Interoperability Of Health Care Data Diagrams
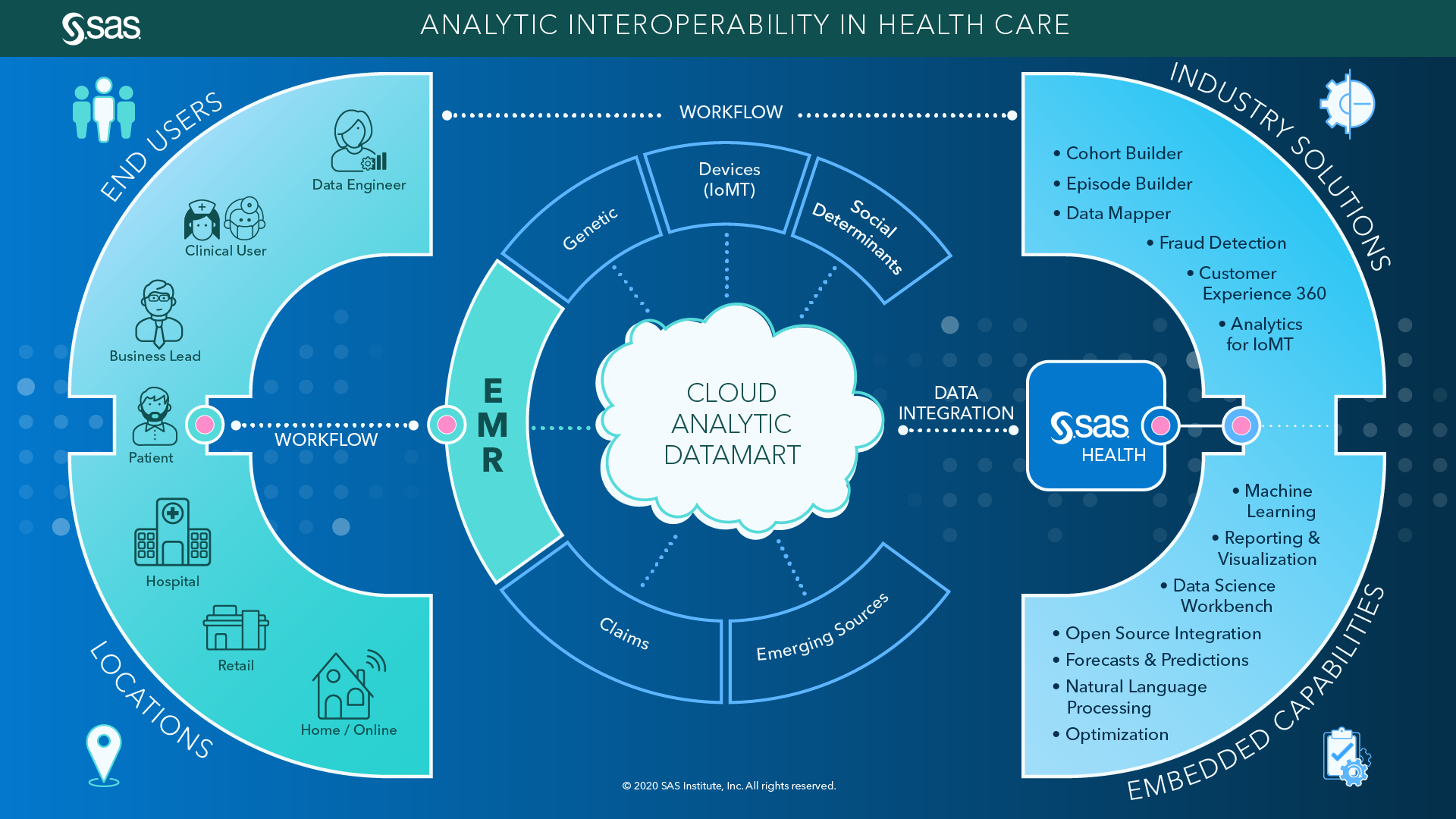
Interoperability Of Health Care Data Diagrams Principle 2: healthcare providers need rich data interoperability. for the past 20 years, data integration and operability have been defined as sending messages to and from the emr. new standards offer more seamless data sharing options and provide a far richer and more impactful set of capabilities. while messages to and from clinical. Figure 6, panel a portrays the functional interoperability required across the three tiers: inter facility (macro tier), intra facility (meso tier), and point of care (micro tier) in the health care ecosystem. it is important to note, however, that the three tier structure represents an organizing schematic with some distinct features and.

Interoperability Of Health Care Data Diagrams This is because interoperability, as a whole, is too complex. to make it a bit more digestible, himss has broken it into 4 levels which we will briefly review before looking deeper at the layer of semantic interoperability and the barriers experienced in that layer. 1. foundational interoperability. in this layer, interoperability lets the data. True person centered interoperability has the potential to empower individuals to become partners in their health care, and allows for their ability to directly contribute to and receive data from the ehr. to ensure that health care dollars are spent in pursuit of a safer, more productive and more cost effective system, interoperability must be. The potential fhir use cases in table 1, below, underscore the following significant interoperability themes moving through the industry, which the cms and onc final rules reinforce: 1. consumer engagement occurs through the technologies they use, with relevant data and simplified access. 2. data is useful, but data sharing with modern. The lack of interoperability between healthcare systems reinforces the information silos that exist in today's paper based medical files, resulting in private ownership over health data. consequently, healthcare costs have risen, patient care quality has deteriorated, and the ability to integrate patient data across healthcare systems has been.

Comments are closed.