Intro To Genetics And Heredity Dna Genes Chromosomes Mitosis Meiosis
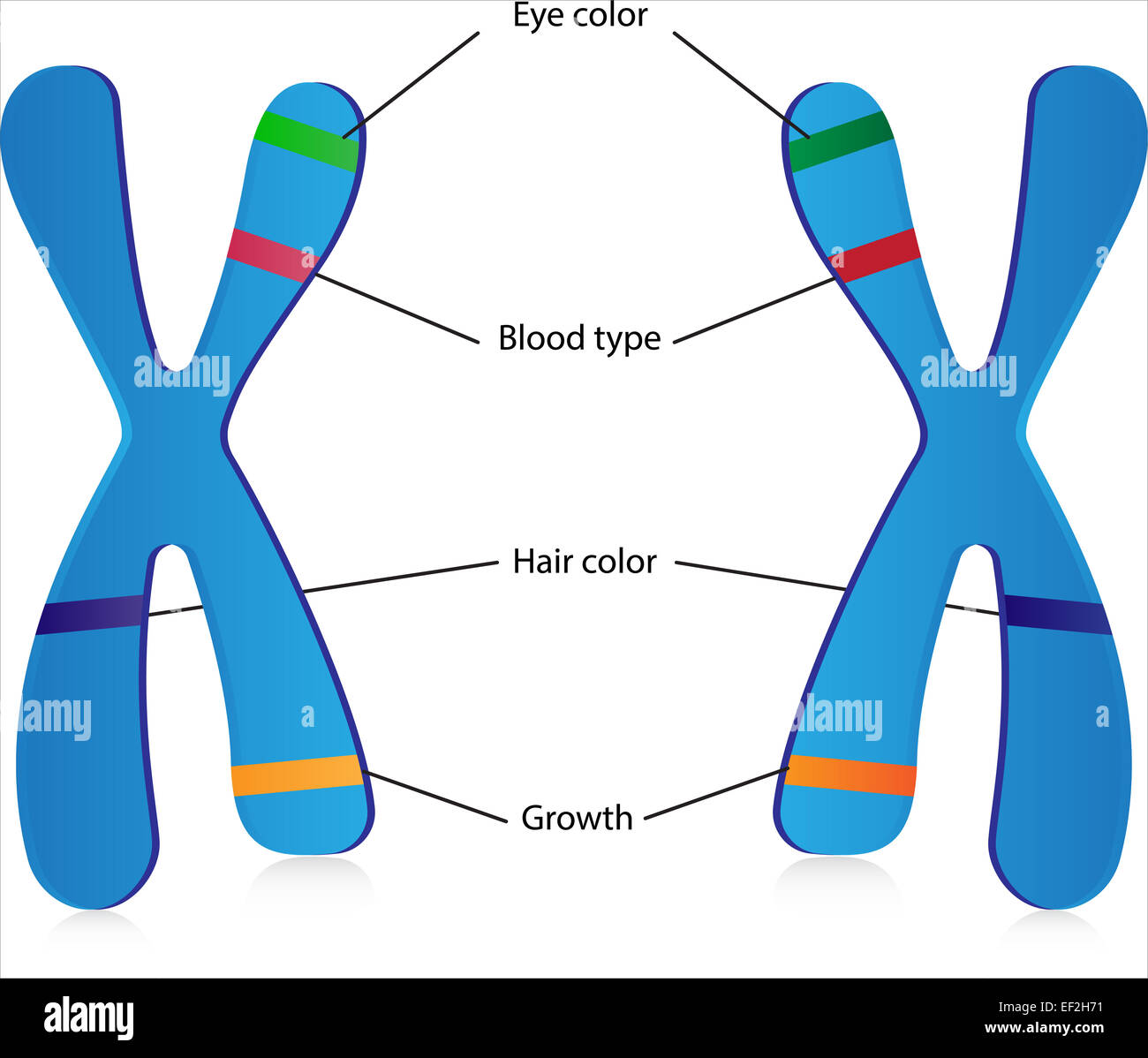
Intro To Genetics And Heredity Dna Genes Chromosomes Mitosis Meiosis Section 2.1: dna is packaged into chromatin. if stretched to its full length, the dna molecule of the largest human chromosome would be 85mm. yet during mitosis and meiosis, this dna molecule is compacted into a chromosome approximately 5µm long. although this compaction makes it easier to transport dna within a dividing cell, it also makes. During the process of meiosis, cells are produced with only half of the genetic content – it’s called reductive cell division because the number of chromosomes has been reduced. then, two cells with half content come together to form a fused cell with a full genome that has genetic information from both parents.
