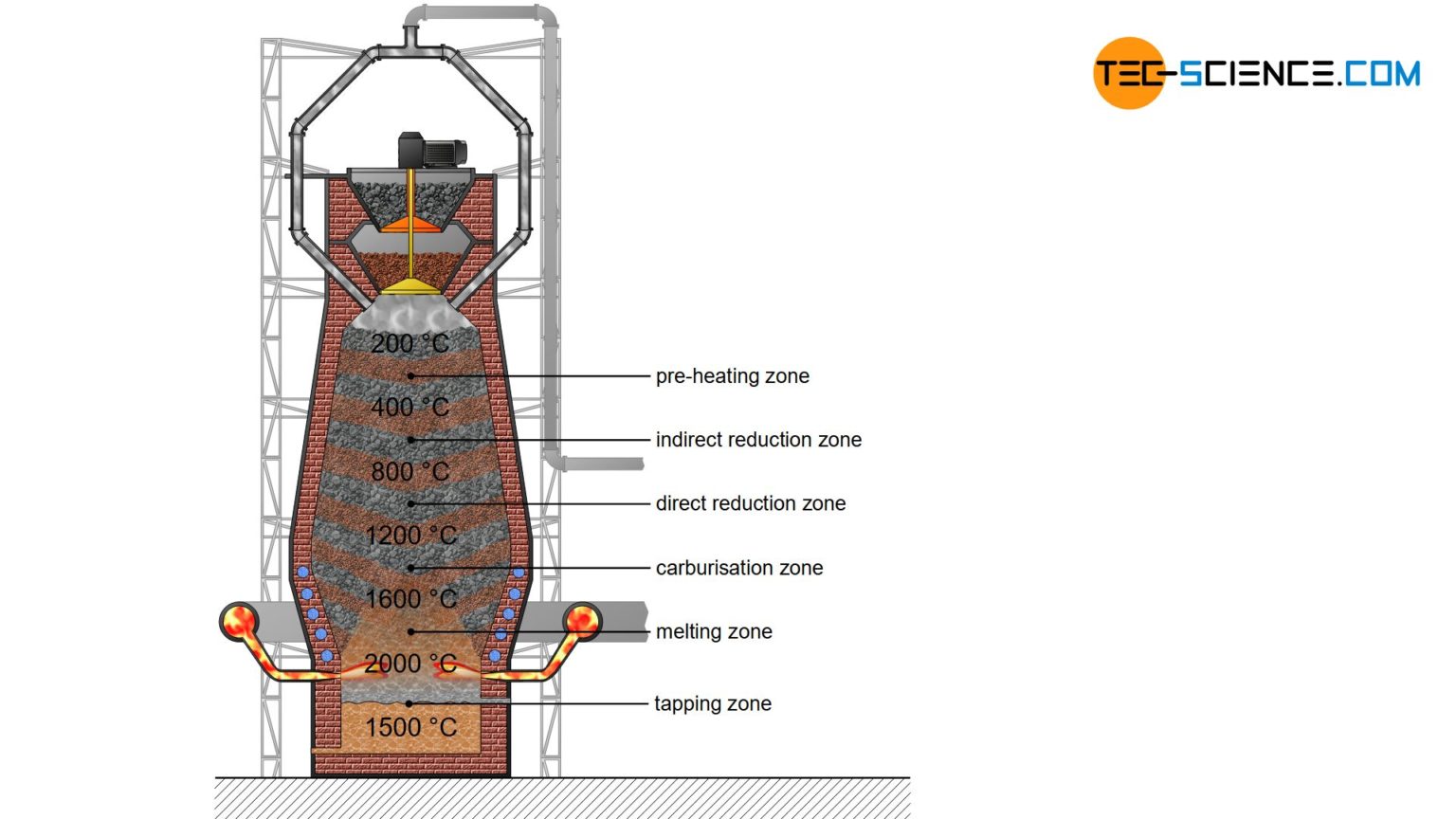
Blast Furnace Process Tec Science This video uses animations to explain how iron is extracted from its ore in the blast furnace. it shows the reactions that occur at different levels of the f. This video explains the reactivity series and extraction method of metals. explains in detail the extraction of iron and all important reactions related to i.

