Intermediary Metabolism

Compilation Of The Main Intermediary Metabolism And Related Pathways Learn how cells use glucose, fats, and proteins as fuel and how they are interconnected by common intermediates. explore the links between catabolism and anabolism, and the role of fructose in metabolism. This article traces the origins and milestones of intermediary metabolism research, from lavoisier to the present day. it also explores how intermediary metabolism is involved in cell fate, epigenetics, apoptosis and immunity.
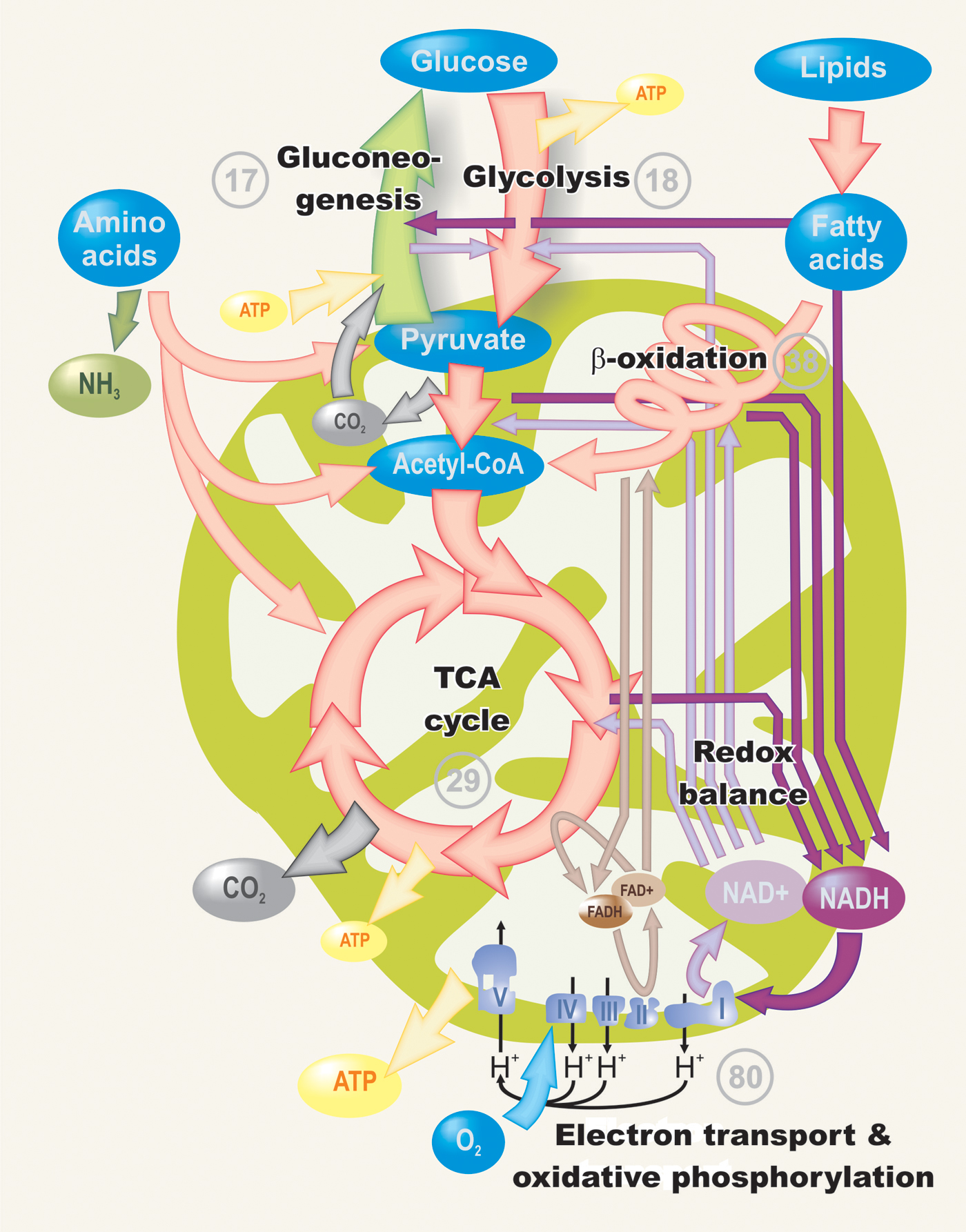
Intermediary Metabolism Learn the principles and types of metabolic reactions, bonds cleavage, bond length and angle, and classification of metabolic reagents. this web page provides basic notes for students of biochemistry and intermediary metabolism. Intermediary metabolism. *. bart p braeckman, koen houthoofd, and jacques r vanfleteren. author information and affiliations. caenorhabditis elegans has orthologs for most of the key enzymes involved in eukaryotic intermediary metabolism, suggesting that the major metabolic pathways are probably present in this species. Learn about the intracellular chemical processes that convert nutritive material into cellular components and generate cellular energy. the article covers topics such as anabolism, catabolism, glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain, lactate, and factors influencing metabolism. Atp production in brain is highly regulated. oxidative steps of carbohydrate metabolism normally contribute 36 of the 38 high energy phosphate bonds ( ~p) generated during aerobic metabolism of a single glucose molecule. about 15% of brain glucose is converted to lactate and does not enter the krebs cycle, also termed the citric acid cycle.

Intermediary Metabolism Learn about the intracellular chemical processes that convert nutritive material into cellular components and generate cellular energy. the article covers topics such as anabolism, catabolism, glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain, lactate, and factors influencing metabolism. Atp production in brain is highly regulated. oxidative steps of carbohydrate metabolism normally contribute 36 of the 38 high energy phosphate bonds ( ~p) generated during aerobic metabolism of a single glucose molecule. about 15% of brain glucose is converted to lactate and does not enter the krebs cycle, also termed the citric acid cycle. To maintain homeostasis, cells need to coordinate the expression of their genes. epigenetic mechanisms controlling transcription activation and repression include dna methylation and post translational modifications of histones, which can affect the architecture of chromatin and or create 'docking platforms' for multiple binding proteins. This chapter reviews the metabolic processes and regulatory mechanisms involved in intermediary metabolism, with a focus on the brain. it covers topics such as anabolism, catabolism, energy production, and metabolic changes during epilepsy and hypoglycemia.

Metabolism Pathway To maintain homeostasis, cells need to coordinate the expression of their genes. epigenetic mechanisms controlling transcription activation and repression include dna methylation and post translational modifications of histones, which can affect the architecture of chromatin and or create 'docking platforms' for multiple binding proteins. This chapter reviews the metabolic processes and regulatory mechanisms involved in intermediary metabolism, with a focus on the brain. it covers topics such as anabolism, catabolism, energy production, and metabolic changes during epilepsy and hypoglycemia.
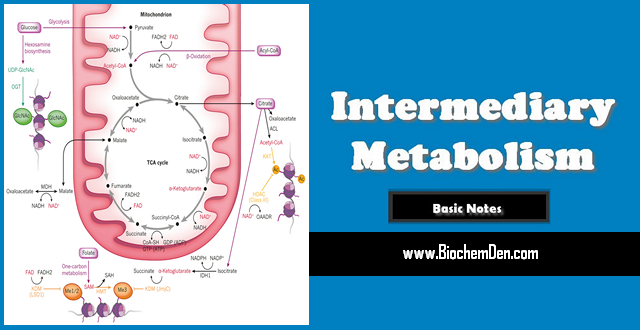
Intermediary Metabolism Basic Notes

Comments are closed.