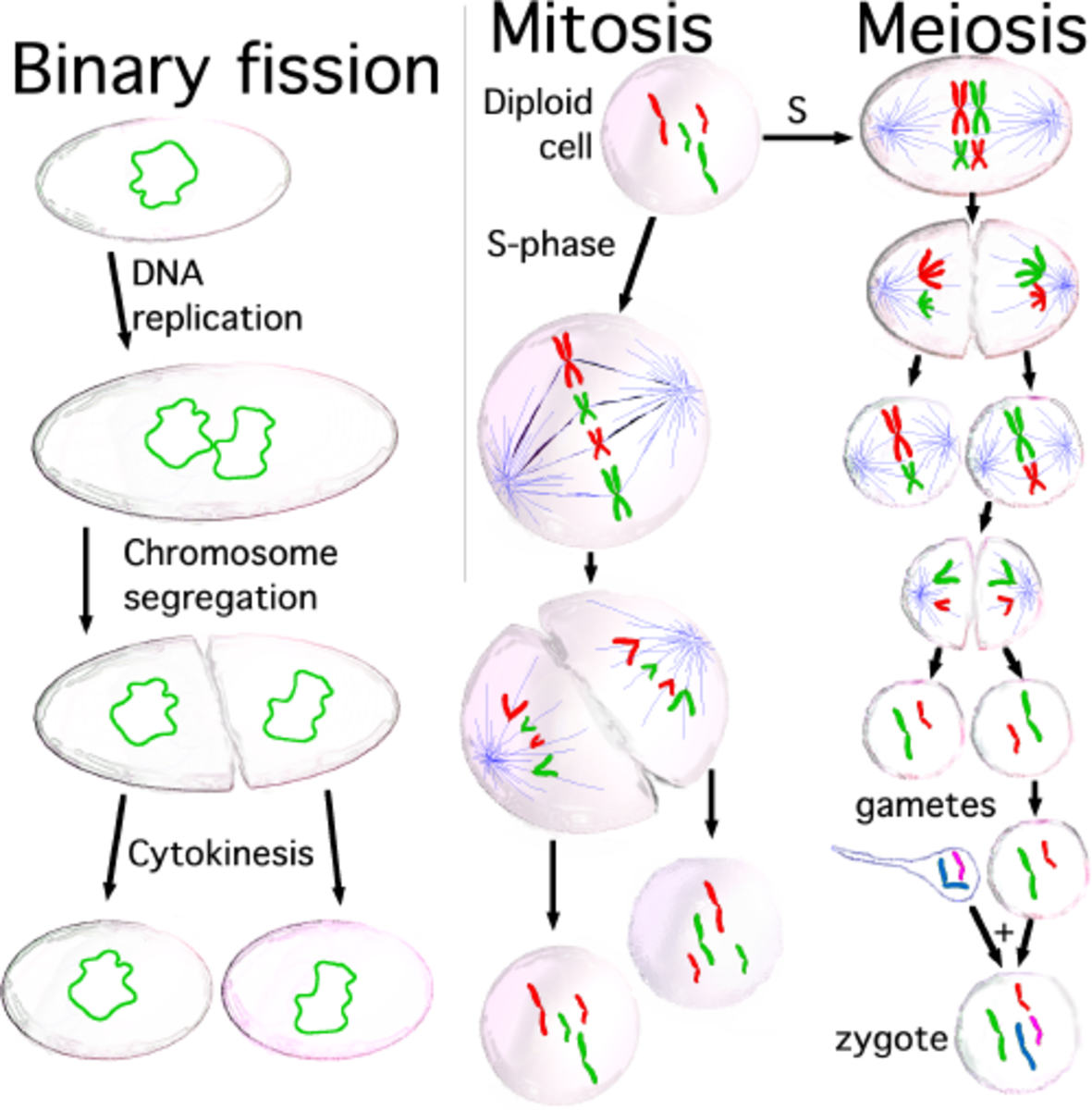
Cell Division Mitosis And Meiosis Owlcation The m phase completes the cell cycle. ’m’ could be mitosis or meiosis depending on the type of cell. for the zygote, the goal is to make more somatic cells. therefore, it goes through mitosis and gives rise to two daughter cells. this completes the life cycle of the zygote and starts the lifecycle of the new cells. Add content to group. although they are both cell division processes, mitosis and meiosis have very different effects on the transmission of genes from one cellular generation to the next. mitotic. Table 3.6.1 differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46) cell processes. mitosis. meiosis. creates. all the cells in your body except sex cells. sex cells only; female egg cells or male sperm cells. definition. process of cell division that forms two new cells (daughter cells), each of which has the same number of chromosomes. During mitosis the sister chromatids separate and go to opposite ends of the dividing cell. mitosis ends with 2 identical cells, each with 2n chromosomes and 2x dna content. all eukaryotic cells replicate via mitosis, except germline cells that undergo meiosis (see below) to produce gametes (eggs and sperm).
Dna Heredity Intro To Genetics Interactive Worksheet By Michelle Table 3.6.1 differences between mitosis and meiosis in humans (diploid #46) cell processes. mitosis. meiosis. creates. all the cells in your body except sex cells. sex cells only; female egg cells or male sperm cells. definition. process of cell division that forms two new cells (daughter cells), each of which has the same number of chromosomes. During mitosis the sister chromatids separate and go to opposite ends of the dividing cell. mitosis ends with 2 identical cells, each with 2n chromosomes and 2x dna content. all eukaryotic cells replicate via mitosis, except germline cells that undergo meiosis (see below) to produce gametes (eggs and sperm). This resource is written for an introductory or intermediate level college genetics course. the work begins with an exploration of dna and genome structure, including landmark experiments that contributed to our early understanding of the relationship between dna, genes, and traits. it continues with the central dogma of molecular genetics: the molecular mechanisms that allow cells to use the. Explore dna structure function, chromosomes, genes, and traits and how this relates to heredity! video can replace old dna structure & function video and in.

Comments are closed.