Introduction Covid 19 And Obesity Series

Obesity And Covid 19 Obesity Research Task Force Symposium 2021 Niddk International journal of obesity obesity in covid 19 era, implications for mechanisms, comorbidities, and prognosis: a review and meta analysis introduction. in december 2019, coronavirus. Introduction; research on the pandemic of covid 19 has demonstrated that there is a higher risk of contracting the disease, increased severity, and poorer outcomes in individuals who are obese.

Covid 19 And Obesity Stop Obesity Alliance Milken Institute School Obesity has reached epidemic proportions in the united states and in much of the westernized world, contributing to considerable morbidity. several of these obesity related morbidities are associated with greater risk for death with coronavirus disease 2019 (covid 19). severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 penetrates human cells through direct binding with angiotensin converting. A systematic search was conducted from covid 19 databases from the pandemic inception through october 13 th, 2021 for full length articles focusing on the association of increased bmi obesity [overweight is defined as a bmi between 25.0 and 29.9, and a bmi of 30 or higher is considered obese ] in covid 19 using a pre specified data extraction. Abstract. emerging data suggest that obesity is a major risk factor for the progression of major complications such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), cytokine storm and coagulopathy in covid 19. understanding the mechanisms underlying the link between obesity and disease severity as a result of sars cov 2 infection is crucial for. The prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and adolescents aged 5–19 has risen dramatically from just 4% in 1975 to just over 18% in 2016. 39 million children under the age of 5 were overweight or obese in 2020. overweight and obesity are linked to more deaths worldwide than underweight.

Covid 19 And Obesity Stop Obesity Alliance Milken Institute School Abstract. emerging data suggest that obesity is a major risk factor for the progression of major complications such as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ards), cytokine storm and coagulopathy in covid 19. understanding the mechanisms underlying the link between obesity and disease severity as a result of sars cov 2 infection is crucial for. The prevalence of overweight and obesity among children and adolescents aged 5–19 has risen dramatically from just 4% in 1975 to just over 18% in 2016. 39 million children under the age of 5 were overweight or obese in 2020. overweight and obesity are linked to more deaths worldwide than underweight. Introduction. obesity has long been associated with worse prognosis of viral infections ().higher mortality rates and a prolonged, more severe clinical course was observed in obese people in the 1957–1960 “asian” and the 1968 “hong kong” influenzas (22, 39), whereas more recently obesity was recognized as a predisposing factor for worse clinical outcomes and death in the 2009 h1n1. Obesity is a major public health concern: at least 11% of men and 15% of women, more than half a billion adults, are obese worldwide. lockhart and o’rahilly 1 point out that, although emerging.
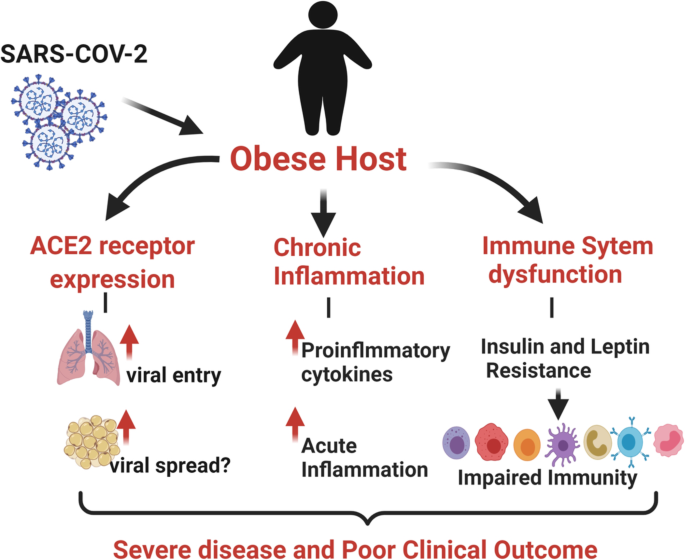
The Complexity Of Obesity Covid 19 Vida Wellness And Beauty Introduction. obesity has long been associated with worse prognosis of viral infections ().higher mortality rates and a prolonged, more severe clinical course was observed in obese people in the 1957–1960 “asian” and the 1968 “hong kong” influenzas (22, 39), whereas more recently obesity was recognized as a predisposing factor for worse clinical outcomes and death in the 2009 h1n1. Obesity is a major public health concern: at least 11% of men and 15% of women, more than half a billion adults, are obese worldwide. lockhart and o’rahilly 1 point out that, although emerging.

Comments are closed.