Introduction To Metabolism Catabolism Vs Anabolism Biochemistry

Introduction To Metabolism Catabolism Vs Anabolism Biochemistry Metabolism refers to the set of chemical reactions that occur within living organisms to maintain life. anabolism is the process of building up larger, more complex molecules from smaller ones. this process requires energy. catabolism is the process of breaking down larger molecules into smaller ones. Introduction to metabolism: anabolism and catabolismwatch the next lesson: khanacademy.org science biology energy and enzymes energy in metabolis.

The Minute But Vital Differences Between Anabolism And Catabolism What is the purpose of metabolism? learn about the two major divisions in metabolism: anabolism (building up) and catabolism (breaking down). by jasmine ran. This video provides an introduction to metabolism. metabolism consists of two contrasting processes; 1. catabolism and 2. anabolism. catabolism involves the. Metabolism is a set of chemical reactions that interconnect in a series of pathways. it is a balancing act between the building and breakdown of molecules in the body. type of metabolism. process. energetics. example. anabolism. builds complex molecules from simple ones. endergonic. Anabolism is the building of complex molecules from numerous simple ones. think of protein synthesis. catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into numerous simple ones. think the break down of glucose. this was such a good overview of metabolism. how is the digestion of food compared to metabolism.
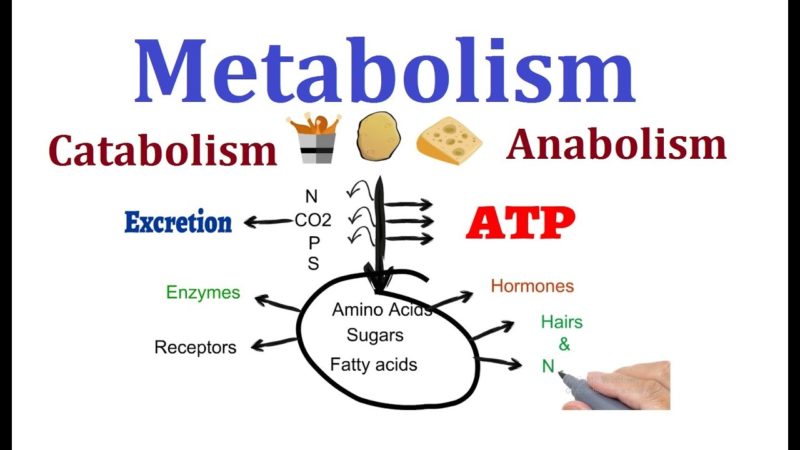
7 Remarkable Difference Between Anabolism And Catabolism Core Differences Metabolism is a set of chemical reactions that interconnect in a series of pathways. it is a balancing act between the building and breakdown of molecules in the body. type of metabolism. process. energetics. example. anabolism. builds complex molecules from simple ones. endergonic. Anabolism is the building of complex molecules from numerous simple ones. think of protein synthesis. catabolism is the breakdown of complex molecules into numerous simple ones. think the break down of glucose. this was such a good overview of metabolism. how is the digestion of food compared to metabolism. Anabolism and catabolism are the two types of biochemical reactions that make up the metabolism. anabolic reactions involve the building of larger, complex molecules from smaller, simpler ones, and require an input of energy. catabolic reactions are the opposite of anabolic reactions, and break the chemical bonds in larger, more complex molecules. Catabolism yields energy that fuels anabolism. metabolism consists of two sets of biochemical pathways called anabolism and catabolism. anabolism builds complex molecules from simpler ones, while catabolism breaks larger molecules into smaller ones. anabolism and catabolism go hand in hand, as each makes the source material for the other.

Differences Between Catabolism And Anabolism Anabolism and catabolism are the two types of biochemical reactions that make up the metabolism. anabolic reactions involve the building of larger, complex molecules from smaller, simpler ones, and require an input of energy. catabolic reactions are the opposite of anabolic reactions, and break the chemical bonds in larger, more complex molecules. Catabolism yields energy that fuels anabolism. metabolism consists of two sets of biochemical pathways called anabolism and catabolism. anabolism builds complex molecules from simpler ones, while catabolism breaks larger molecules into smaller ones. anabolism and catabolism go hand in hand, as each makes the source material for the other.

Comments are closed.