Introduction To Vectors Scalars Tutorial Sophia Learning

Introduction To Vectors Scalars Tutorial Sophia Learning We look at several examples of scalars and vectors and also review how to add and subtract vectors from one another. vectors and scalars are defined along with some commonly used terms in introductory physics. i include some examples to help the student think of vectors both algebraically and geometrically and use these examples to show the. By providing your information, you consent to receive occasional special promotional offers and education opportunities by phone, text message, and email via automated technology from sophia learning or one of its affiliates. consent is not required to purchase goods or services. you can always call us at 1 800 341 0327. see our privacy policy.
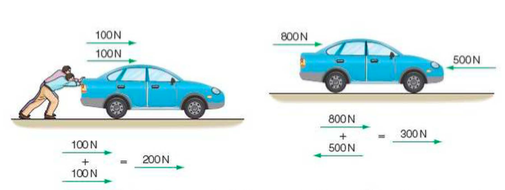
A Comprehensive Introduction To Scalars And Vectors For O Level Physics By providing your information, you consent to receive occasional special promotional offers and education opportunities by phone, text message, and email via automated technology from sophia learning or one of its affiliates. consent is not required to purchase goods or services. you can always call us at 1 800 341 0327. see our privacy policy. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org science physics one dimensional mot. Hence matrices are really vectors that are just written in a two dimensional table like manner. its components are now identified by two indices i and j. i represents the index to the matrix row, while j represents the index to the matrix column. each component of a is identified by a i j. the full m × n matrix can be written as: a = [ a 11 a. Physics tutor. watch step by step video tutorials that guide you through every chapter in your textbook. learn the toughest concepts with ease as our tutors thoroughly explain everything you need to know. personalized study plan that follows your textbook. thousends of concept videos and practice questions. exam prep plan curated by our tutors.

Tutorial 2 Scalars And Vectors 2023 2024 1 The Copperbelt University Hence matrices are really vectors that are just written in a two dimensional table like manner. its components are now identified by two indices i and j. i represents the index to the matrix row, while j represents the index to the matrix column. each component of a is identified by a i j. the full m × n matrix can be written as: a = [ a 11 a. Physics tutor. watch step by step video tutorials that guide you through every chapter in your textbook. learn the toughest concepts with ease as our tutors thoroughly explain everything you need to know. personalized study plan that follows your textbook. thousends of concept videos and practice questions. exam prep plan curated by our tutors. A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. the direction of the vector is from its tail to its head. two vectors are the same if they have the same magnitude and direction. Figure 10.22: illustrating how to add vectors using the head to tail rule and parallelogram law. analytically, it is easy to see that →u →v = →v →u. figure 10.22 also gives a graphical representation of this, using gray vectors. note that the vectors →u and →v, when arranged as in the figure, form a parallelogram.

Solution Basic Introduction To Scalars And Vectors Studypool A vector is an object that has both a magnitude and a direction. geometrically, we can picture a vector as a directed line segment, whose length is the magnitude of the vector and with an arrow indicating the direction. the direction of the vector is from its tail to its head. two vectors are the same if they have the same magnitude and direction. Figure 10.22: illustrating how to add vectors using the head to tail rule and parallelogram law. analytically, it is easy to see that →u →v = →v →u. figure 10.22 also gives a graphical representation of this, using gray vectors. note that the vectors →u and →v, when arranged as in the figure, form a parallelogram.

Solution Basic Introduction To Scalars And Vectors Studypool

Comments are closed.