Intro To Muscles Lecture Notes 9 Structure Of Skeletal Muscle

Skeletal Muscle Structure Layers With Anatomical Arm Closeups Outline Structure of skeletal muscle connective tissue covering 1. epimysium: surrounds entire muscle 2. perimysium: surrounds bundles of muscle fibers 3. endomysium: surrounds individual muscle fibers. a. i. intro to muscles. sunday, november 15, 2020 1:55 pm. r. The muscular system is made up of muscle tissue and is responsible for functions such as maintenance of posture, locomotion and control of various circulatory systems. this includes the beating of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system. the muscular system is closely associated with the skeletal system in facilitating.
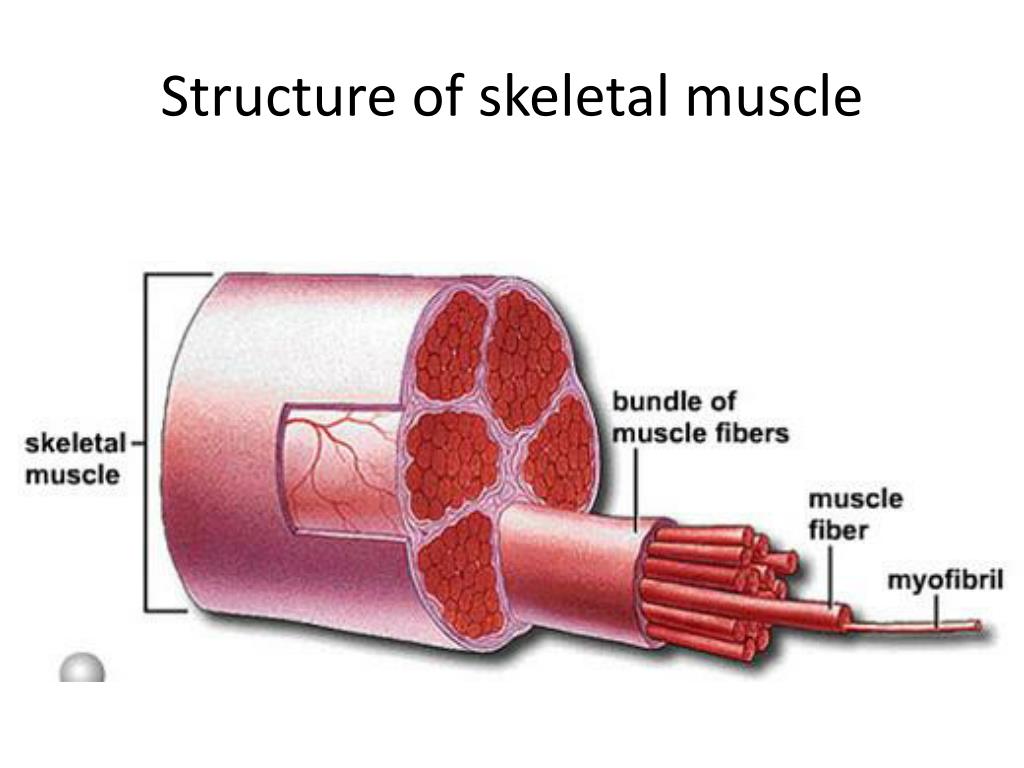
Ppt Structure Of Skeletal Muscle Powerpoint Presentation Free Smooth muscle functions in various involuntary movements, such as having one’s hair stand on end when cold or frightened, or moving food through the digestive system. this chapter will focus on the structure and function of skeletal muscles. figure 9.1.1 9.1. 1: tennis player. athletes rely on toned skeletal muscles to supply the force. Chapter 9: skeletal muscle tissue and organization introduction. humans rely on muscles for: many of our physiological processes (happen because of muscles) (breathing digestion body temp) virtually all our dynamic interactions with the environment (reacting with stimuli) there are three types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle – pulls on skeletal bones voluntary contraction (conscious. Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. this article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions.

Diagram Of Skeletal Muscle Muscles attach to bones directly or through tendons or aponeuroses. skeletal muscles maintain posture, stabilize bones and joints, control internal movement, and generate heat. skeletal muscle fibers are long, multinucleated cells. the membrane of the cell is the sarcolemma; the cytoplasm of the cell is the sarcoplasm. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. it is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. this article will discuss the structure of skeletal muscle tissue, it’s mode of contraction and relevant clinical conditions. Also, the epimysium anchors the muscles to tendons. figure 5.5.6 5.5. 6: each skeletal muscle has a structure of bundles within bundles. bundles of muscle fibers make up a muscle fascicle, and fascicles' bundles make up a skeletal muscle. at each level of bundling, a connective tissue membrane surrounds the bundle. Each muscle’s particular structure allows it to perform a specific function. the muscles are attached to bones or other tissues, to help us maintain position, perform movements and even protect some organs. ok, now muscle tissue is made up of contractile cells, often called muscle fibers. muscle tissue can be grouped into 3 types; skeletal.

Skeletal Muscle Structure With Anatomical Inner Layers Outline Diagram Also, the epimysium anchors the muscles to tendons. figure 5.5.6 5.5. 6: each skeletal muscle has a structure of bundles within bundles. bundles of muscle fibers make up a muscle fascicle, and fascicles' bundles make up a skeletal muscle. at each level of bundling, a connective tissue membrane surrounds the bundle. Each muscle’s particular structure allows it to perform a specific function. the muscles are attached to bones or other tissues, to help us maintain position, perform movements and even protect some organs. ok, now muscle tissue is made up of contractile cells, often called muscle fibers. muscle tissue can be grouped into 3 types; skeletal.

Comments are closed.