Is Height Genetics Determined Only By The Parents Height

How Genetics And Nutrition Influence How Tall You Are Williams The genetics of height. genetics are among the prominent factors that contribute to how tall you’ll be. as a general rule of thumb, your height can be predicted based on how tall your parents. Identifying other height genes, and variants with large or small effects, is an active area of genetic research. because height is determined by multiple gene variants (an inheritance pattern called polygenic inheritance), it is difficult to accurately predict how tall a child will be. the inheritance of these variants from one’s parents.

Is Height Genetic 7 Factors That Influence Human Height In the largest study of its kind to date, members of the giant consortium — including researchers at the broad institute of mit and harvard, harvard medical school, and boston children’s hospital — have identified more than 12,000 genetic variants that influence height. these variants explain 10 percent to 40 percent of all variation in. “height is almost completely determined by genetics, but our earlier studies were only able to explain about 10 percent of this genetic influence,” said dr. joel hirschhorn, of boston children’s hospital and the broad institute at massachusetts institute of technology, in a press release. with their new study, they can now explain about 20 percent of heritability from height. The mid parental height is calculated by adding the mother’s and father’s height, adding 13 cm (5 inches) for boys or subtracting 13 cm (5 inches) for girls, and then finally dividing by 2. most children will reach an adult height within 2 inches of the mid parental height. another way to estimate a child’s adult height is to double a boy. For height, dna is largely destiny. studies of identical and fraternal twins suggest up to 80% of variation in height is genetic. but the genes responsible have largely eluded researchers. now, by amassing genome data for 4 million people—the largest such study ever—geneticists have accounted for a major share of this "missing heritability.

The Genetics Of Height Closer To Cracking The Code Boston Children S The mid parental height is calculated by adding the mother’s and father’s height, adding 13 cm (5 inches) for boys or subtracting 13 cm (5 inches) for girls, and then finally dividing by 2. most children will reach an adult height within 2 inches of the mid parental height. another way to estimate a child’s adult height is to double a boy. For height, dna is largely destiny. studies of identical and fraternal twins suggest up to 80% of variation in height is genetic. but the genes responsible have largely eluded researchers. now, by amassing genome data for 4 million people—the largest such study ever—geneticists have accounted for a major share of this "missing heritability. Researchers have identified over 12,000 genetic variants that influence a person's height. the study, published today (12 october) in nature, is the largest ever genome wide association study. A large genome wide association study of more than 5 million individuals reveals that 12,111 single nucleotide polymorphisms account for nearly all the heritability of height attributable to.
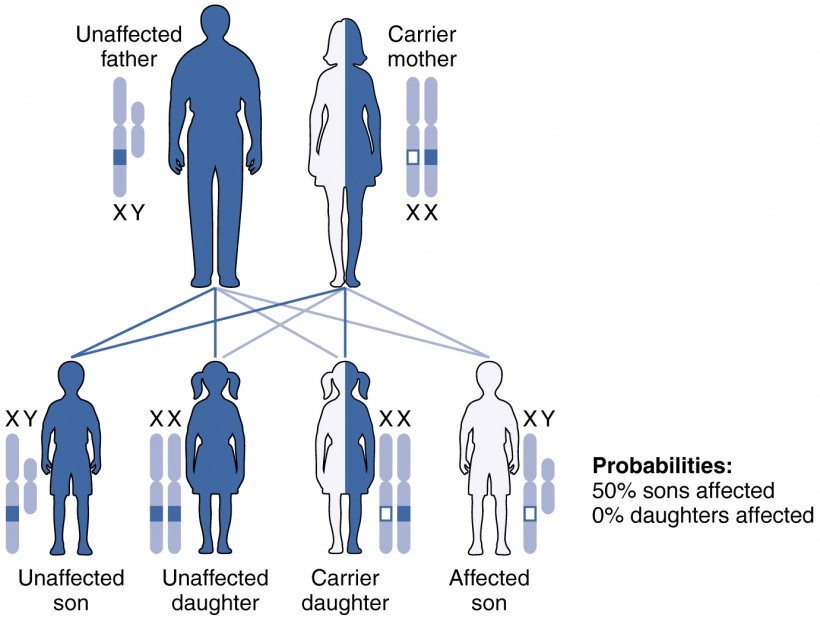
Patterns Of Inheritance Anatomy And Physiology Ii Researchers have identified over 12,000 genetic variants that influence a person's height. the study, published today (12 october) in nature, is the largest ever genome wide association study. A large genome wide association study of more than 5 million individuals reveals that 12,111 single nucleotide polymorphisms account for nearly all the heritability of height attributable to.

Comments are closed.