Introduction To Linear Algebra V 1 Eigenvalue And Eigenvector Pdf

Introduction To Linear Algebra V 1 Eigenvalue And Eigenvector Pdf Most 2 by 2 matrices have two eigenvector directions and two eigenvalues. we will show that det(a − λi)=0. this section explains how to compute the x’s and λ’s. it can come early in the course. we only need the determinant ad − bc of a 2 by 2 matrix. example 1 uses to find the eigenvalues λ = 1 and λ = det(a−λi)=0 1. When a is n by n, equation n. a n λ x: for each eigenvalue λ solve (a − λi)x = 0 or ax = λx to find an eigenvector x. 1 2. example 4 a = is already singular (zero determinant). find its λ’s and x’s. 2 4. when a is singular, λ = 0 is one of the eigenvalues. the equation ax = 0x has solutions.

Linear Algebra вђ Part 6 Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors By Sho Nakagome Definition 4.1.1. given a square n × n matrix a, we say that a nonzero vector v is an eigenvector of a if there is a scalar λ such that. av = λv. the scalar λ is called the eigenvalue associated to the eigenvector v. at first glance, there is a lot going on in this definition so let's look at an example. Yes, say v is an eigenvector of a matrix a with eigenvalue λ. then av=λv. let's verify c*v (where c is non zero) is also an eigenvector of eigenvalue λ. you can verify this by computing a(cv)=c(av)=c(λv)=λ(cv). thus cv is also an eigenvector with eigenvalue λ. i wrote c as non zero, because eigenvectors are non zero, so c*v cannot be zero. The 1 eigenspace of a positive stochastic matrix a is a line. to compute the steady state, nd any 1 eigenvector (as usual), then divide by the sum of the entries; the resulting vector w has entries that sum to 1, and are automatically positive. think of w as a vector of steady state percentages: if the movies are distributed according to these. To obtain the eigenvectors, we must solve systems associated to each eigenvalue: a ( 2)i2 x = 0 and a (4)i2 x = 0. for 1 = 2, this yields a homogeneous system with augmented matrix. 8 8 0. ; 2 2 0. which is solved so long as the components x1 and x2 of x satisfy x2 = x1, thus, e.g., spans the 2 eigenspace.

