Introduction Glycolysis And Pyruvate Metabolism Biochemistry Lecturio

Introduction Glycolysis And Pyruvate Metabolism вђ Biochemistry Sign up here and try our free content: lectur.io freecontentyt if you’re an medical educator or faculty member, visit: lectur.io medytb2u t. Steps 1–5: 1st half of glycolysis. the 1st half of glycolysis requires an energy investment of 2 adenosine triphosphate (atp) molecules and serves to convert the hexose glucose into 2 trioses. the process consists of 5 steps: glucose. glucose a primary source of energy for living organisms.

Glycolysis Pyruvate Metabolism вђ Biochemistry Online Carbohydrate metabolism. by kevin ahern, phd. (63) the generation of energy by breaking down carbohydrates is as old as cells themselves. carbohydrates are the most important substrate for the synthesis of atp via glycolysis, so much so that hepatocytes have the ability to synthesize glucose de novo to meet metabolic needs. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm and consists of 10 reactions, the net result of which is the conversion of 1 c6 glucose to 2 c3 pyruvate molecules. the free energy of this process is harvested to produce adenosine triphosphate (atp) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide hydride (nadh), key energy yielding metabolites. Glycolysis is the name given to a metabolic pathway occurring in many different cell types. it consists of 11 enzymatic steps that convert glucose to lactic acid. glycolysis is an example of: a) aerobic metabolism. b) anabolic metabolism. c) a net reductive process. d) fermentation. e) oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three carbon molecules called pyruvates. glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today 2, 3 .
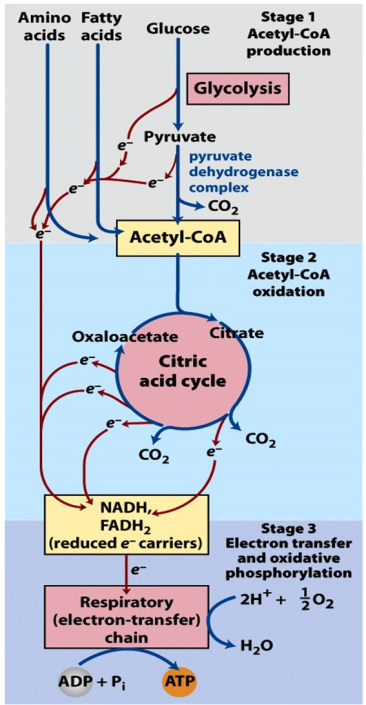
Glycolysis вђ Bioc 2580 Introduction To Biochemistry Glycolysis is the name given to a metabolic pathway occurring in many different cell types. it consists of 11 enzymatic steps that convert glucose to lactic acid. glycolysis is an example of: a) aerobic metabolism. b) anabolic metabolism. c) a net reductive process. d) fermentation. e) oxidative phosphorylation. Glycolysis is a series of reactions that extract energy from glucose by splitting it into two three carbon molecules called pyruvates. glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway, meaning that it evolved long ago, and it is found in the great majority of organisms alive today 2, 3 . The metabolism of glucose, as well as other six carbon sugars (hexoses) begins with the catabolic pathway called glycolysis. glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of cells, not on or in the mitochrondria. the end metabolic products of glycolysis are two molecules of atp, two molecules of nadh and two molecules of pyruvate (figure 6.3), which, in. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose (a 6 carbon sugar) into 2 equivalents of pyruvate (a 3 carbon molecule). by itself, glycolysis can provide energy to the cell. from one molecule of glucose, glycolysis yields 2 atp, 2 nadh, and 2 pyruvates. glycolysis is called anaerobic because it does not use oxygen.

Comments are closed.