Blast Furnace Process Tec Science Blast furnace, a vertical shaft furnace that produces liquid metals by the reaction of a flow of air introduced under pressure into the bottom of the furnace with a mixture of metallic ore, coke, and flux fed into the top. blast furnaces are used to produce pig iron from iron ore for subsequent processing into steel, and they are also employed. Video transcript. in this video, we will look at the extraction of iron from its ore in the blast furnace. we’ll look at the chemicals used in a blast furnace and the temperatures involved. iron is an abundant metal, which is relatively cheap to produce. ores containing a high proportion of iron can be found throughout the world. The purpose of a blast furnace is to reduce the concentrated ore chemically to its liquid metal state. a blast furnace is a gigantic, steel stack lined with refractory brick where the concentrated iron ore, coke, and limestone are dumped from the top, and a blast of hot air is blown into the bottom. all the three ingredients are crushed into. Liquid iron from the blast furnace is then reacted with oxygen in a second step via a basic oxygen furnace (bof) to remove excess carbon, producing even more co 2. this reduced form of iron is steel. the extractive process is particularly emissions heavy because co 2 is a byproduct of both steps along the way – the blast furnace and the basic.
Blast Furnace Process Overview Download Scientific Diagram The purpose of a blast furnace is to reduce the concentrated ore chemically to its liquid metal state. a blast furnace is a gigantic, steel stack lined with refractory brick where the concentrated iron ore, coke, and limestone are dumped from the top, and a blast of hot air is blown into the bottom. all the three ingredients are crushed into. Liquid iron from the blast furnace is then reacted with oxygen in a second step via a basic oxygen furnace (bof) to remove excess carbon, producing even more co 2. this reduced form of iron is steel. the extractive process is particularly emissions heavy because co 2 is a byproduct of both steps along the way – the blast furnace and the basic. A blast furnace can be used to extract iron from its ore. components other than just the ore are added to the furnace to extract the iron. one of these key components is limestone, which is primarily composed of calcium carbonate, caco3. the heat from the blast furnace causes the calcium carbonate to decompose into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. The charge is added to the top of the blast furnace, and hot air is blasted in through the bottom. the oxygen in the air reacts with the coke in the charge to form carbon monoxide. the carbon monoxide in the blast furnace reduces the iron(iii) oxide in the hematite ore to produce molten iron. iron ores contain a large amount of sandy impurities.
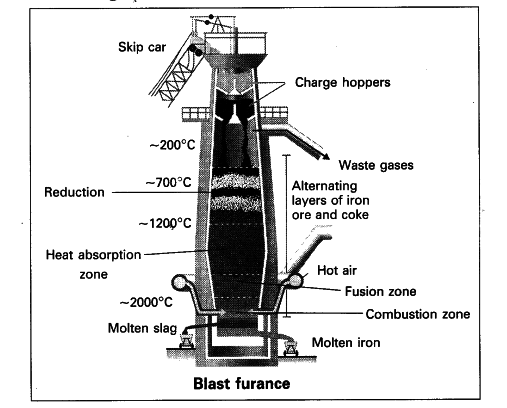
Schematic Diagram Of Blast Furnace A blast furnace can be used to extract iron from its ore. components other than just the ore are added to the furnace to extract the iron. one of these key components is limestone, which is primarily composed of calcium carbonate, caco3. the heat from the blast furnace causes the calcium carbonate to decompose into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide. The charge is added to the top of the blast furnace, and hot air is blasted in through the bottom. the oxygen in the air reacts with the coke in the charge to form carbon monoxide. the carbon monoxide in the blast furnace reduces the iron(iii) oxide in the hematite ore to produce molten iron. iron ores contain a large amount of sandy impurities.

Comments are closed.