Linear Algebra Eigenvalue Eigenvector The 1 eigenspace of a positive stochastic matrix a is a line. to compute the steady state, nd any 1 eigenvector (as usual), then divide by the sum of the entries; the resulting vector w has entries that sum to 1, and are automatically positive. think of w as a vector of steady state percentages: if the movies are distributed according to these. To obtain the eigenvectors, we must solve systems associated to each eigenvalue: a ( 2)i2 x = 0 and a (4)i2 x = 0. for 1 = 2, this yields a homogeneous system with augmented matrix. 8 8 0. ; 2 2 0. which is solved so long as the components x1 and x2 of x satisfy x2 = x1, thus, e.g., spans the 2 eigenspace. Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. ei. envalues and eigenvectors1. diagonalizable linear. transformations and matricesrecall, a matrix, d, is diagonal if it is square and the only non zero. entries are on the diagonal. this is equivalent to d~ei = i~ei where here ~ei are the standard vector and th. i are the diagonal entries. a li. 2 eigenvectors and eigenvalues de!nition 1 (eigenvector, eigenvalue). suppose v is a !nite dimensional vector space over a!eld f, and t: v → v is a linear map. then, a nonzero vector v ∈ v is an eigenvector of t with eigenvalue λ ∈ f if t(v) = λv. λ ∈ f is an eigenvalue of t if there exists v ∈ v so that t(v) = λv. our goal, when.
Math 323 Linear Algebra Lecture 22 Eigenvalues And Eigenvectors Eigenvalues and eigenvectors. ei. envalues and eigenvectors1. diagonalizable linear. transformations and matricesrecall, a matrix, d, is diagonal if it is square and the only non zero. entries are on the diagonal. this is equivalent to d~ei = i~ei where here ~ei are the standard vector and th. i are the diagonal entries. a li. 2 eigenvectors and eigenvalues de!nition 1 (eigenvector, eigenvalue). suppose v is a !nite dimensional vector space over a!eld f, and t: v → v is a linear map. then, a nonzero vector v ∈ v is an eigenvector of t with eigenvalue λ ∈ f if t(v) = λv. λ ∈ f is an eigenvalue of t if there exists v ∈ v so that t(v) = λv. our goal, when.
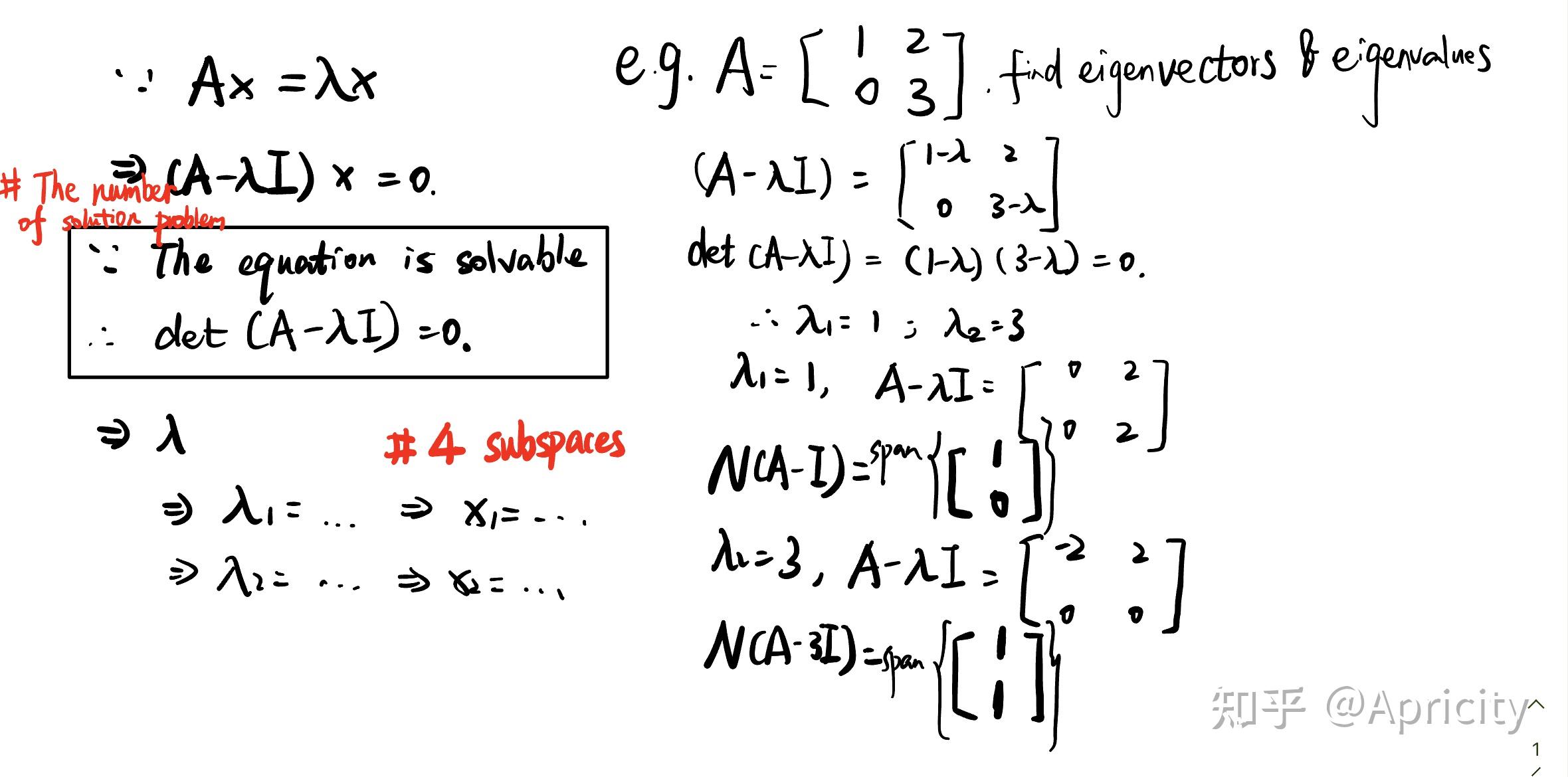
Linear Algebra 2 Eigenvector Eigenvalue зџґд ћ

Comments are closed.